
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
For a power plant producing 10 MW of power using air-standard regenerative Brayton cycle operating
at steady state with intercooling and reheat. Operating data at principal states in the cycle are given in
the table below. The states are numbered as in Fig. below. (a) Sketch the T–s diagram and determine (b)
the mass flow rate of air, in kg/s, (c) the rate of heat transfer, in kW, to the working fluid passing
through each combustor, (d) the thermal efficiency.
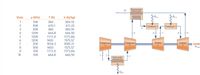
Transcribed Image Text:Regenerator
10
www.
State
p (kPa)
T (K)
h (kJ/kg)
300.19
411.22
1
100
300
300
410.1
CombustorI
Combustor
3
4
300
300
444.8
300.19
446.50
1200
1200
1200
1111.0
1173.84
1450
1034.3
1450
1111.0
1575.57
1085.31
Compressor
Compressor
Turbine
Turbine
300
300
7
1575.57
1173.84
8
cycle
9
100
10
100
444.8
446.50
Intercooler
www.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Rankine Cycle What two conditions can you define for state 2 (pump) that are inferred from other states?arrow_forward(2) Describe briefly why the following statements are wrong. (a) "Hot cup of coffee becoming cold spontaneously is an entropy-decreasing process. So the law of entropy increase can be violated." (b) “Air conditioners require bulky external unit, exhausting heat to outside. With the technology constantly advancing, external unit will be eliminated in the future."arrow_forwardAir as an ideal gas flows through a diffuser at steady State. At thne inlet , the air enters at 290°K, 3 bar, and 512 m/ Sec. At the exit, the air Speed is 110 m/saec, if the diffuser operates wentropically, determine the exit pressure using a constant specific heat ratio of 1.40 in bar using. 5 Signifigant figures.arrow_forward
- A steam turbine drives an air compressor-all power produced by the turbine is sent to the compressor; there is no extra power produced. Steady-state operating data are provided on the figure. Assume the ideal gas model for air, and ignore stray heat transfer and kinetic and potential energy effects. Steam 1 STATE DATA for SYSTEM P, = 30 bar T, = 600°C m = 1.5 kg/s n = 80% P2 = 3 bar P3 = 1 bar T3 = 27°C Turbine Compressor %3D 2 Airarrow_forward1- For modeling a gas turbine power plant producing 10 MW of power, the ideal air-standard Brayton cycle operating at steady state is used. Operating data at principal states in the cycle are given in the table below. The states are numbered as in Fig. below. (a) Sketch the T–s diagram for the cycle and determine (b) the mass flow rate of air, in kg/s, (c) the rate of heat transfer, in kW, to the working fluid passing through the heat exchanger, (d) the thermal efficiency.arrow_forward4Air enters the compressor of a simple gas turbine at p1 = 14 lbf/in2, T1 = 520°R. The isentropic efficiencies of the compressor and turbine are 83 and 87%, respectively. The compressor pressure ratio is 12 and the temperature at the turbine inlet is 2500°R. The volumetric flow rate of the air entering the compressor is 9000 ft3/min. Use an air-standard analysis. a) Determine the net power developed, in Btu/h. b) Determine the thermal efficiency of the cycle. c) The temperatures at the compressor and turbine exits in °R. d) The temperatures at the compressor and turbine enters in °R rmine the net power developed, in Btu/h .arrow_forward
- Air enters a two-stage compressor operating at steady state at 520°R, 14 Ibf/in.2 The overall pressure ratio across the stages is 16 and each stage operates isentropically. Intercooling occurs at constant pressure at the value that minimizes compressor work input, with air exiting the intercooler at 520°R. When the temperature of the air entering each compressor stage is the same, the minimum total compressor work input per unit of mass flowing occurs when the pressure ratio is the same across each stage. Assuming ideal gas behavior, with k = 1.4, determine the work per unit mass of air flowing for the two-stage compressor, in Btu per Ib of air flowing. W. Btu/lb marrow_forwardAir enters a compressor operating at steady state at 14 Ibf/in?, 60°F, with a volumetric flow rate of 6400 ft/min. The compression occurs in two stages, with each stage being a polytropic process with n= 1.27. The air is cooled to 80°F between the stages by an intercooler operating at 45 Ibf/in?. Air exits the compressor at 150 Ibf/in?. Step 1 Determine the magnitude of the total power required by the compressor, in Btu/min. W. i Btu/minarrow_forwardFigure shows a simple vapor power plant operating at steady state with water as the working fluid. Data at key locations are given on the figure. The mass flow rate of the water circulating through the components is 109 kg/s. Stray heat transfer and kinetic and potential energy effects can be ignored. Determine: (a) the mass flow rate of the cooling water, in kg/s. (b) the thermal efficiency. (c) the rates of entropy production, each in kW/K, for the turbine, condenser, and pump. (d) Using the results of part (c), place the components in rank order, beginning with the component contributing most to inefficient operation of the overall system. verlarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY