
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
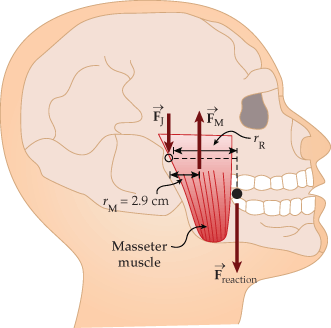
Unlike most of the other muscles in our bodies, the masseter muscle in the jaw, as illustrated in the figure, is attached relatively far from the joint, enabling very large forces to be exerted by the back teeth. This is shown in the figure below, where a person is biting down on a bullet placed between the back teeth. (FM= 210 N and rR = 4.1 cm.)
(a) Using the information in the figure, calculate the magnitude of the force exerted by the teeth on the bullet.
(b) Calculate magnitude of the force on the joint.
(b) Calculate magnitude of the force on the joint.
Transcribed Image Text:T
IM
F
2.9 cm
Masseter
muscle
FM
F₁
reaction
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Two identical, side-by-side springs with spring constant 240 N/m support a 2.00 kg hanging box. Each spring supports the same weight. By how much is each spring stretched?arrow_forwardA cord connected at one end to a block which can slide on an inclined plane has its other end wrapped around a cylinder resting in a depression at the top of the plane as shown in ( Figure 1). Determine the speed of the block after it has traveled 1.40 m along the plane, starting from rest. Assume there is no friction. Express your answer using two significant figures. Figure M = 33 kg R=0.20 m 58° 1 of 1 ΜΕ ΑΣΦ = 0.844 2+ Submit Previous Answers Request Answer ? m/s × Incorrect; Try Again; 2 attempts remaining Part B Determine the speed of the block after it has traveled 1.40 along the plane, starting from rest. Assume the coefficient of friction between all surfaces is -00310. Since the block is much lighter than the cylinder, ignore tension in the string when calculating the normal force on the cylinder. Do not ignore tension in the string when calculating the net torque (including friction) on the cylinder Express your answer using two significant figures. v= ΜΕ ΑΣΦ Submit Request…arrow_forwardA gymnast rises onto her toes, as shown in the picture on the right. The floor pushes up on the ball of her foot with a force of N=313 N. If 0=56.0°, what are FH the forces in her heel (TH) and ankle joint (T), and what is the angle o? Answers: TH=481 N; T,=761 N; b=20.7° N, 0. 4.25 cm 9.66 cm 5.arrow_forward
- Q4.2. A springboard-type diving board is built from high grade aluminum. This particular board has a mass of 65 kg and is 3.85 m long. 33.8 cm wide, and 5 cm thick. (Aside: Most springboards start thick on one end, then get thinner as it moves to the other end. For this problem, assume the springboard has a constant thickness) One end of the springboard is attached to a hinge. The hinge lets the springboard move up and down, but keeps it from sliding out of place. 1.1 m away from the hinge, the springboard rests on (but is not attached to) a fulcrum. A diver with a mass of 65 kg stands on the far end of the springboard (opposite from the hinge), ready to begin their dive. Hinge Fulcrum Note: the measurements for this problem were taken from the springboards used in the 2016 Summer Olympics, 3 m Springboard event.arrow_forwardA speedboat with a mass of 505 kg (including the driver) is tethered to a fixed buoy by a strong 29.7 m cable. The boat's owner loves high speed, but does not really want to go anywhere. So the owner revs up the boat's engine, makes a lot of noise, and runs the boat in circles around the buoy with the cable supplying all the necessary centripetal force. When the tension of the cable is steady at 12300 N, with what force is the boat's engine pushing the boat? Different physics textbooks treat drag force somewhat differently and use different formulas. For the present purpose, take the water's drag force on the boat to be (450 kg/m) × v², where v denotes the boat's speed. Ignore any drag force on the cable. force: N & TOOLS x10arrow_forwardA block of mass mA=20kg on an inclined plane and a bucket of mass mbucket=16kg are attached to the ends of a massless string passing through a massless pulley as shown in the figure below. The inclined plane makes an angle of θ=46o with the horizontal and the coefficients of kinetic and static friction are μk=0.21 and μs=0.58. The system is initially at rest and a student starts to fill the bucket with balls, each of whose mass is 100 grams, one at a time until the system starts to move. Determine the number of balls the student placed in the bucket. Take g=9.80m/s2 and please note that the number balls must be an integer!arrow_forward
- A uniform plank of length 2.00 m and mass 31.5 kg is supported by three ropes, as indicated by the blue vectors in the figure below. Find the tension in each rope when a 715–N person is d = 0.500 m from the left end. magnitude of T1 N magnitude of T2 N magnitude of T3 Narrow_forwardSystems are in equilibrium. If the spring scales are calibrated in newtons, what do they read? Ignore the masses of the pulleys and strings and assume the pulleys and the incline are frictionless. (Let m = 2.66 kg and ? = 29.0°.) scale in (a) N scale in (b) N scale in (c) N scale in (d) Narrow_forwardTo run Slap-chop and use Sham-wow you need to be in shape. For a work out, the man in the figure uses a device consisting of four springs arranged as shown. Each spring has a spring constant of 75.5 N/m. The hands holding the unstretched device are 36.34 cm apart. If the person can extend the springs to 61.87 cm apart, what is the maximum lateral force exerted by each hand?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON