
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
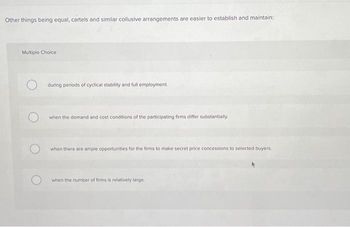
Transcribed Image Text:Other things being equal, cartels and similar collusive arrangements are easier to establish and maintain:
Multiple Choice
during periods of cyclical stability and full employment.
when the demand and cost conditions of the participating firms differ substantially.
when there are ample opportunities for the firms to make secret price concessions to selected buyers.
when the number of firms is relatively large.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- In cases where a cartel controls access to a key production input, firms in the cartel: have less incentive to cheat for fear that they will be cut off from the key input. will always have an incentive to cheat on the agreement, as cheating increases profits. are typically good at finding ways to access the key input outside the cartel. will never cheat on the cartel agreement.arrow_forwardplease explain in stepsarrow_forwardEconomicarrow_forward
- Q16 Suppose we are referring to OPEC, the oil cartel. Which would make it easier to maintain an effective collusive agreement among OPEC members? Multiple Choice the emergence of a number of potential entrant firms a decrease in the elasticity of demand for the OPEC's oil a new method of pricing that makes it more difficult for cartel members to determine the prices at which other cartel members are selling oil an increase in the number of substitutes for the oil produced by the OPEC cartel a pledge of allegiance to the cartelarrow_forwardWhen tacit collusion breaks down and prices collapse, the result is: a price war. formation of a cartel. price leadership. higher profits for the industry as a whole.arrow_forwardWhich of the following methods could a cartel NOT use to prevent its member fırms from breaking their agreements? If a member fırm breaks its agreement, it is a breach of contract and the firm is subject to legal penalties. The cartel acts as a monopolist, maximizing the combined profits of all the member firms. All of the other choices could be used to prevent member firms from breaking agreements. The cartel requires member firms to structure executive pay in such a way that the executives benefit personally from preserving the cartel. If a member firm breaks its agreement, that firm is kicked out of the cartel permanently and can no longer earn cartel profits in the future.arrow_forward
- Monopolistic competition is a market structure in which Question 17 options: firms compete on product quality, price, and marketing. natural or legal barriers prevent the entry of new firms. a small number of firms compete. firms produce identical products.arrow_forwardCartels have a difficult time maintaining their output agreements because an individual firm has an incentive to deviate (increase their output) from the arrangement. T/Farrow_forwardquestion # 24-3 brief explanationarrow_forward
- The inverse demand for a homogeneous-product Stackelburg duopoly is P=24000-5Q. The cost structures for the leader and the follower respectively are CL(QL)=3000QL and CF(QF)=4000QF. a) What is the followers reaction function? b) Determine the equilibrium output level for both the leader and the follower. Leader output: Follower output: c) Determine the equilibrium markert price $ d) Determine the profits of the leader and the follower. Leader profits: $ Follower profits: $arrow_forwardIn the industry structure there are no barriers to entry for new firms.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education