
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
Could you help me produce the expected cash collection from customers?
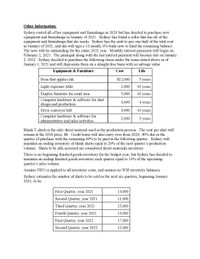
Transcribed Image Text:Other Information:
Sydney rented all of her equipment and furnishings in 2020 but has decided to purchase new
equipment and furnishings in January of 2021. Sydney has found a seller that has all of the
equipment and furnishings that she needs. Sydney has the cash to pay one-half of the total cost
in January of 2021, and she will sign a 12-month, 6% bank note to fund the remaining balance.
The note will be outstanding for the entire 2021 year. Monthly interest payments will begin on
February 2, 2021. The principal along with the last interest payment will become due on January
2, 2022. Sydney decided to purchase the following items under the terms stated above as of
January 1, 2021 and will depreciate them on a straight-line basis with no salvage value:
Equipment & Furniture
Cost
Life
Press that applies ink
$12,000
5 years
Light-exposure table
2,000
10 years
Display furniture for retail area
5,000
10 years
Computer hardware & software for shirt
design and production
4,000
4 years
Dryer conveyer belt
3,000
10 years
Computer hardware & software for
administrative and sales activities
2,000
5 years
Blank T-shirts is the only direct material used in the production process. The cost per shirt will
remain at the 2018 price, $8. Credit terms will also carry over from 2020; 40% due in the
quarter of purchase with the remaining 60% to be paid in the foll owing quarter. Sydney will
maintain an ending inventory of blank shirts equal to 20% of the next quarter's production
volume. Shirts to be silk-screened are considered direct materials inventory.
There is no beginning finished goods inventory for the budget year, but Sydney has decided to
maintain an ending finished goods inventory each quarter equal to 10% of the upcoming
quarter's sales volume.
Assume FIFO is applied to all inventory costs, and assume no WIP inventory balances.
Sydney estimates the number of shirts to be sold in the next six quarters, beginning January
2021, to be:
First Quarter, year 2021
14,000
Second Quarter, year 2021
11,000
Third Quarter, year 2021
15,000
Fourth Quarter, year 2021
13,000
First Quarter, year 2022
17,000
Second Quarter, year 2022
12,000

Transcribed Image Text:The selling price of each shirt will be $15. Ten percent of sales are projected to be cash sales
with the remaining sales on account. Some accounts had to be written off last year, so one
percent of credit sales are going to be budgeted as bad debt in each quarter of 2021. Of the
collectible credit sales, Sydney requires customers to pay 65% in the quarter of the sale and pay
the remaining balance in the following quarter. Assume the remaining balance from 2020 is
100% collectible and that no write-offs for the budget year will occur until 2022.
The estimated cost of ink used in the silk-screen process will be $68,375 in 2021 and will be
applied quarterly based on the number of shirts produced. This cost is treated as an indirect
material cost.
Knowing that the silk-screen process is labor intensive, Sydney plans to hire six students to help
with the process. Based on Sydney's production projections, 5,470 hours of labor will be
incurred during 2019 at an hourly rate of $12. Sydney expects that 95% of each quarter's labor
cost will be paid in the quarter incurred. The remaining cost will be paid in the following
quarter.
Sydney needed one person to handle some administrative duties along with working in sales.
Andy Lane, Director of Student Development at West State, was hired for this position. Andy
knows the officers of all student organizations on campus and is also very active in the
community. Because of his contacts, Sydney is willing to pay Andy $750 per month plus a 5%
sales commission on all sales.
Sydney also had to find a person skilled in computer graphics to generate the designs to be
printed on the shirts. She hired a graphics designer at a rate of $600 per month plus $0.15 for
each shirt printed. The entire cost of the graphic designer is treated as indirect labor.
The lease for a commercial building near the university and the downtown area requires monthly
rent of $1,500. 80% of the building will be used in the silk-screen process and 20% will be used
for sales and administration.
Maintenance and utility costs are both considered mixed costs. Sydney is confident that the
maintenance and utility costs from 2020 can be used to generate the budgeted costs for 2021.
The variable costs budgeted for maintenance and utilities are treated as product costs and driven
by production volume, but the fixed costs for these two items are to be treated like rent; 80%
incurred due to the silk-screen process and 20% incurred for sales and administrative activities.
Data for maintenance and utility costs incurred in 2020 follow:
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Which of the following is an effective internal control for cash payments? A.Payments should be authorised before they are made B.Payments to suppliers should be made as quickly as possible C.An experienced accountant should have total responsibility for all cash payment functions D.Supporting documentation should be destroyed immediately afterpayment to avoid incorrectly paying twicearrow_forwardWhich of the following is true of EFT? It is easy to document purchase and sale transactions. It means Effective Funds Transfer. It cost more than receiving cash payments through the mail. It can process certain cash transactions at less cost than by using the mail.arrow_forwardWhere do I find a businesses internal controls over cash receipts and cash payments?arrow_forward
- What are the four accounts that are typically affected by cash transactions. Please use the following illustration to help you answer this question.arrow_forwardWhat is cash disbursement journal? Why it is useful to auditor in cash audit?arrow_forwardplease answer in detail with explanationarrow_forward
- Explain the primary goal of maintaining a cash book. Use a case study company of your own choice to demonstrate how such a goal (Your arguments must only relate to the main goal of a cash book) can be attained. Provide examples as approperiate Clearly explain how a cash book can be integrated in the extraction/development of the Trial Balance. Are trade discounts included in the cash book? If not or if yes, explain why Are credit transactions included in the cash book? If not or if yes, explain why Ledgers help to organize accounting information into categories normally known as ‘’classes’’. With examples explain the nature and differences between revenue and capital ledgers Using two revenue and capital ledgers, explain how you will treat them in the trial balance. Explain the treatment of the proprietor’s additional contribution to an already existing business. In addition, explain the underlying accounting principle you will apply in answering this question. Thames Cotton Mills…arrow_forwardIf you were the banker, what information would you want from a company to evaluate their riskiness and their ability to repay a loan? What specific information would you need to begin a cash receipts forecast? Identify three items that would be helpful.arrow_forwardDescribe situations in which you might use a certified check, cashiers check or money order.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education