
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Transcribed Image Text:or
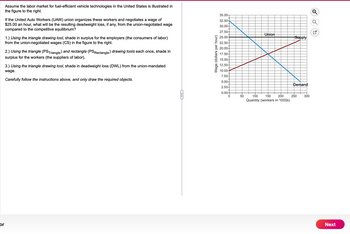
Assume the labor market for fuel-efficient vehicle technologies in the United States is illustrated in
the figure to the right.
If the United Auto Workers (UAW) union organizes these workers and negotiates a wage of
$25.00 an hour, what will be the resulting deadweight loss, if any, from the union-negotiated wage
compared to the competitive equilibrium?
1.) Using the triangle drawing tool, shade in surplus for the employers (the consumers of labor)
from the union-negotiated wages (CS) in the figure to the right.
2.) Using the triangle (PSTriangle) and rectangle (PS Rectangle) drawing tools each once, shade in
surplus for the workers (the suppliers of labor).
3.) Using the triangle drawing tool, shade in deadweight loss (DWL) from the union-mandated
wage.
Carefully follow the instructions above, and only draw the required objects.
G
Wage (dollars per hour)
35.00-
32.50-
30.00-
27.50-
25.00-
22.50-
20.00-
17.50-
15.00-
12.50-
10.00-
7.50-
5.00-
2.50-
0.00+
O
50
Union
100 150 200
Quantity (workers in 1000s)
Supply
Demand
250
300
Next
SAVE
AI-Generated Solution
info
AI-generated content may present inaccurate or offensive content that does not represent bartleby’s views.
Unlock instant AI solutions
Tap the button
to generate a solution
to generate a solution
Click the button to generate
a solution
a solution
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Economics Suppose that Congress passes a law requiring employers to provide employees some benefit (such as healthcare) that raises the cost of an employee by $3 per hour. Assume that firms were not providing such benefits prior to the legislation. On the following graph, use the green line (triangle symbel) to show the effect this employer mandate has on the demand for labor. Demand Supply 20 18 New Demand 10 14 12 New Supply 10 Equilibrium Before Law Equilibrium After Law 0 1 2 5 10 Quantity of Labor (Thousands) Suppose employees place a value on this benefit exactly equal to its cost. On the preceding graph, use the purple line (diamond symbol) to show the effect this employer mandate has on the supply of labor. Suppose the wage is free to balance supply and demand. Use the black point (plus symbol) to indicate the eauilibrium wage and level of employment before this law, and use the grey point (star symbol) to indicate the equilibrium wage and level of employment after this law is…arrow_forward(c) Let us now turn to the labor market for grocery store workers in Little town. Recently one of the last two grocery stores in Little town closed leaving only one employer for grocery store workers in this area. This labor market is not very competitive. What type of market structure is this? (d) Draw a typical supply curve (i.e. average expenditure), marginal expenditure, and demand for the grocery store in Little Town. Label the equilibrium wage and number of grocery store workers. (e) Suppose that some time has passed and the population has grown in Little Town and there are now many grocery stores. Now suppose that the grocery store workers unionize. Draw a graph to depict the equilibrium wage and number of workers in this new market.arrow_forwardConsider the Labor Market in New York and New Jersey. In both markets Demand is given by w = 1000-2E. Assume New York has a perfectly inelastic supply of 400 workers and New Jersey has perfectly inelastic supply of 200 workers. a. Graph the two markets and find the equilibrium wage in each market. b. With costless mobility across markets what would the long-run wage in each market. Show this in your graphs. c. Instead, assume that there are still 400 workers in New York and 200 in New Jersey but now the cost of moving is $ 100. What will be the long-run wage in each market? Explainarrow_forward
- In Tucson there are lots of bars and restaurants all of whom employ many workers. Wages for waitstaff are similar across most locations. What is the most appropriate market structure for the market for waitstaff in Tucson?arrow_forward3) The following data table contains the labor demand and labor supply schedules for low-skilled workers in San Francisco. Use the data to answer the questions below. Qd-labor demand W-wage $23.00 $22.00 $21.00 $20.00 $19.00 $18.00 $17.00 $16.00 $15.00 $14.00 $13.00 $12.00 $11.00 $10.00 $9.00 $8.00 $7.00 $6.00 $5.00 $4.00 $3.00 $2.00 0 5,000 10,000 15,000 20,000 25,000 30,000 35,000 40,000 45,000 50,000 55,000 60,000 65,000 70,000 75,000 80,000 85,000 90,000 95,000 100,000 105,000 Qs-labor supply 210,000 200,000 190,000 180,000 170,000 160,000 150,000 140,000 130,000 120,000 110,000 100,000 90,000 80,000 70,000 60,000 50,000 40,000 30,000 20,000 10,000 0 a) Find the equilibrium wage and quantity of workers for low-skilled workers in San Francisco. Show equilibrium graphically and include the wage intercepts.arrow_forwardOnly type writing allow....don't use pepar work .....arrow_forward
- Minimum Wages and Unions Assume an industry without legal minimum wages and unions. Show in a diagram how the equilibrium wage W* is determined, and briefly explain all the concepts in the diagram. Now suppose a minimum wage, WMIN, is legislated at a level lower than W*, i.e. WMIN<W*. Show it in the diagram and explain whether the labour market outcomes in part a. change, and how. Now suppose a minimum wage is legislated at a level higher than W*, i.e. WMIN>W*. Show it in the diagram and explain what the labour market outcomes will be. Now suppose a workers’ union is created and successfully negotiates wage WUNION, which is above both W* and WMIN, i.e. WUNION>WMIN>W*. Explain what the labour market outcomes will be compared to the previous part.arrow_forwardCan you let me know if i got these correct. thanksarrow_forwardSuppose that in a competitive output market, firms hire labor from a competitive labor market (so that the profit maximization conditions for hiring labor are as we discussed in class). The firm has a fixed number of machines and can produce the following quantities (Q) associated with the number of workers (L) in a given time period. L Q 0 0 1 12 2 20 3 26 4 30 5 32 The market price of the good this firm sells is $5. If the firm pays a wage of w = $19.90 per time period, then how many units of labor should this firm hire to maximize profit? Group of answer choices a) 1 b) 3 c) 4 d) 2 e) 5arrow_forward
- Walmart employs the majority of people in small rural town. It's demand for labor is given by QD=100-2P. The supply of labor is given by Qs=3P. ✓ people would be If the labor market functioned as a competitive market, the wage rate (the price of labor) would be employed, and the producer surplus would be Because Walmart faces little competition for workers, it decides to offer the wage that maximizes consumer surplus (the monopsonist price). This wage is ✓being employed. The producer surplus is now ✓. Note: don't worry if the number of ✓, which results in workers is not an integer.arrow_forward(2) Suppose you find the demand (Qd, as thousands) and supply (Qs, as thousands) for long-haul truck drivers in one market can be specified as functions of the yearly wage paid (W, as thousand $) as following. Demand for drivers: Qd = 155 – 1.5 * W, Supply of drivers: Qs = 36 + 0.25 * W, How much is the market equilibrium level of wage for truck drivers (as thousands) and the how many jobs will be in this market? Now you noticed a company pays 40% higher wage than the market equilibrium level to hire truck drivers, how to explain this case?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education