
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
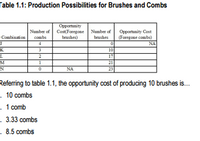
Transcribed Image Text:Table 1.1: Production Possibilities for Brushes and Combs
Opportunity
Number of Cost(Foregone Number of
brushes)
Opportunity Cost
(Foregone combs)
NA
Combinati on
combs
brushes
4
K
3
10
17
M
21
N
NA
Referring to table 1.1, the opportunity cost of producing 10 brushes is.
- 10 combs
. 1 comb
- 3.33 combs
.8.5 combs
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The table below shows Lanark's production possibilities. Wheat Cars A 0 95 B 90 90 C 158 81 204 63 226 F 235 36 a. If Lanark is producing 72 cars, it can produce approximately b. If Lanark is currently producing combination C, the cost of 46 more wheat is (Click to select) c. If Lanark is currently producing combination D, the approximate per unit cost of an additional car is necessary, round your answers to 1 decimal place. Remember to round 0.05 up to 0.10. wheat. (Click to select). Ifarrow_forwardWhat is the per-unit opportunity cost of product Y as production moves from point D to point A?arrow_forwardRefer to the production possibility frontiers for two friends Frodo and Sam who can both produce Ice creams and Jelly beans. Frodo's maximum production of Ice creams is 500 with no Jelly beans, or 2,000 Jelly beans with no Ice creams. Sam's maximum production of Ice creams is 600 with no Jelly beans, or 1,200 Jelly beans with no Ice creams. ICE CREAMS ICE CREAMS 600 500 1200 JELLY BEANS 2000 JELLY BEANS Frodo' PPF Sam's PPF Answer briefly these TWO questions in the box space provided below. Part A: Assuming efficient production without trade, derive the maximum amount of Jelly beans that can be produced by Sam along with 300 Ice creams. Describe your steps in detail. Part B: Assume that Frodo and Sam agree to specialize in production and trade between themselves. Frodo offers 1,000 Jelly beans to Sam in exchange for 300 lce creams. Would Sam agree to this trade?arrow_forward
- help please answer in text form with proper workings and explanation for each and every part and steps with concept and introduction no AI no copy paste remember answer must be in proper format with all workingarrow_forwardEddie Guitars 32 28 24 20 16 12 8 4 0 Tubas 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Dave Guitars 25 20 15 10 5 0 Tubas 0 1 2 3 4 5 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 0 0 2 1 2 4 3 6 4 8 5 10 6 Eddie and Dave both produce guitars and tubas. They produce a given amount of each per month as seen in the tables above. Given the production possibilities curves of each individual above, answer the following: Who has the comparative advantage in the production of guitars? Eddie, because he is able to produce a greater number of guitars compared to Dave Dave, because his opportunity cost of producing a guitar is 5 tubas compared to Eddie's opportunity cost of producing a guitar of 4 tubas Eddie, because his opportunity cost of producing a guitar is 0.25 tubas compared to Dave's opportunity cost of producing a guitar of 0.20 tubas Dave, because he is able to produce a lower number of guitars compared to Eddie Dave, because he is able to produce a greater number of guitars compared to Eddie Dave, because his…arrow_forwardQUESTION 9 product Y product Y 28 # 20 16 12 00 8 4 0 28 24 20 16 12 8 4 0 0 Fig. A Production Possibilities Frontier 4 PPFO PPFO 4 8 PPFn 8 12 Fig. C Production Possibilities Frontier PPFn 16 12 Point E 20 24 product X 16 Point E 20 product Y 2 product Y 28 20 16 12 8 4 0 20 16 12 8 4 0 0 Fig. B Production Possibilities Frontier 0 PPFO 4 8 4 PPFo PPFn 12 8 24 product X 09. In figure A the shift of the Production Possibilities Frontier outward would be best explained by: O (a) a movement towards efficient production. O (b) an increase in demand for both products. (c) an increase in specialization of resources. O (d) an increase in available resources specific to the production of good X. (e) an increase in available resources specific to the production of good Y. Fig. D Production Possibilities Frontier PPF 16 Point E 12 20 24 product X 16 Point E 20 24 product Xarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education