
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
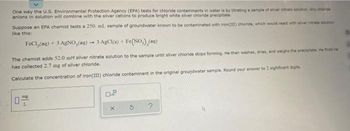
Transcribed Image Text:One way the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) tests for chloride contaminants in water is by titrating a sample of silver nitrate solution. Any chande
anions in solution will combine with the silver cations to produce bright white silver chloride precipitate
Suppose an EPA chemist tests a 250. ml. sample of groundwater known to be contaminated with iron(III) chloride, which would react with silver nitrate solution
like this:
FeCl₂(aq) + 3 AgNO,(aq) → 3 AgCl(s) + Fe(NO), (aq)
The chemist adds 52.0 mM silver nitrate solution to the sample until silver chloride stops forming. He then washes, dries, and weighs the precipitats. He finds he
has collected 2.7 mg of silver chloride.
Calculate the concentration of iron(III) chloride contaminant in the original groundwater sample. Round your answer to 2 sighficant digits.
0
mg
L
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider the reaction: Al(NO3)3 (aq) + MgCl2 (aq) ➝ AlCl3 (aq) + Mg(NO3)2 (aq). You mix together 25.0 mL of 0.85 M Al(NO3)3 and 25.0 mL of 0.90 M MgCl2 in the lab. What will the final concentration of aluminum chloride be?arrow_forwardComplete the table below by deciding whether a precipitate forms when aqueous solutions A and B are mixed. If a precipitate will form, enter its empirical formula in the last column. solution A manganese(II) iodide potassium hydroxide sodium chloride solution B nickel(II) acetate copper(II) sulfate ammonium nitrate Does a precipitate form when A and B are mixed? yes O no O yes O no O yes O no empirical formula of precipitate 0 0 0arrow_forwardIf 20.0 g of LiOH is added to 0.750 L of 1.00 M Cd(NO₃)₂, how many grams of precipitate will be formed in the following precipitation reaction? a) Write a balanced equation. Identify a precipitate. Include states of matter. b) Determine how much precipitate would form if all reactant 1 ( LiOH) would be used up. c) Determine how much precipitate would form if all reactant 2 ( Cd(NO3 )2 would be used up. d) State Limiting reactant , and theoretical yield ( in grams) of the precipitate that would form from the given amounts.arrow_forward
- Solid nickel(II) acetate is slowly added to 75.0 mL of a 0.0349 M potassium hydroxide solution. The concentration of nickel ion required to just initiate precipitation is M.arrow_forwardThe solubility of an ionic compound in water can be expressed in terms of the mass that will dissolve in a given volume of water, or in terms of the solubility product, Ksp. See Periodic Table If only 0.238 g of Ca(OH)2 dissolves in enough water to give 0.243 L of aqueous solution at a given temperature, what is the Ksp value for calcium hydroxide at this temperature?arrow_forward[References] Use the References to access important values if needed for this question. The iodide ion concentration in a solution may be determined by the precipitation of lead iodide. Pb2+(aq) + 21(aq) PbI2(s) A student finds that 16.64 mL of 0.5820 M lead nitrate is needed to precipitate all of the iodide ion in a 25.00-mL sample of an unknown. What is the molarity of the iodide ion in the student's unknown? Submit Answer Try Another Version 1 item attempt remaining ot ot pt pt pt Previous Next ail 6,290 10 15 MAY étv W X 280arrow_forward
- A 1.00 gram sample of anhydrous cerium sulfate was dissolved in water. Barium nitrate solution was then added until no further precipitation occurred. The precipitate was filtered from the solution then dried and was found to weigh 1.41 g. Determine the formula of the cerium sulfate. Encom calt is hydratedarrow_forwardb) Water "softeners" work via the principle of ion-exchange. The tank of a water softener is filled with a soluble salt such as sodium chloride. As "hard" water passes through the tank, the undesirable ions in hard water (e.g., calcium, magnesium, and iron III) are exchanged for the more desirable "soft" (meaning more soluble) ions like sodium. Explain how swapping the "soft"-water sodium ions for "hard"-water ions would influence the behavior (the cleaning effectiveness) of soaps and detergents.arrow_forward4. Using the solublity chart we can see that compound is soluble KNO3 PBCI Ca(OH)2 Aglarrow_forward
- Mercury as an amalgam with copper, silver, and tin is used fro fillings in teeth and in the production of chlorine. Soluble mercury compounds can be toxic and must be removed from wastewater. Aqueous mercury (II) nitrate is a toxic compound formed in wastewater and must be removed. To remove this compound, an aqueous sodium sulfide (Na2S) solution is added to wastewater to form a solid mercury (II) sulfide (HgS) precipitate and aqueous sodium nitrate in solution. From the analysis, 0.051 L of 0.010 M mercury (II) nitrate was reacted with 0.020 L of 0.10 M sodium sulfide. Write a balance equation for this chemical reaction. Determine the limiting reactant. How many grams of mercury (II) sulfide form? How many grams of excess reactant remain after the reaction is finished?arrow_forwardIf 30.0 g of LiOH is added to 0.650 L of 1.00 M Cd(NO₃)₂, how many grams of precipitate will be formed in the following precipitation reaction? a) Write a balanced equation. Identify a precipitate. Include states of matter. b) Determine how much precipitate would form if all reactant 1 ( LiOH) would be used up. c) Determine how much precipitate would form if all reactant 2 ( Cd(NO3 )2 would be used up. d) State Limiting reactant , and theoretical yield ( in grams) of the precipitate that would form from the given amounts.arrow_forwardSome compounds are soluble in water and some compounds are insoluble in water. For each compound below determine if the compound if soluble or insoluble in water. * Soluble Insoluble Mg(NO:): Agcl LIOH Mg:(PO.):arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY