
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
One mole of an ideal gas undergoes the cycle, A⟶B⟶C⟶A, as shown in the graph. For this gas, CV = 1.5R. Step C⟶A is isothermal and reversible.
1) Calculate W for each step in the process.
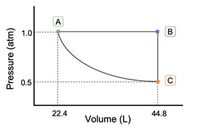
Transcribed Image Text:The image presents a graph titled “Pressure vs. Volume,” illustrating the relationship between pressure (in atmospheres) and volume (in liters) for a gas.
### Axes:
- The vertical axis represents Pressure (atm), ranging from 0.5 atm to 1.0 atm.
- The horizontal axis represents Volume (L), ranging from 22.4 L to 44.8 L.
### Graph Details:
- The curve on the graph is a downward slope from point A to point C.
- **Point A** is located at (22.4 L, 1.0 atm), indicating higher pressure and lower volume.
- **Point B** is at (44.8 L, 1.0 atm), representing the same pressure as Point A but at a larger volume.
- **Point C** is at (44.8 L, 0.5 atm), indicating lower pressure at the maximum volume depicted.
The curve illustrates an inverse relationship between pressure and volume, aligning with Boyle's Law, which states that pressure is inversely proportional to volume for a given mass of gas at constant temperature.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- For which of the following reactions, carried out at constant temperature and pressure does AU = AH? Note: You may ignore work which is not related to gasses. Oa. 2HCI(g) + Mg(s) → MgCl2(s) + H2(g) Ob. O2(g) + N2O5(g) → O3(g) + N½O4(g) Oc. HCI(g) + NH3(g) – NH,CI(s) Od. H20(1) + CaC2(s) → C2H2(g) + Ca(OH)2(s) Oe. 20O2(g) + 4H2O(g) – 302(g) + 2CH;OH()arrow_forwardDescribe the second law of thermodynamics in at least one sentence?arrow_forwardOne mole of an ideal gas is contained in a cylinder with a movable piston. The temperature is constant at 77°C. Weights are removed suddenly from the piston to give the following sequence of three pressures. a. P, = 4.60 atm (initial state) b. P₂ = 2.73 atm c. P3 1.00 atm (final state) What is the total work (in joules) in going from the initial to the final state by way of the preceding two steps? J What would be the total work if the process were carried out reversibly?arrow_forward
- One mole of an ideal gas is contained in a cylinder with a movable piston. The temperature is constant at 78°C. Weights are removed suddenly from the piston to give the following sequence of three pressures. a. P₁ b. P2 c. P3 = 5.20 atm (initial state) = 2.53 atm = 1.00 atm (final state) What is the total work (in joules) in going from the initial to the final state by way of the preceding two steps? J What would be the total work if the process were carried out reversibly? Jarrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardGeneral Chemistry 4th Edition McQuarrie • Rock • Gallogly University Science Books presented by Macmillan Learning Consider an ideal gas enclosed in a 1.00 L container at an internal pressure of 24.0 atm. Calculate the work, w, if the gas expands against a constant external pressure of 1.00 atm to a final volume of 24.0 L. w = J Now calculate the work done if this process is carried out in two steps. 1. First, let the gas expand against a constant external pressure of 1.50 atm to a volume of 16.0 L. 2. From the end point of step 1, let the gas expand to 24.0 L against a constant external pressure of 1.00 atm. w = Jarrow_forward
- Under what temperature conditions (low T, high T, all T, nonspontaneous at all T) would this reaction occur spontaneously? Explain your reasoning. 2NH4NO3(s) → 2N2(g) + 4H2O(l) + O2 (g) , ∆Horxn = -236.0 kJarrow_forward1. Argon is allowed to expand isothermally (at 298 K) and reversibly from an initial molar volume of 5.0 L/mol to a final molar volume of 11 L/mol. (a) Calculate the work (in units of kJ to 4 sig. figs.) done assuming it behaves as an ideal gas (b) Calculate the work (in units of kJ to 4 sig. figs) assuming it is non-ideal using the van der Waals equation where a = 1.34 atm L2 mol-2 b = 3.20 x 10-2 L mol-1arrow_forward00 IN L OUniversity Science Book: presented by Macmillan Learning Stry 4th Edition McQuarrie Rock Gallogly Consider an ideal gas enclosed in a 1.00 L container at an internal pressure of 18.0 atm. Calculate the work, w, if the gas expands against a constant external pressure of 1.00 atm to a final volume of 18.0 L. Now calculate the work done if this process is carried out in two steps. 1. First, let the gas expand against a constant external pressure of 1.80 atm to a volume of 10.0 L. 2. From the end point of step 1, let the gas expand to 18.0 L against a constant external pressure of 1.00 atm. = M Question Source: McQuarrie, Rock, And Gallogly 4e - General Chemsitry Publisher. University Science Books MacBook Pro Q Search or enter website name { [ 7. $4 P. 5. 4. U E. K. H. B. gEarrow_forward
- A system expands in volume from 2.0 L to 24.5 L at constant temperature. Calculate the work (w) if the expansion occurs against a constant pressure of 5.00 atm.arrow_forwardCalculate ΔE for a system that absorbs 506.0 kJ of heat from its surroundings and does 379.0 kJ of work on its surroundings.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY