
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
One kind of slingshot consists of a pocket that holds a pebble and is whirled on a circle of radius r. The pebble is released from the circle at an angle θ, so that it will hit the target. The distance to the target from the center of the circle is d. (See the drawing, which is not to scale.) The circular path is parallel to the ground, and the target lies in the plane of the circle. The distance d is 5.19 times the radius r. Ignore the effects of gravity in pulling the stone downward after it is released and find the angle θ.
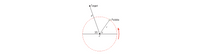
Transcribed Image Text:### Diagram Explanation: Trajectory of a Pebble
In this diagram, we visualize the trajectory path of a pebble aimed at a target point. Here’s a detailed explanation of the components and their roles:
1. **Circle Description**:
- The circle is indicated with a dashed red line and represents the path along which the pebble travels when launched.
- The center of the circle is marked as point \( C \).
2. **Pebble's Position**:
- The point labeled "Pebble" is shown on the circumference of the circle.
- A radius \( r \) extends from the center \( C \) to the pebble's position on the circle.
3. **Target Position**:
- There is a point labeled "Target" located outside the circle.
- The distance from the center \( C \) to the target is marked as \( d \).
4. **Angles and Measurements**:
- The angle between the radius \( r \) and the line connecting the center \( C \) to the target is labeled as \( \theta \).
- An adjacent angle to \( \theta \) is labeled as \( 35^\circ \) which suggests a base angle in the calculations relevant to the scenario.
5. **Direction**:
- A curved arrow is drawn alongside the circle, indicating the direction of pebble's movement along the circular path.
### Contextual Use
This diagram can be used to illustrate concepts related to projectile motion, circular motion dynamics, and trigonometric calculations in physics or mathematics education. The setup helps to explore variables such as angles, radii, and distances when a projectile changes its trajectory from a circular path towards a linear one aimed at a particular target.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- What is the direction of the vector product A × B? Use the legend in the box to indicate direction. a В (out) (out) O (in) zero in C b zero a e h outarrow_forwardFor a vector with components (5.2, 7.5), calculate the magnitude. Your Answer: Answerarrow_forwardThe average distance of the earth from the sun is about 1.5 x 108 km (Figure 1). Assume that the earth's orbit around the sun is circular and that the sun is at the origin of your coordinate system. (a) Estimate the speed of the earth as it moves in its orbit around the sun. Express your answer in miles per hour with the appropriate number of significant figures. (b) Estimate the angle between the position vector of the earth now and what it will be in 4 months. (c) Calculate the distance between these two positions.arrow_forward
- Jack goes for a ride on a ferris wheel that has a radius of 37 meters. The center of the ferris wheel is 49 meters above the ground. He starts his ride at the 12 o'clock position and travels counter clockwise. Define a function g that represents Jack's horizontal distance in meters relative to vertical midline of the wheel in terms of the angle (measured in radians) Jack makes with the center.arrow_forwardConsider the following vectors: A = 1.2i + 4.9j + 3.7k B = -8.5i + 7.5j + 8.3k Part (a) What is the x-component of the vector V = 3(A × 2B)? Part (b) What is the y-component of the vector V = 3(A × 2B)? Part (c) What is the z-component of the vector V = 3(A × 2B)? Part (d) What is the magnitude of the vector V?arrow_forwardI do not know how to get started with my graph. Does my x axis need to be between 7.84 or 15.68 and my y axis between 0.779 or 1.558. If so how should I start my graph and how much should I go up by with both x and y axis's. Please help! I am confused.arrow_forward
- Two vectors have the following magnitude, A = 8.7 m and B = 10.6 m. Their vector product is: A:B = -2.7 m i+ 8.6 m k. What is the angle (in degrees) between the vectors A and B? Hint: Use |A:B| = AB sin(0) Note: Bold face letters represents a vector.arrow_forwardVector R is defined as the vector sum of vectors A and D (?⃗ = ? + ?⃗ ) shown below. What are the vector components of vector R?arrow_forwardFind a unit vector perpendicular to A = (î+ ĵ – Îk) and B = ( 2i + j- 3k). (Hints. One method to find the unit vector C perpendicular to A and B will be to use the fact that the cross product is perpendicular to both vectors A and B, but keep in mind that the magnitude of the unit vector is one. There is another method which is a little bit longer by using the fact that the dot product AC=0 and BC=0 where C is the unit vector )arrow_forward
- What is the relation between A×B and BxA, The magnitudes are the same but they are in opposite directions, i.e., (Ã×B)=-(BxÃ) The order of the vectors in a cross product doesn't matter so they are the same, i.e., (ÃxB)=(BxÃ)arrow_forwardFor the vectors in the figure, with a = 8.0, b = 6.0, and c = 10 what are the magnitude and the direction b×c?arrow_forwardImagine that you take the cross product A x B, where A=2x + 74 and B=2x + € + 1ŷ. What is the z-component of the resulting vector?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON