
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
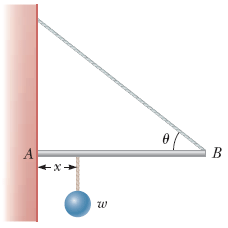
One end of a uniform ℓ = 4.50-m-long rod of weight w is supported by a cable at an angle of θ = 37° with the rod. The other end rests against a wall, where it is held by friction (see figure). The coefficient of static friction between the wall and the rod is μs = 0.480. Determine the minimum distance x from point A at which an additional weight w (the same as the weight of the rod) can be hung without causing the rod to slip at point A.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 11 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Chapter 12, Problem 028 GO In the figure, suppose the length L of the uniform bar is 2.7 m and its weight is 220 N. Also, let the block's weight W = 280 N and the angle 0 = 27°. The wire can withstand a maximum tension of 440 N. (a) What is the maximum possible distance x before the wire breaks? With the block placed at this maximum x, what are the (b) horizontal and (c) vertical components of the force on the bar from the hinge at A? com A (a) Number Units (b) Number Units (c) Number Units Click if you would like to Show Work for this question: Open Show Workarrow_forwardA wrecking ball (weight = 5670 N) is supported by a boom, which may be assumed to be uniform and has a weight of 2760 N. As the drawing shows, a support cable runs from the top of the boom to the tractor. The angle between the support cable and the horizontal is 32°, and the angle between the boom and the horizontal is 48°. Find (a) the tension in the support cable and (b) the magnitude of the force exerted on the lower end of the boom by the hinge at point P. (a) Number (b) Number Mk Support, cable Units Units N N 48 Boomarrow_forwardA ladder of length 12.0 m with a mass of 40.0 kg leans against a smooth wall. The ladder makes a 35.0o angle with the horizontal. Draw an adequate free body diagram of the ladder and determine the minimum coefficient of static friction between the ladder and the ground necessary to prevent the ladder from slipping.arrow_forward
- A uniform ladder 5.0 m long rests against a frictionless, vertical wall with its lower end 3.0 m from the wall. The ladder weighs 160 N. The coefficient of static friction between the foot of the ladder and the ground is 0.40. A man weighing 740 N climbs slowly up the ladder. (a) What is the maximum friction force, in Newtons, that the ground can exert on the ladder at its lower end? (b) What is the actual friction force, in Newtons, when the man has climbed 1.0 m along the ladder? (c) How far, in meters, along the ladder can the man climb before the ladder starts to slip?arrow_forwardOne end of a uniform € = 3.40-m-long rod of weight w is supported by a cable at an angle of 8 = 37° with the rod. The other end rests against a wall, where it is held by friction (see figure). The coefficient of static friction between the wall and the rod is μ = 0.590. Determine the minimum distance x from point A at which an additional weight w (the same as the weight of the rod) can be hung without causing the rod to slip at point A. Barrow_forwardA scaffold of mass 79 kg and length 5.0 m is supported in a horizontal position by a vertical cable at each end. A window washer of mass 84 kg stands at a point 1.1 m from one end. What is the tension in (a) the nearer (relative to the person) cable and (b) the farther (relative to the person) cable? (a) Number i Units (b) Number i Unitsarrow_forward
- One end of a uniform 4.10-m-long rod of weight Fg is supported by a cable at an angle of ? = 37° with the rod. The other end rests against the wall, where it is held by friction as shown in the figure below. The coefficient of static friction between the wall and the rod is ?s = 0.480. Determine the minimum distance x from point A at which an additional object, also with the same weight Fg, can be hung without causing the rod to slip at point A. ------marrow_forwardOne end of a uniform { = 4.30-m-long rod of weight w is supported by a cable at an angle of 0 = 37° with the rod. The other end rests against a wall, where it is held by friction (see figure). The coefficient of static friction between the wall and the rod is µ. = 0.490. Determine the minimum distance x from point A at which an additional weight w (the same as the weight of the rod) can be hung without causing the rod to slip at point A. B Need Help? Read It Watch Itarrow_forwardA fence post of mass m = 8 kg supports a fence with three lengths of barbed wire. The bottom wire is a distance d = 0.35 m from the ground and each wire is a distance 0.35 m above the previous one. Each of these three wires has the tension on it. For this problem, assume that the force exerted by these wires is purely horizontal. An additional guy wire is used to keep the pole upright with a tension of Fa = 490 N. The guy wire attaches to the post at a point h = 0.86 m above the ground and makes an angle of θ = 45 with respect to the horizontal. Write an expression for the tension in any one of the three fence wires. What is the normal force that the ground exerts upward on the post?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON