
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
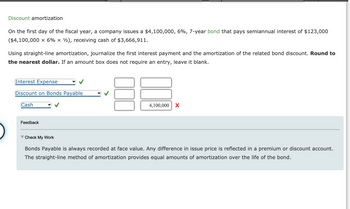
Transcribed Image Text:### Discount Amortization
On the first day of the fiscal year, a company issues a $4,100,000, 6%, 7-year bond that pays semiannual interest of $123,000 ($4,100,000 × 6% × ½), receiving cash of $3,666,911.
Using straight-line amortization, journalize the first interest payment and the amortization of the related bond discount. **Round to the nearest dollar.** If an amount box does not require an entry, leave it blank.
#### Journal Entries
| Account | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
|-------------------------------------|-------------|-------------|
| Interest Expense | | |
| Discount on Bonds Payable | | |
| Cash | | 4,100,000 |
Feedback:
- **Bonds Payable** is always recorded at face value. Any difference in the issue price is reflected in a premium or discount account.
- The straight-line method of amortization provides equal amounts of amortization over the life of the bond.
#### Notes:
- In this section, you need to fill in the journal entries correctly. Ensure you follow the instructions and provide a detailed explanation where necessary.
- Address any potential questions or issues that may arise from this practice problem.
> **Check My Work Explanation:**
> - The table provided is designed to check the accuracy of journal entries concerning bond issues and amortization.
> - Remember, discount or premium on bonds payable should be amortized over the bond's life span, and this exercise helps in achieving proficiency in doing that.
This exercise will aid students in understanding and applying bond accounting concepts specifically surrounding premium and discount amortizations using the straight-line method.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- On January 1, Topeka Outfitters issued $175,000 of 6%, 3-year bonds when the market rate of interest was 10%. The bonds pay interest semiannually on June 30 and December 31. A. How much are the proceeds that Topeka Outfitters? will receive on the issue date of the bonds? B. Prepare an amortization table for the bond issue. C. If the bonds are retired at the end of Year 2 at 104.5% of the maturity value, how much gain or loss on retirement will be reported?arrow_forwardInstructions On the first day of the fiscal year, a company issues a $1,450,000, 5% , five-year bond that pays semiannual interest of $36,250 ($1,450,000 x 5% *%), receiving cash of $1,408,720. Journalize the first interest payment and the amortization of the related bond discount Round to the nearest dollar. Refer to the Chart of Accounts for exact wording of account titles Journal DATE DESCRIPTION JOURNAL POST REF DEBIT CREDITarrow_forwardOn the first day of the fiscal year, a company issues a $5,000,000, 10%, 4-year bond that pays semiannual interest of $250,000 ($5,000,000 × 10% × ½), receiving cash of $5,336,638. Journalize the bond issuance. If an amount box does not require an entry, leave it blank.arrow_forward
- On the first day of the fiscal year, a company issues a $900,000, 9%, 5-year bond that pays semiannual interest of $40,500 ($900,000 x 9% × 1/2), receiving cash of $884,176. Journalize the entry for the issuance of the bonds.If an amount box does not require an entry, leave it blankarrow_forwardOn January 2, current year, Kalahari Limited issued $1,000,000, 10-year bonds for $1,150,000. The bonds pay interest on June 30 and December 31. The stated rate is 10% and the market rate is 8%. The company plans to use the effective interest method of amortizing bond discounts and premiums. The semiannual cash payment on the bonds isarrow_forwardOn the first day of the fiscal year, a company issues a $8,300,000, 6%, 8-year bond that pays semiannual interest of $249,000 ($8,300,000 × 6% × ½), receiving cash of $6,901,364. Journalize the first interest payment and the amortization of the related bond discount. Round to the nearest dollar. If an amount box does not require an entry, leave it blank. Interest Expense fill in the blank 2 fill in the blank 3 Discount on Bonds Payable fill in the blank 5 fill in the blank 6 Cash fill in the blank 8 fill in the blank 9arrow_forward
- On January 1, Year 1, Hanover Corporation issued bonds with a $39,000 face value, a stated rate of interest of 8%, and a 5-year term to maturity. The bonds were issued at 97. Hanover uses the straight-line method to amortize bond discounts and premiums. Interest is payable in cash on December 31 each year. How much interest expense will Hanover report on its income statement on December 31, Year 1? Multiple Choice O O O O $234 $1,170 $3.354 $3,120arrow_forwardWhat would be the required journal entry on the date of issuance if a company issues $100,000 five-year, 10% bond for $103,769 and the interest is to be paid semiannually? debit cash, $100,000, and credit bond payable $100,000 debit cash $103,769, and credit bond payable $100,000 and credit premium on bonds payable $3,769 debit bonds payable $103,769 and debit discount on bonds payable $3,769, and credit cash $100,000 debit cash $103,769 and debit discount on bonds payable $3,769, and credit bonds payable $100,000arrow_forwardAssume that on July 1, Jerome, Inc., paid $100,000 to buy Potter's 8 percent, two-year bonds with a $100,000 par value. The bonds pay interest semiannually on December 31 and June 30. Jerome intends to hold the bonds until they mature. Complete the necessary December 31 entry to record receipt of interest by selecting the account names from the pull-down menus and entering dollar amounts in the debit and credit columns.arrow_forward
- On the first day of the fiscal year, a company issues a $980,000, 8%, 5-year bond that pays semiannual interest of $39,200 ($980,000 x 8% x 1/2), receiving cash of $884,174. Journalize the entry for the issuance of the bonds. If an amount box does not require an entry, leave it blank.arrow_forwardTHIS QUESTION WILL ALSO BE CHECKED MANUALLY (to make adjustments for typos). QUESTION 9 On the first day of the fiscal year, a company issues a $828,000, 12%, 10-year bond that pays semiannual interest of $49,680, receiving cash of $869,400. Journalize the entry for the first interest payment and amortiation of premium using the straight-line method and the chart of accounts below. Bonds Payable Cash Discount on Bonds Payable Interest Revenue Gain on Redemption of Bonds Interest Expense Interest Payable Loss on Redemption of Bonds Premiun on Bonds Payable Enter your answers into the table below. Key the account names carefully (exactly as shown above) and follow formatting instructions below. DO NOT USE A DECIMAL WITH ZEROES FOR WHOLE DOLLAR AMOUNTS AND USE COMMAS APPROPRIATELY. WHEN THE DEBIT/CREDIT DOES NOT REQUIRE AN ENTRY, LEAVE IT BLANK. Account Debit Credit THIS QUESTION WILL ALSO BE CHECKED MANUALLY (to make adjustments for typos). Click Save and Submit to save and submit. Click…arrow_forwardOn the first day of the fiscal year, a company issues a $8,500,000, 6%, 5-year bond that pays semiannual interest of $255,000 ($8,500,000 \times 6% \times (1)/(2)), receiving cash of $7,491, 128. Using straight - line amortization, journalize the first interest payment and the amortization of the related bond discount. Round to the nearest dollar. If an amount box does not require an entry, leave it blank.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education