
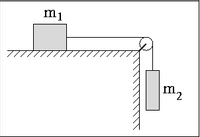
On a table that is frictionless lies a block that is 3.5 kg, which is connected to another hanging block of 5.0 kg. The string and pulley both have negligible masses. The block that is hanging will fall a distance, y, of 0.1m if released.
What is the work done by gravity on the two-block system?
What is the work done by the normal force on block on table?
What is the work done by tension on the block on the table? Please provide answer in the form of an algebraic expression.
Please state if the work done by tension by the hanging block. Is it zero, negative, or positive?
Please state the net work done on the hanging mass as an algebraic expression?
What will be the speed of the hanging block after falling a distance, y?
What is the tension on the string?
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

- A factory worker moves a 20.0 kg crate a distance of 4.40 m along a level floor at constant velocity by pushing horizontally on it. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and the floor is 0.200. Part A: What magnitude of force must the worker apply? Part B: How much work is done on the crate by the worker's push? Part C: How much work is done on the crate by friction? Part D: How much work is done by the normal force and by the gravity? Part E: What is the net work done on the crate?arrow_forwarda 40 N horizontal force is applied to a 6.0 kg box. Friction is negligible. The box moves a horizontal distance of 4.0 meters. The work done by the 40 N force is A. 160 J B. 10 J C. 80 J D. 92 Jarrow_forwardA m=2.90 kg book is pushed by a completely horizontal force Fa=15.0 N a distance d=0.75m up a frictionless incline of angle theta = 25 as in Figure 1. A. Determine the work done on the book by Fa. B. Determine the work done on the book by the gravity. C. Determine the work done on the normal force. D. Determine the net work done on the book. E. If the initial velocity is vi=0 m/s, determine the final velocity of the book.arrow_forward
- A 300-g block is dropped onto a relaxed vertical spring that has a spring constant k-210.0 N/m. The block becomes attached to the spring and compresses the spring 38.5 cm before momentarily stopping. While the spring is being compressed, what work is done on the block by the gravitational force on it? SA Tries 0/5 While the spring is being compressed, what work is done on the block by the spring force? SubArTries 0/5 What is the speed of the block just before it hits the spring? (Assume that friction is negligible.) Tries 0/5 If the speed at impact is doubled, what is the maximum compression of the spring? SA Tries 0/5 Post Discussion Send Feedbackarrow_forwardA grocery cart with a mass of 10 kg is being pushed at constant speed up a 25° ramp by a force Fp which acts parallel to the incline. (Ignore the friction) a. Draw a free-body diagram of the cart showing all the forces acting on it. b. Find the work done by each of the forces (W, Fn, Fp) on the cart if the ramp is 7.5 m long. Hints: The question is very similar to the question of a piano sliding down an incline discussed in class. However, here the object is pushed up the incline. The forces Fn = mgcos(0), and Fp = mgsin(0), so don't spend time getting these using Newton's 2nd law. Also, the weight is W = mg. c. Find the net work done on the cart.arrow_forwardStopping distance. A car is traveling on a horizontal road with speed v_0=13.9 m/s at the instant the brakes are locked, so the tires are sliding instead of rolling. Use the work-energy theorem to calculate the minimum distance the car can stop if the coefficient of kinetic friction \mu_k=0.7 between the tires and the road. B: A: 12 m 16 m C: 17.5 m D: 14 m. E: 23.7 marrow_forward
- A 6 kg block initially at rest is pulled to the right along a rough surface ( c) by a constant horizontal force of F = 12 N at an angle 0 = 30° as shown in the figure. The block is moved over a distance of 3 m and Its final speed is 2 m/s. F Find the following : 1. The normal force? 2. The work done by force F? 3. The total work done on the block? 4. The work done by frictional force? 5. The kinetic frictional force (f)? 6. The coefficient of kinetic friction (u,) between the block and the surface ? 7. The increase in the internal energy?arrow_forwardA crate is placed at the upper end of the 2.0 m long ramp that is inclined at 20° to the horizontal and allowed to slide down the ramp starting from rest. The crate has a mass of 150 KG and the coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and then incline is 0.25. Draw a diagram showing all the forces acting on the crate. How much work is done by the gravity on the crate during the slide? How much work is done by friction during the slide? Use the work energy theorem to calculate the speed attained at the bottom of the ramp.Also,Which force does no work during the slide, and why?arrow_forwardThe work done by a conservative force is indicated in the figure for a variety of different paths connecting the points A and B. What is the work done by this force on path 1? What is the work done by this force on path 2?arrow_forward
- 2. A cart is pulled a distance D on a flat, horizontal surface by a constant force F that actsat an angle θ with the horizontal direction. The other forces on the object during thistime are gravity (Fw), normal forces (FN1) and (FN2), and rolling frictions Fr1 and Fr2,as shown below. What is the work done by each force?arrow_forwardA box of mass M = 5 kg is sliding down a rough inclined plane with a constant velocity of v= 7.6 m/s, as in the figure below. There is friction between the incline and the box. What is the magnitude of the work done by the frictional force during a 5 second interval of the boxes slide? The angle of the incline 0 is 35 degrees. do 0 V Marrow_forwardThe overworked Amazon delivery person is driving up a steep hill with an incline of 26° when a box they forgot to secure starts sliding toward the back of the truck. The 3.5 kg box starts from rest near the drivers seat and slides 2.1 m along the floor to the rear door. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the box and the floor is 0.36. What is the work done by the weight of the box? Wmg 31.6 J What is the work done by the Normal Force? WN = 0 What is the work done by the frictional force? Wfk = 23.31 What is the net work done on the box? Wnet What is the change in kinetic energy for the box? AKE How fast is the box moving just before it hits the rear door? Vfinal = J J X J J msarrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





