
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
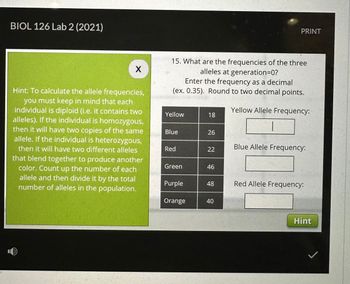
Transcribed Image Text:BIOL 126 Lab 2 (2021)
X
Hint: To calculate the allele frequencies,
you must keep in mind that each
individual is diploid (i.e. it contains two
alleles). If the individual is homozygous,
then it will have two copies of the same
allele. If the individual is heterozygous,
then it will have two different alleles
that blend together to produce another
color. Count up the number of each
allele and then divide it by the total
number of alleles in the population.
15. What are the frequencies of the three
alleles at generation=0?
Enter the frequency as a decimal
(ex. 0.35). Round to two decimal points.
Yellow Allele Frequency:
Yellow
Blue
Red
Green
Purple
Orange
18
26
22
46
48
PRINT
40
Blue Allele Frequency:
Red Allele Frequency:
Hint
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 2) Discuss the genetic variability introduced by crossing-over and independent assortment. How is this important in sexually reproducing populations? Would these be important in a single-celled organism that reproduces asexually by mitosis?arrow_forward19% dominant phenotype 0.19 = p2 + 2pq What is the dominant allele frequency?arrow_forward#9 helparrow_forward
- 23arrow_forward4arrow_forwardA1) The allele for widows peak (H) is dominant for the allele for no widows peak (h). At a different gene locus, the allele for hitchhikers thumb (D) is dominant to the allele for non-hitchhikers thumb (d). A man is heterozygoous for the traits and marries a woman who has no widows peak and is heterozygous for hitchhikers thumb. What fraction of this couples children should have a widow's peak and a hitchhiker's thumb? 3/8 1/4 1/2 3/4 0 A2)The allele for widows peak (H) is dominant for the allele for no widows peak (h). At a different gene locus, the allele for hitchhikers thumb (D) is dominant to the allele for non-hitchhikers thumb (d). A man is heterozygoous for the traits and marries a woman who has no widows peak and has no hitchhikers thumb. What fraction of this couple's children should have no widow's peak and a hitchhiker's thumb? 3/8 0 1/4 1/2 1/8arrow_forward
- ddTtBbqqAA X ddttBbQqaa Based on the cross provided what is the probability of producing an individual that is dominant for B & A and recessive for D, T and Q?arrow_forwardWhich of the Pedigree Diagrams below is most likely to show a family with Becker muscular dystrophy?arrow_forward11:34 Make the following Punnett square. RrYYTT x rrYytt 8*8 or 64 squares. Use a blank sheet as needed. What is the phenotypic ratio of the offspring? Your gametes: 1-3-5; 1-3-6; 1-4-5; 1-4-6; 2-3-5; 2-3-6; 2-4-5; 2-4-6;arrow_forward
- 1 1 11 Q4 - How many individuals had the genotype Nn ? How many were N_? Q5 Using the Punnett square below predict the probability of the grandparents having albino children.arrow_forwardR d 4. (3) D R and D are linked; the distance between R and D is 10 cM. G is unlinked. Now, you test cross this individual. a) (1) What % of the progeny of the test cross will be dominant for both R and D (ignore G)? b) Now, using all 3 genes, figure out the % of each gamete and they should all add up to 100%. I did one for you (see below). Make sure you know how to do a problem like this. These gametes are: RDG Rdg rDG RdG 22.5% rDg RDg rdGarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education