
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
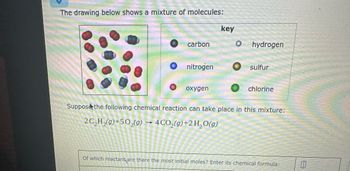
Transcribed Image Text:The drawing below shows a mixture of molecules:
carbon
nitrogen
oxygen
key
O hydrogen
sulfur
chlorine
Suppose the following chemical reaction can take place in this mixture:
2C₂H₂(g) +50₂(g) → 4CO₂(g) + 2 H₂O(g)
Of which reactant are there the most initial moles? Enter its chemical formula:

Transcribed Image Text:oxygen
1
chlorine
Suppose the following chemical reaction can take place in this mixture:
2 C₂H₂(g) +50₂(g) 4 CO₂(g) +2H₂O(g)
Of which reactant are there the most initial moles? Enter its chemical formula:
Of which reactant are there the least initial molès? Enter its chemical formula:
Which reactant is the limiting reactant? Enter its chemical formula:
00
X
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- QUESTION 10 Which of the following statements about the limiting reactant is true? O After the reaction is complete, there will be some amount of the fimiting reactant in your container along with the products. O The amount of the limiting reactant determines the amount of all the products you obtain in a chemical reaction. O The limiting reactant is found on the right-hand side of a chemical equation. O The amount of the limiting reactant increases during a chemical reaction until it is equal with the amount of the excess reactant.arrow_forwardmatch the following terms with a definition or explanation (there is 6 on the right side the sixth and 5th are pushed together at the bottom)arrow_forwardFor the following reaction, 4.20 grams of chlorine gas are mixed with excess carbon disulfide. The reaction yields 1.98 grams of carbon tetrachloride. carbon disulfide (s) + chlorine (g) →carbon tetrachloride (1) + sulfur dichloride (s) What is the theoretical yield of carbon tetrachloride ? What is the percent yield of carbon tetrachloride ? grams %arrow_forward
- Pure magnesium metal is often found as ribbons and can easily burn in the presence of oxygen. When 4.78 g of magnesium ribbon burns with 7.61 g of oxygen, a bright, white light and a white, powdery product are formed. Enter the balanced chemical equation for this reaction. Be sure to include all physical states. equation: What is the limiting reactant? охудen O magnesium The reaction goes to completion, but in the process of recovering the product, some of it was lost. The the percent yield for the reaction is 82.8%. How many grams of product are recovered? mass of product recovered: How many grams of the excess reactant remain? Assume the reaction goes to completion. mass of excess reactant:arrow_forwardbalance the following unbalanced chemical equation showing the combustion of methane. use 1 for a coefficient of one even though typically no number is written. ______CH4 + ______ O2 --> ______ CO2 + ______ H2Oarrow_forwardFor the following reaction, 25.3 grams of sulfur dioxide are allowed to react with 5.89 grams of water. sulfur dioxide (g) + water (1) → sulfurous acid (H₂SO3) (g) What is the maximum amount of sulfurous acid (H₂SO3) that can be formed? grams What is the FORMULA for the limiting reagent? What amount of the excess reagent remains after the reaction is complete? gramsarrow_forward
- Suppose the following chemical reaction can take place in this mixturearrow_forward3. Dry ice is the name for solid carbon dioxide. Instead of melting, solid carbon dioxide sublimes according to the equation: When dry ice is added to warm water, heat from the water causes the dry ice to sublime more quickly. The evaporating carbon dioxide produces a dense fog often used to create special effects. In simple dry ice fog machines, dry ice is added to warm water in a Styrofoam cooler. The dry ice produces fog until it evaporates away, or until the water gets too cold to sublime the dry ice quickly enough. A small Styrofoam cooler holds 15.0 Lof water heated to 85 °C. Use standard enthalpies of formation to calculate the mass of dry ice that should be added to the water so that the dry ice completely sublimes away when the water reaches 25 °C. Assume no heat loss to the surroundings. (The AH°; for CO219) is -427.4 kl/mol.)arrow_forward• Write out the chemical equation for the synthesis of aspirin using ONLY the NAMES of REACTANTS and PRODUCTS!!! (use "+" to separate compounds and "-->" to indicate reactant and product sides of the chemical equation) • Write out the balanced equation for the synthesis of aspirin using chemical formulas: (again use "+" to separate compounds and "-->" to indicate reactant and product sides of the chemical equation, no need for phase labels) • What is the mole ratio of the first reactant and aspirin? What is the mole ratio of the second reactant and aspirin? • Besides aspirin, what its chemical name? The one mentioned in this experiment.arrow_forward
- Balance the chemical equation. CS₂ + NH3 H₂S + NH4SCN Assume the coefficient of NHSCN is 1. What is the balanced equation? CS₂ + NH3→H₂S+NHSCNarrow_forwardConsider the unbalanced equation for the combustion of hexane: αC6H14(g)+βO2(g)→γCO2(g)+δH2O(g) Determine how many moles of O2 are required to react completely with 7.4 mol of C6H14. Express your answer using two significant figures.arrow_forwardA grease fire started on the stove, it was then covered completely with a fire blanket so that the fire goes out. Identify the limiting reactant in this situationarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY