
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Transcribed Image Text:Chrome
← → с
UST MYUSI
Sydney ✓
My Home
Courses
File Edit View History Bookmarks Profiles Tab Window Help
Catalog and Study Tools
Rental Options
eagle sync
College Success Tips
MindTap - Cengage Learning X b Answered: poards Styles s For X +
ng.cengage.com/static/nb/ui/evo/index.html?elSBN=9781337111560&id=1703610906&snapshotId=3315430&
Career Success Tips
RECOMMENDED FOR YOU
Help
Study Tools
100
Study Tools for Principles of
Economics
11
Give Feedback
«
daldassa
O
My Print Center
CENGAGE MINDTAP
22
Back to Assignment
Study Questions and Problems (Ch 07)
Attempts
EDUC 214 Sp2023
Output (Q)
1
2
3
5. Study Questions and Problems #5
4
26
5
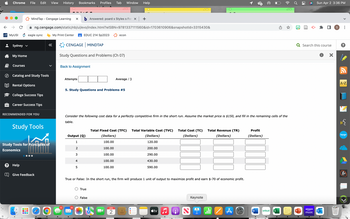
Consider the following cost data for a perfectly competitive firm in the short run. Assume the market price is $150, and fill in the remaining cells of the
table.
True
False
18
100.00
100.00
econ
Total Fixed Cost (TFC) Total Variable Cost (TVC)
(Dollars)
(Dollars)
100.00
120.00
100.00
100.00
Average / 3
APR
2
200.00
290.00
430.00
True or False: In the short run, the firm will produce 1 unit of output to maximize profit and earn $-70 of economic profit.
590.00
48
tv
Total Cost (TC) Total Revenue (TR)
(Dollars)
(Dollars)
Keynote
Ni
اله
A
Profit
(Dollars)
W
cricut
48
X
Ơ
Q Search this course
P
Sun Apr 2 3:36 PM
amazon
music
S :
A-Z
bongo
A+
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A competitive firm faces the following market price: P=200. Variable costs are C(Q)=Q^2. The firm also pays $17000 in costs that do not depend on production (even if q=0). Hint – marginal cost is MC(Q)=2*Q NOTE - KEEP YOUR CALCULATIONS. THIS INFORMATION WILL BE USED IN MULTIPLE QUESTIONS What is the profit of this firm (ACCOUNTING profit, counting sunk costs as well) Question 7 options: 5000 0 -7000 -17000arrow_forward20) - Google Chrome "mod/quiz/attempt.php?attempt%3=1579003&cmid%3812962&page%3D2 em (Academic 20- MC ATC AVC 16 4. 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 Quantity (units per day) The above figure shows the cost curves for a perfectly competitive firm. If all firms in the market have th same cost curves and the price equals $16 per unit Select one: O a. over time, the price will fall as new firms enter the market. O b. over time, firms will leave this market. O c. the market is in its long-run equilibrium. O d. the firm is making zero economic profit. o search hp Price and cost (dollars per unit)arrow_forwardTotal Revenue Total C ost Proit/Loss/ Price( P) Quantity (TR) (TC) Break Even $3 5. 2 9. 3 8. 4 11 5. 15 6. 21 30 8. 42 6. 60 10 85 Yummy Cupcakes is a purely competitive firm. The firm's costs are shown in the table above. The market price is $5 (USE THIS TO FILL IN THE PRICE COLUMN) When Yummy Cupcakes produces 1 cupcakel Q-1).the firm : O breaks even incurs a loss O earns profits will shutdownarrow_forward
- i)arrow_forwardRefer to the diagram to the right which shows the cost and demand curves for a profit-maximizing firm in a perfectly competitive market. What is the amount of its total fixed cost? OA. $1,000 B. $1,440 OC. $2,520 OD. It cannot be determined. Price and cost (5) 40.50 36.00 30.00 28.00 130 180 Quantity MC 240 ATC AVC MRarrow_forwardAnswer the question on the basis of the following demand and cost data for a specific firm. Demand Data Cost Data (1) Price (2) Price (3) Quantity Output Total Cost $ 10.50 $ 10.00 6 6 $ 61 10.00 8.85 7 7 62 9.50 8.00 8 8 64 9.00 7.00 9 9 67 8.50 6.10 10 10 72 8.00 5.00 11 11 79 7.50 4.15 12 12 86 Suppose that entry into the industry changes this firm's demand schedule from columns (1) and (3) to columns (2) and (3). Economic profit will Multiple Choice fall to $4. decline to zero. increase by $6. fall by $8.arrow_forward
- Suppose a competitive firm has the following cost: output(units): 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 Total cost: $50 $52 $56 $62 $70 $80 $92 $106 $122 $140 3. If the market price dropped to $8, how much should this profit maximizing firm produce?arrow_forwardA firm has fixed costs of $40 and variable costs as indicated in the table below. For each level of output (total product) calculate total cost, average fixed cost, average variable cost, average total cost and marginal cost. Write your response in the table provided. b) Discuss why a firm in perfect competition will not charge a price above or below the market price.arrow_forwardPlease help with the following questionarrow_forward
- Given the table below for a firm operating in a perfectly competitive market, what is the short run fixed cost? Output 0 1 2 3 $20 $10 $12 Total Cost $10 $20 $28 $34 Cannot be determinedarrow_forwardTable Cost.EX2.2: Data for a Competitive Firm Marginal Marginal Output Cost Revenue (Q) (MC) (MR) 10 $3.00 $4.00 11 $3.50 $4.00 12 $4.00 $4.00 13 $4.50 $4.00 14 $5.00 $4.00 15 $5.50 $4.00 16 $6.00 $4.00 Refer to Table Cost.EX2.2. If the firm wishes to maximize profit, it should produce units. O 10 O 12 O 11 6.arrow_forwardMarginal cost= 2x+3 Average variable cost= x+3 Variable cost=x^2 + 3x x is the daily output. Product's price is 13 dollars. Part a) Calculate the level of output that will be produced. Part b) Calculate the producer surplus of the firm. Part c) The fixed costs are 5 dollars. In the short run, is the firm making a 0 economic profit, a positive profit, or a negative profit? Explain why.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education