
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
1) In your own words, explain the Theory of this experiment.
2) In your own words, explain the Procedure of this experiment.
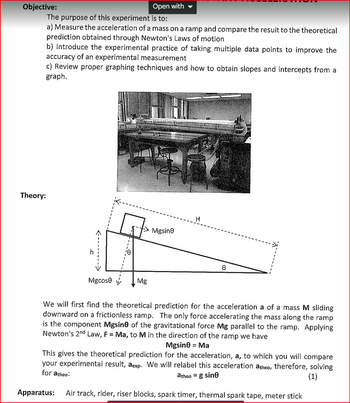
Transcribed Image Text:Objective:
Theory:
The purpose of this experiment is to:
a) Measure the acceleration of a mass on a ramp and compare the result to the theoretical
prediction obtained through Newton's Laws of motion
b) Introduce the experimental practice of taking multiple data points to improve the
accuracy of an experimental measurement
c) Review proper graphing techniques and how to obtain slopes and intercepts from a
graph.
<----
Mgcose
Open with
Mg
Mgsin
H
0
We will first find the theoretical prediction for the acceleration a of a mass M sliding
downward on a frictionless ramp. The only force accelerating the mass along the ramp
is the component Mgsine of the gravitational force Mg parallel to the ramp. Applying
Newton's 2nd Law, F = Ma, to M in the direction of the ramp we have
Mgsin0 = Ma
This gives the theoretical prediction for the acceleration, a, to which you will compare
your experimental result, aexp. We will relabel this acceleration atheo, therefore, solving
for atheo:
atheo = g sine
(1)
Apparatus: Air track, rider, riser blocks, spark timer, thermal spark tape, meter stick

Transcribed Image Text:Procedure:
Open with
0. NEVER MOVE THE RIDER ON THE
TRACK WITHOUT THE AIR SUPPLY
TO THE TRACK TURNED ON
(DOING
SO
WILL
CREATE
SCRATCHES AND FRICTION ON THE
TRACK)
1.
2.
3.
4.
6.
Make sure your air track is level. (How?
There is another way besides using a
level.)
7.
Raise the air track at the end with the single leg by placing two blocks under it; the
height of the blocks is h.
5. Repeat, with the rider moving up the ramp. Start with the rider at the top of the track
but start taking data after it bounces upward at the bottom.
EXPENSION
Determine sine of the ramp by measuring h and Note that sin = h/H.
Measure the acceleration of a rider of mass M≈ 400 grams moving down the ramp
(see Appendix I, below). Your Instructor will demonstrate a "run" on the air track.
Determine the acceleration for each run by graphing velocity vs. time.
The acceleration is equal to the slope of this graph (see Appendix II, below).
From these two graphs, take the average of the two slope values as your
experimentally measured acceleration aexp. (The average will tend to cancel certain
systematic errors in the measurement.)
8. Compare the average acceleration aexp with the theoretical acceleration atheo
obtained from Equation (1). For g, use the local acceleration of gravity: g = 979.9
cm/s².
"Comparing" your experimental results with theory means computing the percent
difference between the experimental value and the theoretical prediction. This is
given by:
%Difference
Experiment -Theory
Theory
-x100%
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Part 3 1. Each group will be given a different set of values for this part of the experiment. Ask your instructor for your group number. Highlight the my, m3, and 0₁ values for your group in the table shown below. Group #1 #2 #3 #4 #5 #6 #7 #8 #9 #10 mj 55g 60g 65g 70g 75g 80g 85g 90g 95g 100g m3 65g 70g 75g 80g 85g 90g 95g 100g 105g 110g 01 25° 30° 35° 40° 45° 50° 55° 60° 65° 70° 2. For the given my, m3, and 01, use static equilibrium conditions to predict the m2 and the 02 values required for the system to reach static equilibrium. Show your work! yd bei noiteups to anobiborandiliups sdt jadi woda of "gi alun ort U asulav lansmaq o m OSF of imag 0₁ 02 my ma Figure 2 I het aqui edi. muil animal od lite blunde I ha ni boa com bdT I bus did (gil ooe) 3021 of em bas smea srl gaiau 0 Tbas TT to bulingani wan edi staleples of noitaupo se Your predicted values: m2 = and 02= 3. Now hang m, and m3, Adjust m₂ until the above given 0₁ is obtained. Measure and record m2 and 0. Calculate the…arrow_forwardSOLVE EXACTLY AS THE PIC BELOW. JUST REPLACE THE 8800 with 7000 . ALSO REPLACE THE 2.127 x 10^25 with 2.19 x 10^25arrow_forward2. A student makes the following measurements in the lab: x 2.51 ± 0.01 cm y = 1.0592 ± 0.0005 cm z = 4.939 ± 0.002 cm (4 pts) The experiment requires that the student calculates the quantity q = xyz² + x1/2y2z3/2 Calculate the q and its uncertainty.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON