
Database System Concepts
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780078022159
Author: Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
For IP address: 175.30.101.205, use the provided version of the subnet mask to calculate the:
- slash notation
- binary subnet mask
- dotted decimal subnet mask
- Increment
- Network ID
- Broadcast ID
- Host Range
Complete the Increment by determining the value of the last network bit for the given subnet mask. It is easiest to observe in the binary representation.
Since network IDs will always be multiples of the increment (after the zero subnet) – in the octet that holds the last network bit, use the increment to determine the network ID, broadcast, and host range for the IP address displayed above
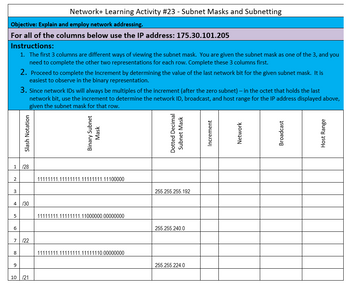
Transcribed Image Text:Objective: Explain and employ network addressing.
For all of the columns below use the IP address: 175.30.101.205
Instructions:
1. The first 3 columns are different ways of viewing the subnet mask. You are given the subnet mask as one of the 3, and you
need to complete the other two representations for each row. Complete these 3 columns first.
1
2
3
5
6
4 /30
8
co
2. Proceed to complete the Increment by determining the value of the last network bit for the given subnet mask. It is
easiest to observe in the binary representation.
9
3. Since network IDs will always be multiples of the increment (after the zero subnet) - in the octet that holds the last
network bit, use the increment to determine the network ID, broadcast,
given the subnet mask for that row.
and host range for the IP
address
displayed above,
Slash Notation
7 122
Network+ Learning Activity #23 - Subnet Masks and Subnetting
128
10 /21
Binary Subnet
Mask
11111111.11111111.11111111.11100000
11111111.11111111.11000000.00000000
11111111.11111111.11111110.00000000
Dotted Decimal
Subnet Mask
255.255.255.192
255.255.240.0
255.255.224.0
Increment
Network
Broadcast
Host Range
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, computer-science and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- CIS269 Packet Translation Lab Break down the following IP datagram into its individual fields, listing the value of each. Hint: It’s an IP datagram containing a TCP segment containing another protocol… 45 00 00 31 94 00 40 00 80 06 1B 9F 80 A3 C9 29 D8 45 29 15 04 09 00 15 00 00 C3 A1 DF 65 A8 45 50 18 20 AA 8E 8C 00 00 43 57 44 20 66 75 6E 0D 0Aarrow_forwardThe message to be sent from source to destination is 4000B. The link MTU's from source to destination are 1500, 1000, and 750. If we DO NOT use Path MTU, what are the respective fragment sizes to be reassembled? If we DO use Path MTU, what are the respective fragment sizes to be reassembled? Remember, assume that the L3 and L4 headers have length=0.arrow_forwardSMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) is the standard protocol for transferring mail between hosts. A TCP connection is set up between a user agent and a server program. The server listens on TCP port 25 for incoming connection requests. The user end of the connection is on a TCP port number above 1023. You have defined the packet filter rule set shown in the table below. These rules permit and/or deny inbound and outbound traffic between the user agent and the mail server. Describe the purpose of each packet filter rule in the table. Rule Direction Source Address Destination Address Protocol Destination Port Action A2 In External Internal TCP 25 Permit B2 Out Internal External TCP > 1023 Permit C2 Out Internal External TCP 25 Permit D2 In External Internal TCP > 1023 Permit E2 Either Any Any Any Any Denyarrow_forward
- Q1: The following is a dump of a UDP header in binary form 0100 0001 0010 0011 0100 0001 0010 0111 0000 0000 0010 1111 0100 0001 0011 1111 Find in decimal form the following: (a) Source port number (b) Destination port number (c) Total length of the UDP (d) Length of the data (e) Check sum. (5 Marks)arrow_forwardShow your work for the following conversion. a) Convert the following block of IP addresses into CIDRized addresses: 11000110 10110111 10100000 00000000 to 11000110 10110111 10111111 11111111arrow_forwardPlease solve it correctly. You receive a packet whose data length is 900 bytes, ID is 2398 and the MF flag is set to 0.You received the remaining 12 packets, each of whose total length is 1945 bytes, ID is 2398and the MF flag is set to 1. All of these packets’ header size is 25 bytes.I. Find the packet size of the original datagramII. Find the value of the offset field of the 2nd last packet [First data byte number starts at0]III. How would you identify the last packet in a group of fragmented packets?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Database System Concepts
Computer Science
ISBN:9780078022159
Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780134444321
Author:Tony Gaddis
Publisher:PEARSON

Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780132737968
Author:Thomas L. Floyd
Publisher:PEARSON

C How to Program (8th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780133976892
Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey Deitel
Publisher:PEARSON

Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...
Computer Science
ISBN:9781337627900
Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven Morris
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Computer Science
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education