
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
Can I please get help on question #2 and the 7th through tenth bullet points starting with "State whether the results..." and ending with "Find a way to change..."
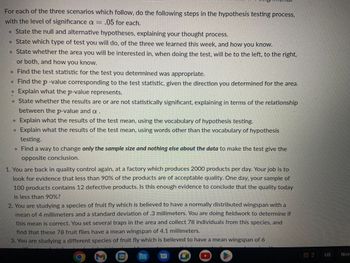
Transcribed Image Text:**Hypothesis Testing Steps for Three Scenarios**
For each of the three scenarios below, follow the steps in the hypothesis testing process with a significance level of \( \alpha = 0.05 \).
1. **State the null and alternative hypotheses, explaining your thought process.**
2. **Determine the type of test to use**, from the three learned this week, and explain your choice.
3. **Identify the area of interest for the test**, specifying whether it will be to the left, right, or two-tailed, and how you know.
4. **Calculate the test statistic** appropriate for the test you've chosen.
5. **Find the p-value** corresponding to the test statistic, taking into consideration the direction determined for the area.
6. **Explain what the p-value represents.**
7. **Determine if the results are statistically significant**, based on the relationship between the p-value and \( \alpha \).
8. **Interpret the test results** using the vocabulary of hypothesis testing.
9. **Interpret the test results in simple terms**, without specialized vocabulary.
10. **Modify only the sample size** to produce the opposite conclusion, changing nothing else about the data.
**Scenarios:**
1. **Quality Control at a Factory:**
- The factory produces 2000 products daily. You're tasked with evaluating if less than 90% of products are of acceptable quality. A sample of 100 products reveals 12 defective items. Is this sample sufficient evidence to conclude that today's product quality is below 90%?
2. **Fruit Fly Species Study:**
- This species is supposed to have a normally distributed wingspan with a mean of 4 millimeters and a standard deviation of 0.3 millimeters. You are collecting data to validate this mean. In a sample of 78 fruit flies, the mean wingspan is 4.1 millimeters.
3. **Different Fruit Fly Species Research:**
- This species is believed to have a mean wingspan of 6 millimeters. You're studying if there is evidence to suggest a deviation from this mean.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Ll.52.arrow_forwardThis question is not on any test. The table below shows the number of people for three different race groups who were shot by police that were either armed or unarmed. These values are very close to the exact numbers. They have been changed slightly for each student to get a unique problem. Race/Armed Suspect was Armed Suspect was unarmed Total Black 543 60 603 White 1176 67 1243 Hispanic 378 38 416 Total 2097 165 2262 Give your answer as a decimal to at least three decimal places. If you compare answers d, e and f it shows the highest percentage of unarmed people being shot is most likely white. Why is that? This is because there are more white people in the United States than any other race and therefore there are likely to be more white people in the table. Since there are more white people in the table, there most likely would be more white and unarmed people shot by police than any other race. This pulls the percentage of white and unarmed up. In addition, there…arrow_forwardHow do I determine each individual time on this box plot? i dont know how Im supposed to answer the questions following without knowing each individual time.arrow_forward
- Jermaine developed a new test to measure IQ. He claimed that using his test, someone with an IQ of 180 would be considered twice as intelligent as someone with an IQ of 90 and that someone with an IQ of 90 was three times as intelligent as someone with an IQ of 30. Jermaine's test treats IQ as Select one: a. a ratio variable b. an interval variable c. an ordinal variable d. a nominal variablearrow_forwardOne question with parts ...arrow_forwardbe quick pls needed urgently...arrow_forward
- Dr. A. Ventura is interested in determining what kinds and how many pets people own in Bakersfield. He stands outside Petco and asks people what kind of pet they own. This is the result of his survey: dog=1; cat=2; bird=3; reptile=4; fish=5; other=6 1,1,2,2,2,1,1,3,2,3,1,1,1,2,2,4,4,2,2,1,1,1,5,4,3,4,1,1,1,2,2,6,1,1,2,2,1,2,1,2,6,3,4,5arrow_forward2) Sheila scored 75, 80, 100, 60, and 85 on her last five history tests. She has a final exam that will count as two exams. What score must Shiela obtain on this final exam in order to earn the grade of B? the grading scale for B is 80-89.arrow_forwardWhich of the following could be the number of players on each team?arrow_forward
- C. 0.4638. O d. 0.1587 O e. Cannot be determinedarrow_forwardRecently a community college offered a 2-credit course to help students with math anxiety. At the beginning of the course, each student took a 30-question survey (called MARS-S); the higher the score, the more anxiety experienced by the student. The nine students remaining in the class took the same survey at the end of the course. The before and after scores for each of the nine students who completed the course are shown below, student before after 1 72 69 66 52 3 83 71 97 85 95 61 78 45 95 56 8. 52 43 93 62 Compute the correlation between before and after scores for these students. (Assu conditions have been satisfied and round your answer to the nearest 0.001.) the correlation Question Help: D Video O Message instructor Submit Question 目 Cip Co %23 24 96 & 4. 5 7 8. 9.arrow_forwardWhat is the value of X to the nearest 10th?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman