
Microeconomics: Principles & Policy
14th Edition
ISBN: 9781337794992
Author: William J. Baumol, Alan S. Blinder, John L. Solow
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
None
Transcribed Image Text:O Macmillan Learning
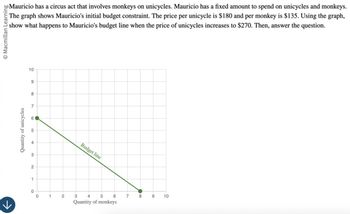
Mauricio has a circus act that involves monkeys on unicycles. Mauricio has a fixed amount to spend on unicycles and monkeys.
The graph shows Mauricio's initial budget constraint. The price per unicycle is $180 and per monkey is $135. Using the graph,
show what happens to Mauricio's budget line when the price of unicycles increases to $270. Then, answer the question.
Quantity of unicycles
10
10
88
9
7
6
5
3
2
1
0
0
1
2
3
✓
Budget line
4
5
6
7
8
Co
Quantity of monkeys
9
10
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Why does a change in income cause a parallel shift in the budget constraint?arrow_forwardIn an analysis of the market for paint, an economist discovers the facts listed below. State whether each of these changes will affect supply or demand, and in what direction. There have recently been some important cost-saving inventions in the technology for making paint. Paint is lasting longer so that property owners need not repaint as often. Because of severe hailstorms, many people need to repaint now. The hailstorms damaged several factories that make paint, forcing them to close down for several months.arrow_forward
Recommended textbooks for you
 Microeconomics: Principles & PolicyEconomicsISBN:9781337794992Author:William J. Baumol, Alan S. Blinder, John L. SolowPublisher:Cengage Learning
Microeconomics: Principles & PolicyEconomicsISBN:9781337794992Author:William J. Baumol, Alan S. Blinder, John L. SolowPublisher:Cengage Learning Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning

 Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781285165875Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781285165875Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning

Microeconomics: Principles & Policy
Economics
ISBN:9781337794992
Author:William J. Baumol, Alan S. Blinder, John L. Solow
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781337617383
Author:Roger A. Arnold
Publisher:Cengage Learning



Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou...
Economics
ISBN:9781285165875
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning