
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
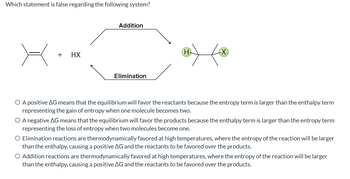
Transcribed Image Text:Which statement is false regarding the following system?
+ HX
Addition
Elimination
H
-X
O A positive AG means that the equilibrium will favor the reactants because the entropy term is larger than the enthalpy term
representing the gain of entropy when one molecule becomes two.
O A negative AG means that the equilibrium will favor the products because the enthalpy term is larger than the entropy term
representing the loss of entropy when two molecules become one.
Elimination reactions are thermodynamically favored at high temperatures, where the entropy of the reaction will be larger
than the enthalpy, causing a positive AG and the reactants to be favored over the products.
Addition reactions are thermodynamically favored at high temperatures, where the entropy of the reaction will be larger
than the enthalpy, causing a positive AG and the reactants to be favored over the products.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A reaction has AHTXN 533 kJ/mol and ASTxn = -57 J/K mol. What can be said about this %3D reaction? O The reaction is always spontaneous The reaction is never spontaneous O The reaction is spontaneous at low enough temperatures The reaction is spontaneous at high enough temperaturesarrow_forwardCalculate standard free energy (in kJ/mol) of the following reaction knowing the standard free energy of formation of A: -88.262 kJ/mol; B: 0 kJ/mol; C: -52.594 kJ/mol. (Give your answer as a pure number in 3 significant figures without the unit) 2A(g) + B (g) --> 2C (g)arrow_forwardConsider the reaction2N2(g) + O2(g)2N2O(g)Using the standard thermodynamic data in the tables linked above, calculate Grxn for this reaction at 298.15K if the pressure of each gas is 42.24 mm Hg. kJ/molarrow_forward
- What is the change in the energy of surroundings when the system absorbs 17.5 kJ of energy and performs 5.00 x 10^3 J of work on the surroundings? a. +22.5kJ b. +17.5 kJ c. –22.5 kJ d. +12.5kJ e. –12.5 kJarrow_forwardConsider the reaction CO(g) + 3H2(g)CH4(g) + H20(g) Using the standard thermodynamic data in the tables linked above, calculate G for this reaction at 298.15K if the pressure of each gas is 22.02 mm Hg. Thermodynamic Data: CO: -137.2, H2: 0, CH4: -50.7, H2O: -228.6 Consider the reaction CO(g) + 3H2(g) CH4(g) + H20(g) Using the standard thermodynamic data in the tables linked above, calculate AG for this reaction at 298.15K if the pressure of each gas is 22.02 mm Hg. ANSWER: kJ/mol Submit Answer Retry Entire Group No more group attempts remainarrow_forward2req Consider the reaction 2CO₂(g) + 5H₂(g) C₂H₂(g) + 4H₂O(g) Using the standard thermodynamic data in the tables linked above, calculate AG for this reaction at 298.15K if the pressure of each gas is 20.84 mm Hg. ANSWER: Submit Answer Important values if needed for this question. kJ/mol Retry Entire Group 9 more group attempts remainingarrow_forward
- Consider the reactionCO(g) + Cl2(g)COCl2(g)Using the standard thermodynamic data in the tables linked above, calculate Grxn for this reaction at 298.15K if the pressure of each gas is 37.65 mm Hg.arrow_forwardQ: Pure ZnO is reduced by the stoichiometric amount of carbon as in the following Reaction: ZnO (s) + C (graphite) Zn (s) + CO (g) = Heat of fusion of zinc at melting point (420°C) = 1.74 kcal/mole and heat of evaporation of zinc at boiling point (907°C) = 27.3 kcal/mole. Calculate the change in free energy for the reaction at 907 °C. Given that: Material AH°298 (kcal/mole) S° 298 C, (cal/deg/mole) (cal/deg/mole) 51+5.2x10 T- 5.7x10 T 6.8+1×10 T- 0.11×10° T ZnO(s) CO (g) C (s) Zn (s) Zn (1) & Zn (g) -83.2 10.24 - 26.42 47.14 1.48 0.71 10 5.35 + 2.4×10T 7.75arrow_forward(please type answer not write by hend)arrow_forward
- How to determine the overall ΔHo for a reaction ?arrow_forwardSolve 5. Investigate and analyse energy changes and rates of reactionin physical and chemical processes, and solve related problemsarrow_forwardch.6.8. the specific heat capacity of silver is 0.24 j/oC g a. calculate the energy required to raise the temperture of 158.0 g Ag from 271 K to 297 K b. calculate the energy required to raise the tempertyre of 1.0 mole of Ag by 1.0oC (called the molar hat capacity of silver). c. it takes 1.07kJ of energy to heat a sample of pure silver from 11.5oC to 14.8oC. calculate the mass of the sample of silver .arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY