
Essentials Of Investments
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781260013924
Author: Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.
Publisher: Mcgraw-hill Education,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
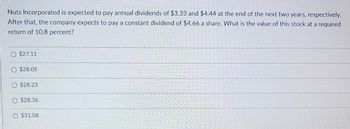
Transcribed Image Text:**Stock Valuation Problem**
Nuts Incorporated is projected to distribute annual dividends of $3.33 and $4.44 at the end of the next two years, respectively. Following these two years, the company anticipates paying a constant dividend of $4.66 per share. The question is: What is the value of this stock if the required return is 10.8 percent?
**Options:**
- $27.11
- $28.05
- $28.23
- $28.36
- $31.08
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1: Introduction:
The constant growth model is a stock valuation method used in finance to determine a stock's intrinsic value based on dividends. The model assumes that dividend growth will continue at a steady rate. It might not be appropriate for businesses with unpredictable dividend payout schedules, and the correctness of the model depends on the consistency of the growth rate assumption. This concept only applies to dividends with a constant growth rate. Or, more precisely, it is only relevant for stocks of companies with stable growth rates in dividends per share.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, finance and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Crane Corp. will pay dividends of $5.00, $6.25, $4.75, and $3.00 in the next four years. Thereafter, management expects the dividend growth rate to be constant at 6 percent. If the required rate of return is 15.50 percent, what is the current value of the stock?arrow_forwardSouth Side Corporation is expected to pay the following dividends over the next four years: $ 0.74 , $ 1.79 , $ 3.69 , $ 5.95 . Afterwards, the company pledges to maintain a constant 3.8 percent growth rate in dividends, forever. If the required rate of return on the stock is 10.2 percent, what is the current share price?arrow_forwardABD Ltd expects dividends per share on its ordinary shares for the next two years to be $2.3 and $3, respectively. Then the dividend will grow by 12% per annum till infinity. If investors require a rate of return of 21% p.a., what is the fair value of an ABD ordinary share today?arrow_forward
- Apocalyptica Corpoioration is expected to pay the following dividends over the next four years: $5.00, $16.00, $21.00 and $2.80. Afterwards, the company pledges to maintain a constant 5.00 percent growth rate in divdends, forever. If the required dreturn on the stock is 11.00 percent, what is the current share price?arrow_forwardSimco is planning to pay dividends on its common stock in the next four years as follows; $3.00 next year, $3.50 the following year, $0 in year 3, and $4.50 in year 4. After that, Simco has an expectation that their dividends will grow at 6.5% indefinitely. What should be the price of the stock today at a 10% discount rate?arrow_forwardCEPS Group announced today that it will begin paying annual dividends next year. The first dividend will be OMR 0.52 a share. The following dividends will be OMR 0.67, OMR 0.72, OMR 0.81, and OMR 0.90 a share annually for the following 4 years, respectively. After that, dividends are projected to increase by 5 percent per year. How much are you willing to pay to buy one share of this stock today if your desired rate of return is 9.5 percent?arrow_forward
- Stag Corp. will pay dividends of $ 4.75, $5.25, $5.75, and $7 for the next four years. Thereafter, the company expects 7 percent growth - | n dividends. If the required rate of returnis 15 percent, what is the current market price of the stock?arrow_forwardCEPS Group announced today that it will begin paying annual dividends next year. The first dividend will be OMR 0.65 a share. The following dividends will be OMR 0.72, OMR 0.85, OMR 0.89, and OMR 0.95 a share annually for the following 4 years, respectively. After that, dividends are projected to increase by 4 percent per year. How much are you willing to pay to buy one share of this stock today if your desired rate of return is 11.5 percent?arrow_forwardA firm recently paid a $0.70 annual dividend. The dividend is expected to increase by 14 percent in each of the next four years. In the fourth year, the stock price is expected to be $54. If the required return for this stock is 16.50 percent, what is its current value? (Do not round intermediate calculations and round your final answer to 2 decimal places.)arrow_forward
- NU inc. is going to pay dividends of $2/share, $3/share, and $4.1/share in the next three years, respectively. Starting in the fourth year, dividends will grow at a rate of 6.8%. If the required return is 10%, what is the current stock price? (Keep two decimal places)arrow_forwardKeidis Industries will pay a dividend of $4.15, $5.25, and $6.45 per share for each of the next three years, respectively. In four years, you believe that the company will be acquired for $59.00 per share. The return on similar stocks is 11.7 percent. What is the current stock price?arrow_forwardCoolibah Holdings is expected to pay dividends of $1.50 every six months for the next three years. If the current price of Coolibah stock is $22.20, andCoolibah's equity cost of capital is 14%, what price would you expect Coolibah's stock to sell for at the end of three years?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

 Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson,
Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson, Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Essentials Of Investments
Finance
ISBN:9781260013924
Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,



Foundations Of Finance
Finance
ISBN:9780134897264
Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. William
Publisher:Pearson,

Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...
Finance
ISBN:9781337395250
Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. Houston
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...
Finance
ISBN:9780077861759
Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education