
Stock Return Performance Analysis:
An investment firm monitors the daily returns of a particular stock in the S&P 500. The daily return is defined as the percentage change in the stock's price from the previous day. The firm recorded the stock's daily returns at random times during the last quarter of the year. Assume that the standard deviation of the population of daily returns is known to be σ = 2.8%.
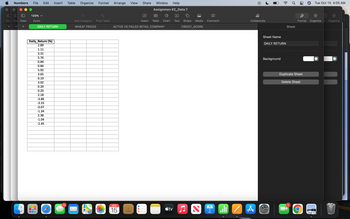
The data for daily return for the particular stock in the S&P 500 is given in Excel under “DAILY RETURN” sheet.
a) Based on a 95% confidence level, what is the margin of error for the mean estimate of the daily return?
b) Given the margin of error computed in part (b), provide a 95% confidence interval for μ, the mean daily return for this stock. The stock’s long-term average daily return is stated as 1.5%. Are the results of this analysis consistent with the stock’s long-term performance?
to generate a solution
a solution
- Suppose for a particular week, the forecasted sales were $4,000. The actual sales were $3,000. What is the value of the mean absolute percentage error?arrow_forwardAn instructor who taught two sections of engineering statistics last term, the first with 25 students and the second with 40, decided to assign a term project. After all projects had been turned in, the instructor randomly ordered them before grading. Consider the first 15 graded projects. (a) What is the probability that exactly 10 of these are from the second section? (Round your answer to four decimal places.) (b) What is the probability that at least 10 of these are from the second section? (Round your answer to four decimal places.) (c) What is the probability that at least 10 of these are from the same section? (Round your answer to four decimal places.) (d) What are the mean value and standard deviation of the number among these 15 that are from the second section? (Round your mean to the nearest whole number and your standard deviation to three decimal places.) mean projectsstandard deviation projects (e) What are the mean value and standard deviation of…arrow_forwardTo ensure that there is no mathematical error, the following condition needs to be fulfilled: Question Select one: A. Σ Back-Sights – Σ Foresights = Last Reduced Level – First Reduced Level B. Rises - Falls = Last Reduced Level – First Reduced Level C. Σ Intermediate-Sights – Σ Foresights = First Reduced Level – Last Reduced Level D. All of the abovearrow_forward
- A plan view sketch of a benchmark leveling run is shown below. Along each line representing a sight is the value of the rod reading for that sight. The numbering of TPs shows the direction of the level run. Place the data in the form of field notes. Assuming that the average length of each BS and FS is 125 ft, determine the order of leveling (accuracy) of the survey BM 14 48.292 7.485 不 10.260 T 2.641 1.485 TP 1 TP 3 3.982 π 2.247 8.643 不 TP 2 8.636 9.829 T 7.642 BMarrow_forwardAfter college, a group of students of a certain height planned to go to the movies. The cinema they go to is quite unique because the number of cinema rows is always 2 and the number of seats is as many as the number of students. Because this is a unique cinema, the way they sit is also unique. They will try to minimize their height difference with the one next to it so that the biggest height difference of each pair of students next to each other is as minimal as possible. Example: There are 6 students with height of 1, 6, 9, 7, 2, and 3. There are various sequences that can produce the biggest difference in height. Ordering 1:1 3 62 7 9Difference 1 and 3 is 2.Difference 3 and 6 is 3.Difference 2 and 7 is 5.Difference 7 and 9 is 2.So the biggest difference in height is 5. Ordering 2:1 3 26 7 9The biggest difference in height is 2.This difference is also an optimal answer. Format Input : There are T test cases. Each testcase contains integers N which indicates the number of students…arrow_forwardIn the US Higher Education sector, a degree is classified using a Grade Point Average (GPA). The grades ‘A’, ‘B’, ‘C’, ‘D’ or ‘F’ are called academic grades. Each ‘A’ is worth 4 points, each ‘B’ is worth 3 points, each ‘C’ is worth 2 points, each ‘D’ is worth 1 point and each ‘F’ is worth 0 points. The GPA is found by calculating the number of points and then dividing by the number of academic grades. A student may also have a non-academic grade of ‘W’ (for withdrew) which is not counted at all in the calculation. You can assume that the student will have at least one academic grade in their list of grades. There are many ways of calculating a GPA from a list of grades, but you must follow the algorithm given by this top-level decomposition: > Find GPA. >> Input a list of academic and non-academic grades. >> Create a new list that consists of the number of points for each academic grade in the input list. >> Add up the values in the new list and divide by the…arrow_forward
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





