
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
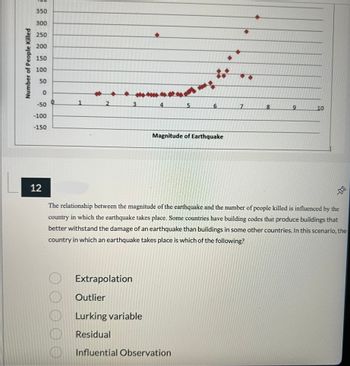
Transcribed Image Text:### Understanding Earthquake Impact on Human Casualties
#### Graph Analysis: Magnitude of Earthquake vs. Number of People Killed
The graph displayed illustrates the relationship between the magnitude of an earthquake (on the x-axis) and the number of people killed (on the y-axis). Key details observed in the graph include:
- **X-Axis (Magnitude of Earthquake):** Ranges from 0 to 10.
- **Y-Axis (Number of People Killed):** Ranges from -150 to 400.
- **Data Plot:** A series of red diamond-shaped data points representing the number of casualties at varying earthquake magnitudes.
From the visualization, it is apparent that as the magnitude of the earthquake increases beyond a certain point, the number of fatalities tends to rise significantly. However, there is considerable variability indicating that not all high-magnitude earthquakes result in high fatality numbers, suggesting the influence of other factors.
#### Question 12: Factor Analysis in Earthquake Impact
"The relationship between the magnitude of the earthquake and the number of people killed is influenced by the country in which the earthquake takes place. Some countries have building codes that produce buildings that better withstand the damage of an earthquake than buildings in some other countries. In this scenario, the country in which an earthquake takes place is which of the following?"
**Options:**
A. Extrapolation
B. Outlier
C. Lurking variable
D. Residual
E. Influential Observation
#### Explanation:
The country and its building codes play a critical role in the number of casualties. This suggests that while the earthquake magnitude is a primary factor, other elements, such as the country’s preparedness and infrastructure, also affect casualty numbers. The term that best fits this situation is "lurking variable," as it is a variable that was not included in the analysis but affects the results observed.
Therefore, the correct answer to Question 12 is:
- **C. Lurking variable**
This explanation considers that factors not directly studied (e.g., building codes, preparedness) are influencing the relationship being studied between earthquake magnitude and the number of fatalities.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Professor Fair believes that extra time does not improve grades on exams. He randomly divided a group of 300 students into two groups and gave them all the same test. One group had exactly 1 hour in which to finish the test, and the other group could stay as long as desired. The results are shown in the following table. Test at the 0.01 level of significance that time to complete a test and test results are independent. Time A B C F Row Total 1 h 20 43 58 11 132 Unlimited 19 48 84 17 168 Column Total 39 91 142 28 300 (i) Give the value of the level of significance.State the null and alternate hypotheses. H0: Time to take a test and test score are not independent.H1: Time to take a test and test score are independent. H0: The distributions for a timed test and an unlimited test are the same.H1: The distributions for a timed test and an unlimited test are different. H0: The distributions for a timed test and an unlimited test are different.H1: The distributions for a…arrow_forward10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 Wind speed (km/h The inter quartile range for the wind speeds isarrow_forwardCounty Hospitalizations Use variable Hospitalizations to perform the calculations. All results should be displayed in this column. Round your answer to zero decimal places. Dougherty 283 2.1 Compute 82nd percentile Cobb 431 2.2 Compute Q1 Hall 154 2.4 Compute 7th decile Clayton 113 2.5 Compute Software Coefficient of Skewness Unknown 115 Henry 54 Cherokee 71 Richmond 108 Sumter 87 Carroll 61 Lee 44 Mitchell 66 Bartow 116 Douglas 89 Muscogee 50 Forsyth 36 Bibb 64 Houston 73 Chatham 52 Upson 14 Early 9 Spalding 33 Coweta 32 Baldwin 39 Habersham 39 Colquitt 10 Fayette 28 Newton 30 Terrell 29 Rockdale 38 Paulding 48 Thomas 35 Randolph 21 Crisp 32 Columbia 23 Worth 28 Lowndes 25 Troup 39 Floyd 36 Clarke…arrow_forward
- Plz answer question 1arrow_forwardQuestion Help v A website reports that 70% of their users are from outside the United States and that 40% of their users log on to their website every day. Suppose that 20% of their users are United States users who log on every day. Complete parts a through e below. a) What percentage of the website's users are from the United States? The percentage of the website's users that are from the United States is %.arrow_forwardI Physics 105 - Onlir x b My Questions | ba x Y Brigham Young Un x 8 BYU Learning Suite x Y Quiz: Credit Quiz b My Questions | ba x G What percentage + A byu.instructure.com/courses/7512/quizzes/174153/take A person took a sample of 200 people to see the relationship between those who liked the movies "Titanic" and "Star Wars". Below is a table of the results: Like "Star Wars" Dislike "Star Wars" Total Like "Titanic" 60 40 100 Dislike "Titanic" 30 70 100 Total 90 110 200 What is the conditional distribution of opinion about "Star Wars" for those who like "Titanic"? 36%, 64% 33%, 67% O 30%, 70% O 60%, 40% 8:03 PM P Type here to search 68 11/17/2020arrow_forward
- Answer parts d and e pleasearrow_forwardProfessor Fair believes that extra time does not improve grades on exams. He randomly divided a group of 300 students into two groups and gave them all the same test. One group had exactly 1 hour in which to finish the test, and the other group could stay as long as desired. The results are shown in the following table. Test at the 0.01 level of significance that time to complete a test and test results are independent. Time 1h A 22 Unlimited 17 Column Total 39 B 43 49 92 C 64 84 148 F 12 9 21 Row Total 141 159 300 Classify the problem as one of the following: Chi-square test of independence or homogeneity, Chi-square goodness of fit, Chi-square for testing oor o Chi-square goodness of fit Chi-square test of independence Chi-square test of homogeneity Chi-square for testing oor o (i) Give the value of the level of significance. State the null and alternate hypotheses. Ho: The distributions for a timed test and an unlimited test are different. H₁: The distributions for a timed test and…arrow_forward1/26 Classwork @ D Present 2 Shan Slide Arrange Tools Add-ons Help Accessibility Last edit was 2 minutes ago Source San. - IUA 三三 E E 20 | 2 | 1 I 1 2 3 . 4 5 6 I.7 15.2 Audienc Size- The music concert was attended by 250 people.Attendance at literacy night was 44% of attendance at the concert, how many people attended literacy night? Number of Percentage people Use the table to show or explain below how you found your answer: 250 100 Click to add text! to add speaker notes 12:29 PM 1/26/2021 DELLarrow_forward
- Professor Fair believes that extra time does not improve grades on exams. He randomly divided a group of 300 students into two groups and gave them all the same test. One group had exactly 1 hour in which to finish the test, and the other group could stay as long as desired. The results are shown in the following table. Test at the 0.01 level of significance that time to complete a test and test results are independent. Time A B C F Row Total 1 h 22 41 65 12 140 Unlimited 17 49 86 8 160 Column Total 39 90 151 20 300 (ii) Find the sample test statistic. (Round your answer to two decimal places.)arrow_forwardI need help understanding how to solve the wrong parts.arrow_forwardI Format Arrange View 125% v Zoom Person A B C F D E A Covariance Calculation G View Share Window Add Page Person X 2 5 6 8 7 4 3 Correlation Calculation X 2 Help HW8 Covariance and Correlation Ca ¶ T E Insert Table Chart Text Shape Media Comme HW8: Covariance and Correlation Calculation Y 7 600 Use population equations for this (the one with N in the denominators, not N-1). Means: 5 for X, 10 for Y 13 12 1 의 11 10 7arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman