
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
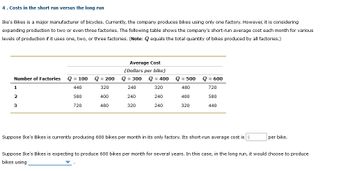
Transcribed Image Text:4. Costs in the short run versus the long run
Ike's Bikes is a major manufacturer of bicycles. Currently, the company produces bikes using only one factory. However, it is considering
expanding production to two or even three factories. The following table shows the company's short-run average cost each month for various
levels of production if it uses one, two, or three factories. (Note: Q equals the total quantity of bikes produced by all factories.)
Number of Factories
1
2
3
Q = 100
440
580
720
Q = 200
320
400
480
Average Cost
(Dollars per bike)
Q = 300
Q = 400
240
320
240
240
320
240
Q = 500
480
400
320
Q = 600
720
580
440
Suppose Ike's Bikes is currently producing 600 bikes per month in its only factory. Its short-run average cost is $
per bike.
Suppose Ike's Bikes is expecting to produce 600 bikes per month for several years. In this case, in the long run, it would choose to produce
bikes using
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Q) Economies of Scale What will happen to the cost of producing Teslas if the Shanghai gigafactory doesn’t achieve economies of scale?arrow_forwardCraigsburg enterprises has a fixed cost of 10,000. It’s variable costs are shown in the table below. These costs remain unchanged as market prices change over the next few years:arrow_forwardTC = 188 +38Q +4Q² What is the average fixed cost when 18 units are produced? Enter as a value. ROUND TO TWO DECIMAL PLACES.arrow_forward
- Graph the average total cost curve by first using the point tool to plot points for the average total cost for Q-1, Q-5, and Q-14 and then using the curved-line tool to connect them. You may assume that all total costs for these quantities are multiples of $25. Use the formula ATC=for your calculations. To refer to the graphing tutorial for this question type, please click here P arh NO m 956 *** PAY TH ww 178 9 Q ** See Hint wakaarrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardImagine a smartphone company has the following costs when they produce 200 phones: $50 in average fixed cost and $140 in average total cost. What would be the total variable cost for this company when they produce 200 phones? Type your numeric answer and submitarrow_forward
- shows the long-run average costs for Inmode, a manufacturer of Internet modems. Quantity per Day Average Cost ($) a) At what output is minimum efficient scale achieved? Output: b) with what output do diseconomies of scale begin? Output: 1 95 2 85 3 75 4 70 5 65 6 65 7 75 8 100arrow_forwardLabor (workers) Output(units) Total fixed cost, TFC (dollars) Total variable cost, TVC (dollars) Total cost, TC (dollars) 0 0 20 0 20 1 4 20 25 45 2 9 20 50 70 3 13 20 75 95 4 16 20 100 120 5 18 20 125 145 Using the data in the above table, the average fixed cost of producing 16 units is $1.25 a unit. $1.54 a unit. $2.22 a unit. $1.11 a unit.arrow_forwarda) Calculate the marginal product (MP1) for the mixers. Does the production function have increasing, decreasing, constant marginal product for the mixers? b) Suppose in the short run the amount of machines she has is fixed at 27. How many mixers should she use? How many baklavas will she produce? How much profit will she make? c)Usinag an isoprofit, as well as the production function, draw a diagram of your soltuion from part (b). carefully label all the slopes and intercepts. d) In the long run, how many mixers should she use? How many machines? How many baklavas will she make? e) Suppose that the government decides to provide a $1 subsidy per mixer. What is the profit-maximizing amount of input to use now?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education