
Now that you have developed an understanding of the policy tools that are available to address economic challenges, your task is to prepare material that will go towards a Policy Brief analysing Australia’s economic recovery from the COVID pandemic and building an equitable and resilient economy in the future.
Imagine you are now employed as a Graduate Economist working for the Australian Treasury. Your team is responsible for putting together a Policy Brief for the department that summarises some key aspects of the government’s policy responses to the COVID-19 recession and provides policy analysis to strengthen Australia’s economy in the future. You have a very important job!
Your task is to provide clear answers to the following queries that have been requested from your department manager, using the knowledge and skills that you have gained from your
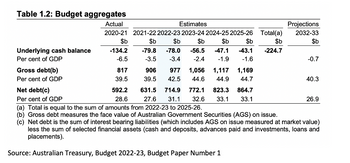
- The large increase in Government spending to support the economy during the pandemic contributed to a large budget deficit. Last year’s Budget reported that the Government ran a budget deficit of $134.2 billion in 2020-21 (as measured by the underlying cash balance) and was
forecast to accumulate a net debt of $864.7 billion (equivalent to 33.1% ofGDP ) by 2025-26. See the Budget Aggregates below.
Your team of economists is aware that there is concern among the general public and business community about running a large budget deficit and the increasing size of the government debt. This concern needs to be addressed in the Policy Brief.
Write a simple explanation of what is meant by a budget deficit. You should make reference to the formula for the government’s budget balance that we learnt in class. Explain in what circumstances would a government’s fiscal position be in deficit, and in what circumstances would it be running a budget surplus? Using your economic knowledge, give your expertise on whether Australians should be worried about running a large budget deficit and accumulating a large debt as a result of the government’s response to the pandemic? Provide reasons to support you answer why or why not. (4-5 sentences)
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

- Which of the following would a Laissez-Faire economist advocate in a time of economic recessionarrow_forwardNow that you have developed an understanding of the policy tools that are available to address economic challenges, your task is to prepare material that will go towards a Policy Brief analysing Australia’s economic recovery from the COVID pandemic and building an equitable and resilient economy in the future. Imagine you are now employed as a Graduate Economist working for the Australian Treasury. Your team is responsible for putting together a Policy Brief for the department that summarises some key aspects of the government’s policy responses to the COVID-19 recession and provides policy analysis to strengthen Australia’s economy in the future. You have a very important job! Your task is to provide clear answers to the following queries that have been requested from your department manager, using the knowledge and skills that you have gained from your macroeconomics course. c. In last year’s Budget (2022-23), the previous Australian Treasurer Josh Frydenberg announced that the…arrow_forwardAfter World War II, Germany was divided into two parts, the German Democratic Republic (informally known as East Germany) and the Federal Republic of Germany (West Germany). East Germany was controlled by the former Soviet Union, while West Germany was controlled by the other Allied governments: the United States, the United Kingdom, and France. The war had destroyed most of Germany’s economy. The Soviet Union as well as the Allied occupation forces sought to rebuild the economies of their respective parts. Before the fall of the Berlin Wall reunited East and West Germany in 1990, West Germany’s economy grew at an annual average growth rate of 4.4 percent, which was about 3 times higher than East Germany’s rate. Draw the parallel between the natural experiment discussed in the chapter and the case of East and West Germany. Based on the information given in the question and your own research, why do you think two otherwise similar areas had such divergent growth rates?arrow_forward
- Discuss the role of artificial intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), and Cloud Computing in driving the digital economy. Provide examples of how each of these technologies is used in the industry, and discuss their benefits and limitationsarrow_forwardEconomics In terms of Classical Economics and not Keynesian: World trade has boosted growth rates in many countries. In around 1980, mainland China opened its economy to trade and foreign investment. The Chinese also implemented many institutional reforms promoting capitalism. 1) Calculate Chinese pre-reform cumulative and annualized growth rates from 1950 to 1979. 2) Calculate Chinese post-reform cumulative and annualized growth rates from 1980 to 2019. 3) Please explain the differences in your calculated numbers using the changes the Chinese government implemented. Hint: Use Classical Economic fundamentals to determine the pre-reform cumulative and annualized growth rates for the above years and then explain them. The GDP and growth rates can be found online in many different places.arrow_forwardSometimes the exports of developing nations are concentrated in only one or a few primary products. For example, according to World Bank data, coffee constitutes almost 90% of Burundi’s total exports. Therefore, changes in demand or supply of coffee can have significant effects on the health of Burundi’s economy. The current world price of coffee is $5.00 per pound, but there is uncertainty about the shape of the demand and supply curves. The following graphs (scenario A and scenario B) show two possibilities for demand and supply in the market for coffee. Suppose that favorable growing conditions cause an increase in the global supply of coffee. On the following graph, shift the demand or supply curve of scenario A to show what happens in the market for coffee as a result of this event. Note: Select and drag one or both of the curves to the desired position. Curves will snap into position, so if you try to move a curve and it snaps back to its original position, just drag it…arrow_forward
- h Technical College X Bb CH7 PowerPoint Slides - EC X S https://savannahtech.blackl X Bb Take Test: Final Exam (ECON X Bb ECON 1101 Final Exam Stuc X Homeless Man Giving Rich X + savannahtech.blackboard.com/webapps/assessment/take/launch.jsp?course_assessment_id%3D_99611_1&course_id=_18157_1&content_id%3D_1769819_1&ste... Q Game Library | Origin 它 Tp YouTube google classroom Logout = GAfutures.org | Geo... N Netflix * Member Login - US... Google Docs Watch Dance Mom... its itslearning Remaining Time: 1 hour, 05 minutes, 17 seconds. A Question Completion Status: 70 100 12 |140| 150| | 16凸|| 170| | 18凸| | 190 | 20凸|| 210| 22 230240 | 25凸 13 The following payoff matrix shows the possible profits that each firm will earn under different pricing strategies. The firms can choose to have lower prices in order to lure away customers from the competitors or higher prices in order to increase their profits. The profits are measured in million dollars. In the game, Figure 9.5: Kellogg's Price…arrow_forwardEssay about Sustainability a Economist's Perspective by solowarrow_forwardState planners in country A met to decide what country should focus on producing.After much deliberation,they decided it would be the country's best interest to use their limited resources to produce automobiles instead of other consumer goods,such as electronics or textiles.The state planners passed their decision down to factories,and allocated to them raw materials,workers,and other resources needed to produce automobiles.Factories were then told how much they should produce with these resources and who the final products should be shipped to.What type of economic system is this? How would you know?arrow_forward
- Hello! Would you be able to professionally assess my answer for accuracy to the following question below? Thank you in advance! Question You won a ticket to a hockey playoff game by having your name drawn from a hat at a charity event. You were excited about going, but on the day of the game, a major snowstorm has hit and conditions are miserable. Would you be more likely to go if you had bought the ticket yourself instead of winning it? Relate your answer to opportunity costs and sunk costs. My Answer: If I bought the hocky playoff ticket myself and decided to stay home and not go to the game due to a major snowstorm and the resulting conditions, the opportunity cost would be watching the hockey playoff game in person. Because the ticket is already purchased, if I would be unable to resale the ticket (it may be quite difficult to resale from home the day of the game, particularly during a major storm), the price of the ticket would be a sunken cost, a past expenditure unable to be…arrow_forwardCountry A has a natural climate that is perfect for growing strawberries - long sunny seasons and plenty of rich, well drained soil. Country A also has a big labor force with agriculture knowledge and can produce 80,000 baskets of strawberries in one growing season. By contrast, Country B’s climate is less well-appointed for strawberries - a shorter summer season with large areas of red clay. They also have a smaller population trained in agriculture. Country B can only produce 30,0000 baskets of strawberries in one growing season. In this scenario and with this information, Country A has Group of answer choices Absolute advantage for producing strawberries Comparative advantage for producing strawberries The lowest synthetic advantage for producing strawberries Elastic advantage for producing strawberriesarrow_forwardThis is an intermediate macroeconomics subject question. Please explain clearly.arrow_forward

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





