
"Since you have asked a question with multiple sub-parts, we will solve first three sub-parts for you .. If you want other sub-parts to be solved, Please repost question by specifying the number of the sub-parts"
In an economy, required reserve ratio is the ratio of total reserves that banks are mandated to keep aside from their total reserves so that they can use it in case of emergency withdrawals. This ratio is set by the central bank of a nation.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Now, suppose that, rather than immediately lending out all
worth of U.S. government bonds in order to increase the money supply by $100.
Now, suppose that, rather than immediately lending out all
worth of U.S. government bonds in order to increase the money supply by $100.
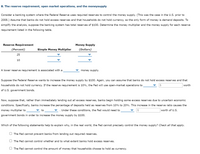
- I only need Help with part (B)arrow_forward8. Study Questions and Problems #8 Suppose the Federal Reserve's trading desk buys $500,000 in T-bills from a securities dealer, who then deposits the Fed's check in Best National Bank. Assuming that the required reserve ratio is 5%, complete the following table by showing changes in Best National Bank's balance sheet. Best National Bank Assets (Dollars) Reserves: Addendum: Changes in Reserves Actual reserves Required reserves Excess reserves Liabilities (Dollars) Checking deposits: Total liabilities Consider the money multiplier. The maximum increase in the money supply that can result from this open market transaction isarrow_forward8. The reserve requirement, open market operations, and the money supply Consider a system of banking in which the Federal Reserve uses required reserves to control the money supply (as was the case in the United States before 2008). Assume that banks do not hold excess reserves and that households do not hold currency, so the only money exists in the form of demand deposits. To further simplify, assume the banking system has total reserves of $400. Determine the money multiplier as well as the money supply for each reserve requirement listed in the following table. Reserve Requirement Simple Money Multiplier Money Supply (Percent) (Dollars) 20 10 A higher reserve requirement is associated with a money supply. Suppose the Federal Reserve wants to increase the money supply by $200. Maintain the assumption that banks do not hold excess reserves and that households do not hold currency. If the reserve requirement is 10%,…arrow_forward
- Suppose the reserve requirement is 8% and a new deposit of $900 billion is made into the banking system. Create T accounts to analyze the following questions. a) Initially, reserves would increase by? b) Required reserves would increase by? c) Excess reserves would increase by? d) The first round of loans would amount to? e) The second round of loans would amount to approximately? f) The third round of loans would amount to approximately? g) For the entire macroeconomy, after the infinite rounds of loans were taken into account, money supply would increase by? h) If the Federal Reserve bought bonds worth $600 billion, money supply would increase by? i) If the Federal Reserve sold bonds worth $600 billion, money supply would decrease by?arrow_forward5. If reserves are scarce, how would the federal funds rate change (increase or decrease) if the Fed: 1) sells mortgage-backed securities 2) decreases the (minimum) reserve requirements 3) conducts overnight repo operations 4) conducts overnight reverse repo operationsarrow_forward5. Consider the T-table of the Bank of Boston. Suppose the Federal Reserve Bank buys an additional $2 million in government bonds from the Bank of Boston. Assume (1) the required reserve ratio is 10 percent, and (2) the Bank of Boston issues all excess reserves in loans (I.e., there are no excess reserves). The new money supply equals $ million. Submit Balance sheet of the Bank of Boston Liabilities -55,000,000 Checkable deposits +$5,000,000 Assets Government bonds Currency (= bank reserves) +$5,000,000 Loans $0arrow_forward
- 4) Listen If the money multiplier decreased from 20 to 4, then the Fed increased the reserve ratio from 5 percent to 8 percent. the Fed increased the fed funds rate from 5 percent to 8 percent. the Fed increased the reserve ratio from 5 percent to 25 percent. the Fed decreased the fed funds rate from 8 percent to 5 percent. Question 30 (1 point) )Listen The FOMC is able to increase the money supply when it buys US government securities. The increase will be larger, the larger is the reserve ratio. buys US government securities. The increase will be larger, the smaller is the reserve ratio. sells US government securities. The increase will be larger, the smaller is the reserve ratio. sells US government securities. The increase will be larger, the larger is the reserve ratio.arrow_forwardAnswer question 1arrow_forward1. Suppose that a bank’s customer deposits $20,000 in her checking account. The required reserve ratio is 0.125. What are the required reserves on the new deposit? What is the largest loan that the bank can make on the basis of the new deposit? What is the maximum the banking system can increase demand deposits as a result of this deposit? -------------arrow_forward
- 9. How can banks create money? A) By lending required reserves B) By borrowing excess reserves C) By telling the Fed they need more money; and the Fed creates it D) By lending excess reserves 10. What is the formula for figuring the total possible change in the money supply from excess reserves? A) (1/Excess reserves) × / Total Reserves B) (R/1) × A Reserves C) / Excess Reserves / Total Reserves D) (1/R)x A Reservesarrow_forward4. The combined balance sheet of all the commercial banks in the economy is as follows (in billions of dollars): Assets Liabilities Reserves 25 Deposits 250 Government Securities 75 Loans 150 a) Assume this bank has no excess reserves, what is the reserve requirement? b) If the Fed purchases securities of $25 billion, how much in excess reserves do the banks have immediately after this transaction? c) By how much would the money supply increase if the banks fully utilized their lending capacity capacity and all money lent was redeposited into the banking system? hparrow_forward

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





