
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
I have tried this problem before but I got the second half wrong, How do I shift the graph correctly?
- Now, suppose that Mexico experiences a sudden bout of political turmoil, which causes world financial markets to become uneasy. Because people now view Mexico as unstable, they decide to pull some of their assets out of Mexico and put them into more stable economies. This unexpected shock to the
demand for assets in Mexico is known as capital flight.
- Shift the NCO curve to illustrate the effect of capital flight. Then, on the graph representing the market for loanable funds, shift the demand curve, the supply curve, or both to reflect the change caused by the shift in NCO.
-
Determine the equilibrium interest rate after capital flight occurs, and enter it into the second row of the table. Then determine the level of NCO that occurs along the new NCO curve at the new equilibrium interest rate.

Transcribed Image Text:The following graphs depict the market for loanable funds and the relationship between the real interest rate and the level of net capital outflow (NCO)
measured in terms of the Mexican currency, the peso.
The Market for Loanable Funds in Mexico
Mexican Net Capital Outflow
6.
Supply
3
3
1
NCO
Demand
-1
-2
-2
6 7
0 1 2 3 4 5
LOANABLE FUNDS (Billions of pesos)
1 2 3 4
NET CAPITAL OUTFLOW (Billions of pesos)
8.
-4
-3
-2
-1
6.
REAL INTEREST RATE (Percent)
REAL INTEREST RATE (Percent)
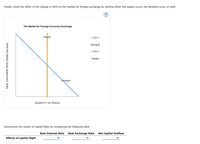
Transcribed Image Text:Finally, show the effect of the change in NCO on the market for foreign exchange by shifting either the supply curve, the demand curve, or both.
The Market for Foreign-Currency Exchange
Supply
Demand
Supply
Demand
QUANTITY OF PESOS
Summarize the results of capital flight by completing the following table.
Real Interest Rate
Real Exchange Rate
Net Capital Outflow
Effects of capital flight
REAL EXCHANGE RATE (Dollars per peso)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider the Inter-temporal Model with two time periods, t=0 and t=1. Home is a small open economy that can borrow and lend in the first period at the world real interest rate of 5%. In the first period, output is Yo = 100 and in the second period Y1 = 100. The country wants to smooth consumption as much as possible. The country ended period t=-1 with positive external wealth, W-1 = 50. What is the value of aggregate consumption in period 0 and 1?arrow_forwardThe following graph shows the market for loanable funds. For each of the glven scenarios, adjust the appropriate curve on the graph to help you complete the questions that follow. Treat each scenario separately by resetting the graph to its original state before examining the effect of each. individual scenarlo. (Note: You will not be graded on any changes you make to the graph.) Demand Supply Supply Demand LOANABLE FUNDS (Billions of dollars) INTEREST RATE (Percent)arrow_forwardQ1. The experience of Greece illustrates some of the challenges of the eurozone. As a resultof the global financial crisis that began in 2007–2008, the eurozone entered its first official recession.The severity of this downturn came close to breaking up the eurozone as financially weak memberssuch as Greece, Portugal, Cyprus, and Spain teetered on the verge of bankruptcy.In 2008, Greece was in deep recession, its economy was uncompetitive with northern eurozonemembers like Germany, and its debt was more than three times as large as previously estimated.With debt piling up, investors feared that Greece could not pay its international obligations. To shoreup Greece’s financial position, other eurozone countries, in conjunction with the InternationalMonetary Fund (IMF), agreed on a packagethat gave Greece 110 billion euros in loans. When this bailout was agreed to, it was feared thatGreece's exit from the eurozone would cause so much panic in the markets that other vulnerablecountries…arrow_forward
- The economy of a hypothetical country has been stable for two or three years with very low unemployment. Wages have been gradually increasing during this time. Now stock market prices begin significant increases, causing peoples’ investments, such as their retirement accounts and other investments, to increase in value. People feel very good about the future and use their new-found wealth to buy things that they had been hesitant to purchase in the past. Include detailed answers to the following questions: 1. What would be the likely impact on the government budget and national debt of the use of these fiscal policy tools (taxes, government expenditure, transfer payments, and interest rates)? 2. How would the use of these fiscal policy tools stabilize the economy?arrow_forwardQ1.The experience of Greece illustrates some of the challenges of the eurozone. As a resultof the global financial crisis that began in 2007–2008, the eurozone entered its first official recession.The severity of this downturn came close to breaking up the eurozone as financially weak memberssuch as Greece, Portugal, Cyprus, and Spain teetered on the verge of bankruptcy.In 2008, Greece was in deep recession, its economy was uncompetitive with northern eurozonemembers like Germany, and its debt was more than three times as large as previously estimated.With debt piling up, investors feared that Greece could not pay its international obligations. To shoreup Greece’s financial position, other eurozone countries, in conjunction with the InternationalMonetary Fund (IMF), agreed on a packagethat gave Greece 110 billion euros in loans. When this bailout was agreed to, it was feared thatGreece's exit from the eurozone would cause so much panic in the markets that other vulnerablecountries…arrow_forwardConsider the Economist article: "Wild Horses" April 20th 2011 (https://www.economist.com/the-americas/2011/04/20/wild-horses) and other sources to comprehensively answer the following question. a) How did the international Dilemma explain the Brazilian experience? b) What was the best option for the Brazilian Central Bank/government in that situation?arrow_forward
- Consider the Ramsey Model of the macroeconomy. Explain using a phase diagram how an economy starting from any point in phase space reaches the unique steady state solution. Now suppose once the steady state is reached that there is an unexpected permanent fall in government spending. Explain, using a phase diagram, how the c = 0 and k = 0 curves are affected and how the economy moves to a new steady state. How are interest rates affected during the transition to the new steady state? Explain your answer.arrow_forwardExercise 6 (Dark Matter Versus Return Differentials). Suppose net investment income is N II = 300, the net international investment position is N IIP = −2000, the international liability position is L = 5000, and the interest rate on international liabilities is 4 percent (r L = 0.04). Part 1: Economic consultant Jim Taylor, a strong advocate of the return differential hypothesis, maintains that the rate of return on the country’s international assets, denoted r A, is different from the return on its net international liabilities, r L. Find the value of r A consistent with Taylor’s view. Part 2: Economist Carol Powell does not support the idea of return differentials. Instead, she defends the dark matter hypothesis. Specifically, she believes that A is not accurately recorded and that the rate of return is 4 percent on both, A and L. Calculate the amount of dark matter and the ‘true’ international asset position, which we will denote T A, consistent with Powell’s view.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education