
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
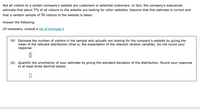
Transcribed Image Text:Not all visitors to a certain company's website are customers or potential customers. In fact, the company's executives
estimate that about 5% of all visitors to the website are looking for other websites. Assume that this estimate is correct and
that a random sample of 50 visitors to the website is taken.
Answer the following.
(If necessary, consult a list of formulas.)
(a) Estimate the number of visitors in the sample who actually are looking for the company's website by giving the
mean of the relevant distribution (that is, the expectation of the relevant random variable). Do not round your
response.
(b) Quantify the uncertainty of your estimate by giving the standard deviation of the distribution. Round your response
to at least three decimal places.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- The premiere of Game of Thrones' seventh season set a series record of 10.1 million viewers tuning in to the live broadcast, and the season finale got even more than that at 12.1 million. A researcher at HBO believes that the average number of viewers watching live is not equal to the average number of those streaming online. The data below demonstrate a sample the number of of people watching live for each episode and the number of people streaming for each of the same episode. Episode Live (millions) Streaming (millions) Season 1 Episode 1 2.9 0.7 Season 3 Episode 4 8.4 5.0 Season 5 Episode 1 8.7 6.3 Season 5 Episode 5 8.6 6.0 Season 6 Episode 3 9.3 8.4 Season 7 Episode 1 10.11 6.4 Season 7 Episode 5 10.72 6.7 Season 7 Episode 7 12.10 7.5 Based on the results of your t-test, can we conclude that the mean number of people viewing live is different from the mean number of people streaming online? Group of answer choices a) No, because the p value is greater…arrow_forwardAccording to a retail organization, holiday shoppers spent an average of $935.58 over the Thanksgiving weekend in 2016. The accompanying data show the amount spent by a random sample of holiday shoppers during the same weekend in 2017. $1,029 $875 $969 $838 $825 $813 $962 $1,032 $990 $996 $921 $664 $1,013 $1,030 $979 $878 Complete parts a through c. Test the hypothesis that shoppers spent less than an average of $935.58 over the Thanksgiving weekend in 2017 using α=0.05.arrow_forwardIn politics, marketing, etc. we often want to estimate a percentage or proportion p. One calculation in statistical polling is the margin of error - the largest (reasonble) error that the poll could have. For example, a poll result of 72% with a margin of error of 4% indicates that p is most likely to be between 68% and 76% (72% minus 4% to 72% plus 4%). In a (made-up) poll, the proportion of people who like dark chocolate more than milk chocolate was 37% with a margin of error of 2.5%. Describe the conclusion about p using an absolute value inequality. . That lets you type in a vertical bar | to represent absolute values. Also, when you type in < and then =, the symbolic entry option will automatically convert that to ≤ . In the same way, if you type in > and then =, the symbolic entry option will automatically convert that to ≥. Be sure to use decimal numbers in your answer (such as using 0.40 for 40%).arrow_forward
- Suppose an internet marketing company wants to determine the current percentage of customers who click on ads on their smartphones. How many customers should the company survey in order to be 90% confident that the estimated proportion is within five percentage points of the true population proportion of customers who click on ads on their smartphones?arrow_forwardFind the sample size required to estimate the percentage of statistics students who take their statistics course online. Assume that we want 95% confidence that proportion from the sample is within two percentage points of the true population percentage.arrow_forwardThe average total dollar purchase at a convenience store is less than that at a supermarket. Despite smaller-ticket purchases, convenience stores can still be profitable because of the size of operation, volume of business, and the markup. A researcher is interested in estimating the average purchase amount for convenience stores in suburban Long Island. To do so, she randomly sampled 24 purchases from several convenience stores in suburban Long Island and tabulated the amounts to the nearest dollar (shown below). $9 $7 $1 $2 $14 $11 $7 $8 $6 $7 $3 $3 $2 $5 $4 $4 $1 $2 $3 $10 $8 $8 $6 $4 Assume that the population standard deviation is 3.23 and the population is normally distributed. Using the above data, a 90% confidence interval for the population average amount of purchases is 4.54 to 6.71 4.495 to 6.76 4.44 to 6.81 4.49 to 6.76 4.26 to 6.99arrow_forward
- A survey conducted by a song rating service finds that the percentages of listeners familiar with "Poker Face" by Lady Gaga who would give the song ratings of 5, 4, 3, 2, and 1 are, respectively, 43 percent, 21 percent, 22 percent, 7 percent, and 7 percent. Assign the numerical values 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 to the (qualitative) ratings 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 and find an estimate of the probability distribution of x = this song’s rating by a randomly selected listener who is familiar with the song. Find the expected value of the estimated probability distribution. (Round your answer to 2 decimal places.)arrow_forwardIn politics, marketing, etc. we often want to estimate a percentage or proportion p. One calculation in statistical polling is the margin of error - the largest (reasonble) error that the poll could have. For example, a poll result of 72% with a margin of error of 4% indicates that p is most likely to be between 68% and 76% (72% minus 4% to 72% plus 4%). In a (made-up) poll, the proportion of people who like dark chocolate more than milk chocolate was 44% with a margin of error of 2.2%. Describe the conclusion about p using an absolute value inequality. The answer field below uses the symbolic entry option in Mobius. That lets you type in a vertical bar | to represent absolute values. Also, when you type in and then =, the symbolic entry option will automatically convert that to >.arrow_forwardFind the sample size required to estimate the percentage of statistics students who take their statistics course online. Assume that we want 95% confidence that proportion from the sample is within two percentage points of the true population percentage. Answer: Sample size n =arrow_forward
- The council leaders of a small town would like to determine the average number of people living in each household. To accomplish this, they send a questionnaire to each residence listed in the town address records, asking the head of the household to record the number of people living in the dwelling. They follow this up with visits to those households that have not responded to the questionnaire until the data collection process is complete. Which of the following is the best description of the method for data collection used by the council leaders? (A) A convenience sample (B) A simple random sample (C) A stratified random sample (D) A cluster random sample (E) A censusarrow_forwardThe Student Union President conducted a survey to estimate the proportion of first year students who participated in the social activities organized by the Student Union. Which of the following surveying options does NOT affect the presidents ability to generalize the survey to all first year students. The president put the survey on the Student Union webpage a Monday and collected the responses at the end of the week. All of the other options present a problem for generalizing the results. The president polled all students coming out of the Student Union on a given Monday. The freshmen class consists of 3000 students. A random sample of only 300 were sent a survey. Only 150 responded. The survey was sent only to first year students enrolled in statistics courses because all students need to satisfy a statistics general education requirement.arrow_forwardIn a typical set of numerical data, what fraction of the data values lie above Q3?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman