
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
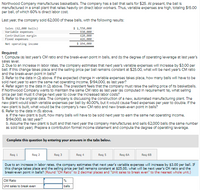
Transcribed Image Text:Northwood Company manufactures basketballs. The company has a ball that sells for $25. At present, the ball is
manufactured in a small plant that relies heavily on direct labor workers. Thus, varlable expenses are high, totaling $15.00
per ball, of which 60% Is direct labor cost.
Last year, the company sold 62.000 of these balls, with the following results:
Sales (62,809 balls)
Variable expenses
Contribution margin
Fixed expenses
$ 1,558, e08
930,e00
620, e00
426,e00
$ 194, e00
Net operating income
Required:
1. Compute (a) last year's CM ratio and the break-even polnt in balls, and (b) the degree of operating leverage at last year's
sales level.
2 Due to an increase in labor rates, the company estimates that next year's varlable expenses will increase by $3.00 per
ball. If this change takes place and the selling price per ball remalns constant at $25.00, what wll be next year's CM ratio
and the break-even polnt In balls?
3. Refer to the data in (2) above. If the expected change In varlable expenses takes place, how many balls will have to be
sold next year to eam the same net operating Income, $194,000, as last year?
4. Refer agaln to the data In (2) above. The president feels that the company must ralse the selling price of Its basketballs.
If Northwood Company wants to malntaln the same CM ratio as last year (as computed In requirement 1a), what selling
price per ball must It charge next year to cover the Increased labor costs?
5. Refer to the orlginal data. The company is discussing the construction of a new, automated manufacturing plant. The
new plant would slash varlable expenses per ball by 40.00%, but It would cause fixed expenses per year to double. If the
new plant is bult, what would be the company's new CM ratio and new break-even polnt in balls?
6. Refer to the data In (5) above.
a. If the new plant is bult, how many balls will have to be sold next year to earn the same net operating income.
$194.000, as last year?
b. Assume the new plant is bullt and that next year the company manufactures and sells 62,000 balls (the same number
as sold last year). Prepare a contribution format Income statement and compute the degree of operating leverage.
Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs belovw.
Req 1
Reg 2
Req 3
Req 4
Req 5
Req 6A
Req 68
Due to an increase in labor rates, the company estimates that next year's variable expenses will increase by $3.00 per ball. If
this change takes place and the selling price per ball remains constant at $25.00, what will be next year's CM ratio and the
break-even point in balls? (Round "CM Ratio" to 2 decimal places and "Unit sales to break even" to the nearest whole unit.)
CM Ratio
%
Unit sales to break even
balls
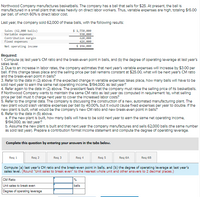
Transcribed Image Text:Northwood Company manufactures basketballs. The company has a ball that sells for $25. At present, the ball is
manufactured in a small plant that relies heavily on direct labor workers. Thus, varlable expenses are high, totaling $15.00
per ball, of which 60% Is direct labor cost
Last year, the company sold 62.000 of these balls, with the following results:
Sales (62,809 balls)
Variable expenses
Contribution margin
Fixed expenses
$ 1,558, 000
930,e00
620, e00
426, e00
Net operating income
$ 194,e00
Required:
1. Compute (a) last year's CM ratio and the break-even polnt In balls, and (b) the degree of operating leverage at last year's
sales level.
2 Due to an Increase In labor rates, the company estimates that next year's varlable expenses will Increase by $3.00 per
ball. If this change takes place and the selling price per ball remalns constant at $25.00, what will be next year's CM ratio
and the break-even polnt in balls?
3. Refer to the data in (2) above. If the expected change In varlable expenses takes place, how many balls will have to be
sold next year to eam the same net operating Income, $194,000, as last year?
4. Refer agaln to the data In (2) above. The president feels that the company must ralse the selling price of Its basketballs.
If Northwood Company wants to malntaln the same CM ratio as last year (as computed In requirement la), what selling
price per ball must it charge next year to cover the Increased labor costs?
5. Refer to the orlglinal data. The company is discussing the construction of a new, automated manufacturing plant. The
new plant would slash varlable expenses per ball by 40.00%, but It would cause fixed expenses per year to double. If the
new plant Is bult, what would be the company's new CM ratlo and new break-even polnt in balls?
6. Refer to the data in (5) above.
a. If the new plant Is bult, how many balls will have to be sold next year to earn the same net operating Income.
$194,000, as last year?
b. Assume the new plant is bult and that next year the company manufactures and sells 62,000 balls (the same number
as sold last year). Prepare a contributlon format Income statement and compute the degree of operating leverage.
Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs belovw.
Req 1
Req 2
Req 3
Req 4
Req 5
Req 6A
Req 68
Compute (a) last year's CM ratio and the break-even point in balls, and (b) the degree of operating leverage at last year's
sales level. (Round "Unit sales to break even" to the nearest whole unit and other answers to 2 decimal places.)
CM Ratio
Unit sales to break even
balls
Degree of operating leverage
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Markham Farms reports the following contribution margin income statement for the month of August. The company has the opportunity to purchase new machinery that will reduce its variable cost per unit by $2 but will increase fixed costs by 10%. MARKHAM FARMS Contribution Margin Income Statement Sales (1,500 Units @ $70 per unit) $105,000 Variable Costs (1,500 Units @ $15 per Unit) 22,500 Contribution Margin $82,500 Fixed Cost 40,000 Net Income (Loss) $42,500 Prepare a projected contribution margin income statement for Markham Farm assuming it purchases the new equipment. Assume sales level remains unchanged. blankMARKHAM FARMSContribution Margin Income Statement $Sales Variable Costs $Contribution Margin Fixed Cost $Net Income (Loss)arrow_forwardCandyland Inc. produces a particularly rich praline fudge. Each 10-ounce box sells for $5.60.Variable unit costs are as follows:Pecans $0.70Sugar 0.35Butter 1.85Other ingredients 0.34Box, packing material 0.76Selling commission 0.20Fixed overhead cost is $32,300 per year. Fixed selling and administrative costs are $12,500per year. Candyland sold 35,000 boxes last year.Required:1. What is the contribution margin per unit for a box of praline fudge? What is thecontribution margin ratio?2. How many boxes must be sold to break even? What is the break-even sales revenue?3. What was Candyland’s operating income last year?4. What was the margin of safety in sales dollars? 5. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION Suppose that Candyland Inc. raises the price to $6.20 perbox but anticipates a sales drop to 31,500 boxes. What will be the new break-even point inunits? Should Candyland raise the price? Explain.arrow_forwardThe Colin Division of Crane Company sells its product for $30.00 per unit. Variable costs per unit include: manufacturing, $13.80; and selling and administrative, $4.00. Fixed costs are: $322000 manufacturing overhead, and $54000 selling and administrative. There was no beginning inventory. Expected sales for next year are 46000 units. Matthew Young, the manager of the Colin Division, is under pressure to improve the performance of the Division. As part of the planning process, he has to decide whether to produce 46000 units or 54000 units next year. What would the manufacturing cost per unit be under variable costing for each alternative? 46000 units 54000 units $13.80 $13.80 $17.80 $17.80 $19.55 $20.80 $20.80 $19.55arrow_forward
- Daily Kneads, Inc., is considering outsourcing one of its many products rather than making it internally. The supplier will charge $20,000 for 20,000 pounds of the product. The costs per pound to make this product include: Cost per Pound $0.30 Direct Labor Direct Materials $0.60 $0.70 Allocated Unavoidable Overhead If Daily Kneads outsources, what is the savings (or loss) per pound for the company as a whole? If the amount is a loss include a negative sign (not parentheses) in your answer. "_"arrow_forward4 Lowwater Sailmakers manufactures sails for sailboats. The company has the capacity to produce 25,000 sails per year, but is currently producing and selling 20,000 sails per year. The following information relates to current production. If a special sales order is accepted for 4,500 sails at a price of $120 per unit, and fixed costs remain unchanged, how would operating income be affected? (NOTE: Assume regular sales are not affected by the special order.) Sale price per unit $150 Variable costs per unit: Manufacturing Marketing and administratrve $60 $20 Total fixed costs: Manufacturing Marketing and administrative $600,000 S200,000 Increase by $160,000 ) Increase by $150,000 ) Increase by $140,000 Increase by S170,000 ) Increase by S180,000 ()arrow_forwardNorthwood Company manufactures basketballs. The company has a ball that sells for $25. At present, the ball is manufactured in a small plant that relies heavily on direct labor workers. Thus, variable expenses are high, totaling $15.00 per ball, of which 60% is direct labor cost. Last year, the company sold 34,000 of these balls, with the following results: Sales (34,000 balls) $ 850,000 Variable expenses 510,000 Contribution margin 340,000 Fixed expenses 212,000 Net operating income $ 128,000 Required: 1. Compute (a) last year's CM ratio and the break-even point in balls, and (b) the degree of operating leverage at last year’s sales level. 2. Due to an increase in labor rates, the company estimates that next year's variable expenses will increase by $3.00 per ball. If this change takes place and the selling price per ball remains constant at $25.00, what will be next year's CM ratio and the break-even point in balls? 3. Refer to the data in (2)…arrow_forward
- Maple Enterprises sells a single product with a selling price of $75 and variable costs per unit of $30. The company’s monthly fixed expenses are $22,500.A. What is the company’s break-even point in units?B. What is the company’s break-even point in dollars?C. Construct a contribution margin income statement for the month of September when they will sell 900 units.D. How many units will Maple need to sell in order to reach a target profit of $45,000?E. What dollar sales will Maple need in order to reach a target profit of $45,000?F. Construct a contribution margin income statement for Maple that reflects $150,000 in sales volume.arrow_forwardLast year, Bread City had sales of 70,000 loaves resulting in revenues of $350,000. Variable costs were $3.50 per loaf, and fixed costs were $90,000. How many loaves must the company sell to earn $30,000?arrow_forwardBridgeport Racers makes bicycles. It has always purchased its bicycle tires from the Cullumber Tires at $26 each but is currently considering making the tires in its own factory. The estimated costs per unit of making the tires are as follows: Direct materials $9 Direct labor $5 Variable manufacturing overhead $8 The company’s fixed expenses would increase by $73,000 per year if managers decided to make the tire.(a1) Calculate total relevant cost to make or buy if the company needs 11,300 tires a year. Make Buy Total relevant cost $enter a dollar amount $enter a dollar amount (a2) Ignoring qualitative factors, if the company needs 11,300 tires a year, should it continue to purchase them from Balyo or begin to produce them internally? The company select an option should not continueshould continue to purchase the tires.arrow_forward
- A local toolmaker makes the best hammers on the market. The head of the hammer costs $15.56 and the handle costs $4.24. It takes 1.4 minutes to assemble the hammer and the hourly cost is $91 for assembly time. The company has fixed operating costs of $26348 per month. They sell the hammers for three times their total variable cost. The company wants to make a monthly profit of $8619. How many hammers must they sell? Round to the nearest whole number Answer:arrow_forwardTrey's Trucks uses a standard part in the manufacture of several of its trucks. The cost of producing 60,000 parts is $160,000, which includes fixed costs of $90,000 and variable costs of $70,000. The company can buy the part from an outside supplier for $3.30 per unit and avoid 30% of the fixed costs. If the company makes the part, how much will its operating income be? O A. $135,000 greater than if the company bought the part O B. $101,000 greater than if the company bought the part O C. $101,000 less than if the company bought the part O D. $135,000 less than if the company bought the partarrow_forwardNorthwood Company manufactures basketballs. The company has a ball that sells for $25. At present, the ball is manufactured in a small plant that relies heavily on direct labor workers. Thus, variable expenses are high, totaling $15.00 per ball, of which 60% is direct labor cost. Last year, the company sold 56,000 of these balls, with the following results: Sales (56,000 balls) Variable expenses Contribution margin Fixed expenses $ 1,400,000 840,000 560,000 373,000 Net operating income $ 187,000 Required: 1. Compute (a) last year's CM ratio and the break-even point in balls, and (b) the degree of operating leverage at last year's sales level. 2. Due to an increase in labor rates, the company estimates that next year's variable expenses will increase by $3.00 per ball. If this change takes place and the selling price per ball remains constant at $25.00, what will be next year's CM ratio and the break-even point in balls? 3. Refer to the data in (2) above. If the expected change in…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education