
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
The square surface shown in the figure measures 3.3 mm on each side. It is immersed in a uniform electric field with magnitude E = 1700 N/C and with field lines at an angle of 35° with a normal to the surface, as shown. Take that normal to be "outward," as though the surface were one face of a box. Calculate the electric flux through the surface.
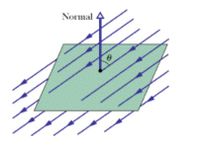
Transcribed Image Text:Normal
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- What is the net electric flux passing through a cylindrical surface shown below, whose axis is the dashed line? The cylindrical surface is of diameter 4.0 cm, and a length of 15.0 cm, with its axis parallel to, but offset radially by 1.0 cm, from an infinitely long line of charge having a uniform linear charge density A = 3.0 μC/m? The line of charge is the solid line. 1.0 cm 10 O 4.4 x 10³ Nm²/C O 8.7 x 10³ Nm²/C O 1.8 x 105 Nm²/C O 5.1 x 104 Nm²/C O 7.6 x 104 Nm²/C 2 harrow_forwardThe square surface shown in the figure measures 3.5 mm on each side. It is immersed in a uniform electric field with magnitude E = 2100 N/C and with field lines at an angle of 35° with a normal to the surface, as shown. Take that normal to be "outward," as though the surface were one face of a box. Calculate the electric flux through the surface. Normal 4arrow_forwardA cube of side L = 2.1 m lies in a region where the electric field is given by E = [-2(x^2/m^2+3.6) i - 2.0 k] N/C. We wish to find the net electric flux through the cube by first calculating the flux through each of the six faces. Here, x1=1.5m. (a) What is the flux through the left face of the cube? (b) What is the flux through the right face of the cube? (c) What is the flux through the top face of the cube? (d) What is the flux through the bottom face of the cube? (e) What is the flux through the front face of the cube? (f) What is the flux through the back face of the cube? (g) What is the net flux through the cube?arrow_forward
- An electric field given by E=3.01-9.6(y² +4.3) pierces the Gaussian cube of edge length 0.180 m and positioned as shown in the figure. (The magnitude E is in newtons per coulomb and the position x is in meters.) What is the electric flux through the (a) top face, (b) bottom face, (c) left face, and (d) back face? (e) What is the net electric flux through the cube? (a) Number i -8e-6 Units N•m^2/C Gaussian surface -Xarrow_forwardIn the space between two parallel planes separated by a distance 2d some charge is uniformly distributed with density po. Calculate the electric field in all space as a function of x 2darrow_forwardA uniform charge density of 660 nC/m3 is distributed throughout a spherical volume of radius 6.00 cm. Consider a cubical Gaussian surface with its center at the center of the sphere. (a) What is the electric flux through this cubical surface if its edge length is 2.30 cm?___________N · m2/C(b) What is the electric flux through this cubical surface if its edge length is 17.0 cm? ___________N · m2/Carrow_forward
- The figure shows a prism‑shaped object that is 40.0 cm high, 30.0 cm deep, and 80.0 cm long. The prism is immersed in a uniform electric field of 700 N/C directed parallel to the x-axis. Calculate the electric flux ΦI out of Surface I (the back surface). Calculate the electric flux ΦII out of Surface II (the bottom surface). Calculate the electric flux ΦIII out of Surface III (the left end). Calculate the electric flux ΦIV out of Surface IV (the right end). Calculate the electric flux ΦV out of Surface V (the front surface). Calculate the net electric flux Φ out of the entire closed surface.arrow_forwardConsider a closed triangular box resting within a horizontal electric field of magnitude E = 8.26 104 N/C as shown in the figure below. (a) Calculate the electric flux through the vertical rectangular surface of the box.arrow_forwardThe square surface shown in the figure measures 3.4 mm on each side. It is immersed in a uniform electric field with magnitude E = 1400 N/C and with field lines at an angle of 35° with a normal to the surface, as shown. Take that normal to be "outward," as though the surface were one face of a box. Calculate the electric flux through the surface. Normal 4 Number i Unitsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON