
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Which of the following possess reflectional symmetry? (Choose all that apply.)
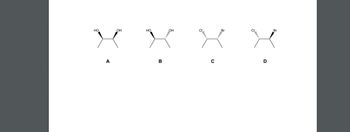
Transcribed Image Text:The image displays four different stereoisomers, labeled A, B, C, and D. Each molecule consists of a central carbon chain with substituents, showing stereochemistry through wedge and dash bonds, indicating different spatial orientations.
**A.** The molecule features two hydroxyl (OH) groups attached to adjacent carbon atoms, with both groups in the plane of the screen.
**B.** Similar to molecule A, this molecule also has two hydroxyl (OH) groups. However, the group on the left is coming out of the plane (solid wedge) and the one on the right is going into the plane (hashed wedge).
**C.** This molecule has chlorine (Cl) and bromine (Br) as substituents. The chlorine is coming out of the plane (solid wedge) and the bromine is going into the plane (hashed wedge).
**D.** The positions of the bromine (Br) and chlorine (Cl) are reversed compared to molecule C. The bromine is now coming out of the plane (solid wedge) and the chlorine is going into the plane (hashed wedge).
These diagrams are an excellent example to illustrate the concept of stereoisomerism, specifically enantiomers and diastereomers, in organic chemistry.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1. Pyridine (shown below) is a planar delocalized molecule Similar to benzene H 1) Identify its principal rotation axis (draw it it on picture) 11) Determine its point group and give your resoning / explainin H H C IC H 。 H and label 1211arrow_forwardDetermine the elements of symmetry and the point group of the following species. Show procedure and point structures. (SF2. SF5Cl, BrF3, XeF4, CH2O)arrow_forward1. Below are two views of the triflate anion, CF3SO3−. a. Using the conventions learned in class, draw the following: i. A cartesian coordinate system. Indicate which view your coordinate system corresponds to. ii. The principal axis of rotation. Give the axis using the proper notation for symmetry elements. iii. One of the mirror planes. Name the mirror axis, including the name of the cartesian plane. b. List ALL unique symmetry operations present for triflate. You do not need to include redundant ones (e.g. since, C33 = E, you do not need to include C33). c. What is the point group of triflate?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY