
Organic Chemistry
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781305580350
Author: William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
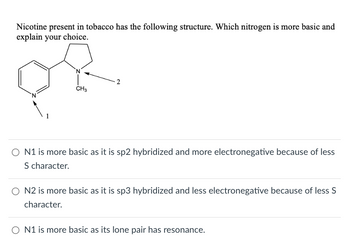
Transcribed Image Text:Nicotine present in tobacco has the following structure. Which nitrogen is more basic and
explain your choice.
CH3
2
○ N1 is more basic as it is sp2 hybridized and more electronegative because of less
S character.
O N2 is more basic as it is sp3 hybridized and less electronegative because of less S
character.
ON1 is more basic as its lone pair has resonance.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- For each molecule below, draw the conjugate acid or conjugate base or both if the molecule hasboth a conjugate acid and a conjugate base (e.g., water).arrow_forwardArrange the molecules and ions in set in order of increasing acidity (from least acidic to most acidic).arrow_forwardCan you explain which has more acidic and draw the structure, conjugate base, and resonance structure that support the answer?arrow_forward
- Use following: a) Atoms b) Resonance c) Induction d) Orbitalsarrow_forwardPhysostigmine is used in the treatment of glaucoma. Within this structure, the atom indicated by least basic. 2 CH3 H₂C souf 1 NHCH3 4 2 (most basic), 4 (least basic) 1 (most basic), 4 (least basic) 2 (most basic), 3 (least basic) 1 (most basic), 3 (least basic) None of the above is most basic, while atom isarrow_forwardWhich carbon has the most acidic proton in the molecule below? B D 4 B D C CH₂arrow_forward
- Predict the position of the equilibrium for the reaction and provide a brief explanation. (The acidic protons are shown in red.) A B Forward direction is favored because oxygen is more electronegative, making B the weaker base and D the stronger acid. O Reverse direction is favored because oxygen is more electronegative, making B the weaker base and D the stronger acid. O Forward direction is favored because sulfur is larger, making C the weaker base and A the stronger acid. Reverse direction is favored because sulfur is larger, making C the weaker base and A the stronger acid.arrow_forwardWhich compound would be the strongest acid? O CH3CCI2CH2CO2H O CH3CHCICHCICO2H O CH3CH2CCI2CO2H O CICH2CHCICH2CO2Harrow_forwardMatch each species with its correct description. fluoride (F-) v [ Choose ] its conjugate acid is HF+ its conjugate base is NO3- its conjugate base is CH3NH- its conjugate base is OH is the conjugate base of sulfate (SO4 2-) is the conjugate base of NO3- is the conjugate base of HF its conjugate acid is H30+ is the conjugate acid of CH3NH2 is the conjugate base of NH4 its conjugate acid is H2SO4 is the conjugate acid of NH2- water (H2O) ammonia (NH3) hydrogen sulfate (HSO4-) nitric acid (HNO3) [Choose] methylaminium (CH3NH3+) [Choose ]arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780618974122
Author:Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:Cengage Learning