
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
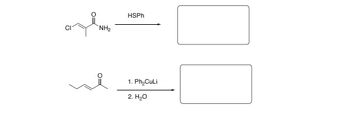
Transcribed Image Text:NH2
HSPh
1. Ph₂CuLi
2. H₂O
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 5. Calculate the concentration of the hydrochloric acid if a 20.00 mL sample is titrated with standard sodium carbonate solution. 2 HCI (aq) + Na₂CO3(aq) → H₂O (1) + CO₂(g) + 2 NaCl (aq) The titration required 10.00 mL of 0.250 mol/L sodium carbonate to neutralize the acid. rn Lakes Collegearrow_forwardit is time for the titration. You measure 15.0 mL of the H2C2O4 solution with a 100-mL graduated cylinder and add it to a 125-mL Erlenmeyer flask. Then you add two drops of the indicator, phenolphthalein, to the oxalic acid solution in the flask. You dispense the NaOH solution from the buret into the flask (while swirling the flask) until you reach the endpoint. At the endpoint, the solution in the flask turns light pink. You repeat the titration two additional times for a total of three trials. H2C2O4 (aq) + 2 NaOH (aq) --> Na2C2O4 (aq) + 2 H2O (l) (I) (II) (III) Volume of H2C2O4 used 15.00 mL 15.00 mL 15.00 mL Initial Buret Reading 0.00 mL 0.05 mL 0.10 mL Final Buret Reading 14.45 mL 14.38 mL 15.40 mL Volume NaOH used ________mL ________mL ______mL Moles NaOH _______M ________M _________M…arrow_forwardA railroad tank car carrying 1.5 103 L of concentrated sulfuric acid derails and spills its load. The acid is 93.2% H2SO4 by mass and has a density of 1.84 g/mL. How many kilograms of sodium carbonate (soda ash) are needed to neutralize the acid? (Hint: What is the neutralization reaction?)arrow_forward
- The solubility product constant for a certain metal phosphate, M3(PO4)2 is Ksp = 2.1 × 10−27. Its molar mass is ℳ = 279.04 g/mol. What is its solubility in g/L? Report your answer to TWO significant figures. Enter your answer in scientific notation using the appropriate boxes. Remember, a number like 1.6, in scientific notation is 1.6 × 100.arrow_forwardGg.190.arrow_forward4. A student did not read the directions to the experiment properly and mixed up where to put the NaOH and the HCl solutions. He put the HCl in the buret and the NaOH in the flask. He then added a drop of the phenolphthalein to the solution in the flask. Does the student need to empty out all of the solutions and start over again or can he go ahead and run the titration? Explain qalb ribidw qid edini olddud ris ogrel s znisimos tund entd nousu 5. How many liters of 3.4 M HI will be required to reach the equivalence point with 2.1 L of 2.0 M KOH? 9no vino to beateni nolusius to alsid sigulum ob of insttoqmi ti al VW Sarrow_forward
- Sodium hydrogen carbonate NaHCO3 , also known as sodium bicarbonate or "baking soda", can be used to relieve acid indigestion. Acid indigestion is the burning sensation you get in your stomach when it contains too much hydrochloric acid HCl , which the stomach secretes to help digest food. Drinking a glass of water containing dissolved NaHCO3 neutralizes excess HCl through this reaction: HCl (aq) + NaHCO3 (aq) → NaCl (aq) + H2O (l) + CO2 (g)The CO2 gas produced is what makes you burp after drinking the solution. Suppose the fluid in the stomach of a woman suffering from indigestion can be considered to be 150.mL of a 0.053 M HCl solution. What mass of NaHCO3 would she need to ingest to neutralize this much HCl ? Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits.arrow_forwardSodium hydrogen carbonate NaHCO3 , also known as sodium bicarbonate or "baking soda", can be used to relieve acid indigestion. Acid indigestion is the burning sensation you get in your stomach when it contains too much hydrochloric acid HCl , which the stomach secretes to help digest food. Drinking a glass of water containing dissolved NaHCO3 neutralizes excess HCl through this reaction: HCl (aq) + NaHCO3 (aq) → NaCl (aq) + H2O (l) + CO2 (g)The CO2 gas produced is what makes you burp after drinking the solution. Suppose the fluid in the stomach of a woman suffering from indigestion can be considered to be 150.mL of a 0.023 M HCl solution. What mass of NaHCO3 would she need to ingest to neutralize this much HCl ? Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits.arrow_forwardIII O Chemical Reactions Solving for a reactant in solution 1/5 Bis Sodium hydrogen carbonate (NaHCO3), also known as sodium bicarbonate or "baking soda", can be used to relieve acid indigestion. Acid indigestion is the burning sensation you get in your stomach when it contains too much hydrochloric acid (HCI), which the stomach secretes to help digest food. Drinking a glass of water containing dissolved NaHCO3 neutralizes excess HCI through this reaction: HCl(aq) + NaHCO3(aq) NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) + CO₂(9) The CO2 gas produced is what makes you burp after drinking the solution. Suppose the fluid in the stomach of a woman suffering from indigestion can be considered to be 150. mL of a 0.024 M HCl solution. What mass of NaHCO3 would she need to ingest to neutralize this much HCI? Round your answer to 2 significant digits. Ов X Garrow_forward
- A student is asked to standardize a solution of calcium hydroxide. He weighs out 1.09 g potassium hydrogen phthalate (KHC8H404, treat this as a monoprotic acid). It requires 37.2 mL of calcium hydroxide to reach the endpoint. A. What is the molarity of the calcium hydroxide solution? This calcium hydroxide solution is then used to titrate an unknown solution of hydrobromic acid. B. If 18.1 mL of the calcium hydroxide solution is required to neutralize 24.6 mL of hydrobromic acid, what is the molarity of the hydrobromic acid solution? M Marrow_forwardSoluble Insoluble (NH4)2S MgS Hg2Br2 FeF3 CaSO4 Pb(NO3)2 NaCH3CO2 K3PO4 KF Ba(CH3CO2)2arrow_forwardYou are preparing standard acid and base solutions for the laboratory, using potassium hydrogen phthalate (KHC₈H₄O₄, abbreviated KHP) as the primary standard. KHP (molar mass = 204.22 g/mol) has one acidic hydrogen. You prepared solutions of both NaOH and HCl. It took 22.65 mL of the NaOH solution to titrate (react exactly with) 1.55 g KHP. It then took 32.35 mL of HCl solution to titrate 25.00 mL of the NaOH solution. What is the molarity of the HCl solution?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY