
Concept explainers
Need the answer to be in the form of the image with exact data in the question
[The following information applies to the questions displayed below.]
The following transactions apply to Jova Company for Year 1, the first year of operation:
- Issued $20,000 of common stock for cash.
- Recognized $220,000 of service revenue earned on account.
- Collected $173,000 from
accounts receivable . - Paid $135,000 cash for operating expenses.
- Adjusted the accounts to recognize uncollectible accounts expense. Jova uses the allowance method of accounting for uncollectible accounts and estimates that uncollectible accounts expense will be 1 percent of sales on account.
The following transactions apply to Jova for Year 2:
- Recognized $330,000 of service revenue on account.
- Collected $345,000 from accounts receivable.
- Determined that $2,650 of the accounts receivable were uncollectible and wrote them off.
- Collected $1,800 of an account that had previously been written off.
- Paid $215,000 cash for operating expenses.
- Adjusted the accounts to recognize uncollectible accounts expense for Year 2. Jova estimates uncollectible accounts expense will be 0.5 percent of sales on account.
Complete the following requirements for Year 1 and Year 2. Complete all requirements for Year 1 prior to beginning the requirements for Year 2.
b. Show the effect of each transaction on the elements of the financial statements, using a horizontal statements model. Use + for increase, − for decrease, and leave cell blank for not affected. Also, in the Statement of
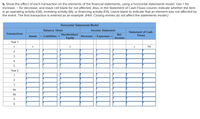
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

- Selected financial data for Wilmington Corporation is presented below. WILMINGTON CORPORATION Balance Sheet As of December 31 Year 7 Year 6 Current Assets Cash and cash equivalents $ 634,527 $ 335,597 Marketable securities 166,106 187,064 Accounts receivable (net) 284,226 318,010 Inventories 466,942 430,249 Prepaid expenses 60,906 28,060 Other current assets 83,053 85,029 Total Current Assets 1,695,760 1,384,009 Property, plant and equipment 1,384,217 625,421 Long-term investment 568,003 425,000 Total Assets $3,647,980 $2,434,430 Current Liabilities Short-term borrowings $ 306,376 $ 170,419 Current portion of long-term debt 155,000 168,000 Accounts payable 279,522 314,883 Accrued liabilities 301,024 183,681 Income taxes payable 107,509 196,802 Total Current Liabilities 1,149,431…arrow_forwardUse the information in each of the following separate cases to calculate the unknown amount. a. Corentine Company had $157,000 of accounts payable on September 30 and $135,000 on October 31. Total purchases on credit during October were $286,000. Determine how much cash was paid on accounts payable during October. b. On September 30, Valerian Company had a $105,000 balance in Accounts Receivable. During October, the company collected $105,390 from its credit customers. The October 31 balance in Accounts Receivable was $94,000. Determine the amount of sales on credit that occurred in October. c. During October, Alameda Company had $107,500 of cash receipts and $108,150 of cash disbursements. The October 31 Cash balance was $21,100. Determine how much cash the company had at the close of business on September 30. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required A Required B Required C On September 30, Valerian Company had a $105,000 balance in Accounts…arrow_forwardThe following data were taken from the balance sheet of Nilo Company at the end of two recent fiscal years: Line Item Description Current Year Previous Year Current assets: Cash $417,200 $318,000 Marketable securities 483,100 357,800 Accounts and notes receivable (net) 197,700 119,200 Inventories 1,167,500 905,200 Prepaid expenses 601,500 578,800 Total current assets $2,867,000 $2,279,000 Current liabilities: Accounts and notes payable (short-term) $353,800 $371,000 Accrued liabilities 256,200 159,000 Total current liabilities $610,000 $530,000 a. Determine for each year (1) the working capital, (2) the current ratio, and (3) the quick ratio. Round ratios to one decimal place. Line Item Description Current Year Previous Year 1. Working capital ? ? 2. Current ratio ? ? 3. Quick ratio ? ? from the preceding year to the current year. The working capital, current ratio, and quick…arrow_forward
- Please help mearrow_forwardRequired Information Use the following information for the Exercises below. (Algo) [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Simon Company's year-end balance sheets follow. At December 31 Assets Cash Accounts receivable, net Merchandise inventory Prepaid expenses Plant assets, net Total assets Liabilities and Equity Accounts payable Long-term notes payable Common stock, $10 par value Retained earnings Total liabilities and equity Current Year 1 Year Ago 2 Years Ago $ 29,387 58,429 $ 29,125 40,023 66,638 $ 23,920 69,328 88,056 7,860 224,536 $ 413,700 7,564 282,628 $ 356,638 81,206 162,500 54,468 $101,981 76,998 $ 58,464 162,500 72,221 $ 413,780 $ 356,638 For both the current year and one year ago, compute the following ratios: 43,855 3,236 184,761 $ 300,200 $ 38,438 64,354 162,580 34,988 $ 300,200 Exercise 17-6 (Algo) Common-size percents LO P2 1. Express the balance sheets in common-size percents. 2. Assuming annual sales have not changed in the last three…arrow_forwardRequired information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Simon Company's year-end balance sheets follow. At December 31 Assets Cash Accounts receivable, net Merchandise inventory Prepaid expenses Plant assets, net Total assets Liabilities and Equity Accounts payable Long-term notes payable. Common stock, $10 par value Retained earnings Total liabilities and equity Current Year $ 30,800 88,100 111,000 10,900 280,000 $ 520,800 $ 128,400 98,000 163,500 130,900 $ 520,800 Current Year 1 Year Ago $ 35,000 61,500 82,400 9,300 250,500 $ 438,700 $ 478,850 243,350 12,100 9,550 $73,750 101,750 163,500 99,700 $438,700 The company's income statements for the Current Year and 1 Year Ago, follow. For Year Ended December 31 Sales Cost of goods sold Other operating expenses $785,000 Interest expense Income tax expense Total costs and expenses Net income Earnings per share For both the Current Year and 1 Year Ago, compute the following ratios: 743,850 $ 41,150 $ 2.52 2…arrow_forward
- Blooming Flower Company was started in Year 1 when it acquired $61,400 cash from the issue of common stock. The following data summarize the company's first three years' operating activities. Assume that all transactions were cash transactions. Purchases of inventory Sales Cost of goods sold Selling and administrative expenses Income Statements Balance Sheets Assets Cash Required Prepare an income statement (use multistep format) and balance sheet for each fiscal year. (Hint: Record the transaction data for each accounting period in the accounting equation before preparing the statements for that year.) Merchandise inventory Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Total assets Liabilities Stockholders' equity Common stock Retained earnings Total stockholders' equity Total liabilities and stockholders' equity Year 1 $22,300 26,500 12,400 5,310 $ 60,290 9,900 Prepare a balance sheet for each fiscal year. (Hint: Record the transaction data for each accounting…arrow_forwardThe balance sheet of RS Corp. as at December 31, 1979 contained the following current assets: Cash 96, 578 Accounts receivable 452,800 Inventories 376,300 925,678 An examination of the accounts disclosed that the accounts receivable consisted of the following items: Trade customers’ accounts 357,742 Due from employees – current 43,658 Equity in 50,000 of uncollected accounts receivable assigned under guaranty 16,000 Selling price of merchandise on consignment at 140% of cost and not sold 50,400 Allowance for doubtful accounts…arrow_forwardOxford Company has the following account balances: Cash, $40,000; Accounts Receivable, $28,000; Inventory, $12,000; Land, $110,000; Building, $100,000; Accounts Payable, $30,000; Short-term Notes Payable, $10,000; Bonds Payable, $80,000; Oxford, Capital, $170,000; Sales, $120,000; Salaries Expense, $40,000; Utilities Expense, $15,000; and Interest Expense, $5,000. The current ratio for Oxford Company is a. 2.42:1. b. 2.67:1. c. 2:1. d. 2.27:1.arrow_forward
- The following selected information is taken from the financial statements of Arnn Company for its most recent year of operations: Beginning balances: Inventory $200,000 Accounts receivable 300,000 Ending balances: Inventory 250,000 Accounts receivable 400,000 Cash 100,000 Marketable securities (short-term) 200,000 Prepaid expenses 50,000 Accounts payable 175,000 Taxes payable 85,000 Wages payable 90,000 Short-term loans payable 50,000 During the year, Arnn had net sales of $2.45 million. The cost of goods sold was $1.3 million. Required: When required, round your answers to two decimal places. Assume 365 days per year. 1. Compute the current ratio. 2. Compute the quick or acid-test ratio. 3. Compute the accounts receivable turnover ratio. times 4. Compute the accounts receivable turnover in days. days 5. Compute the inventory turnover ratio. times 6. Compute the inventory turnover in days. daysarrow_forwardZirkle Company borrowed $129,000 from Plains Bank on July 31, Year 1. The note carried a 6% interest rate with a one-year term to maturity Required: a. Show the effects of borrowing the money and the December 31, Year 1 adjustment on the accounting equation. b. What is the amount of interest expense for Year 1? c. Prepare a statement of cash flows for the Zirkle Company for Year 1. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required A Required B Required C Show the effects of borrowing the money and the December 31, Year 1 adjustment on the accounting equation. Note: Enter any decreases to account balances with a minus sign. Leave cells blank if no input is needed. ZIRKLE COMPANY Effect of Adjustment on the Accounting Equation Event Year 1 July 31 December 31 December 31, Year 1 Assets Liabilities Stockholders' Equity Raquinad A Required B > 13arrow_forwardA company had beginning accounts receivable of $175,000. All sales were on account and totaled $550,000. Cash collected from customers totaled $650,000. Calculate the ending accounts receivable balance.arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





