
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
i need the answer quickly
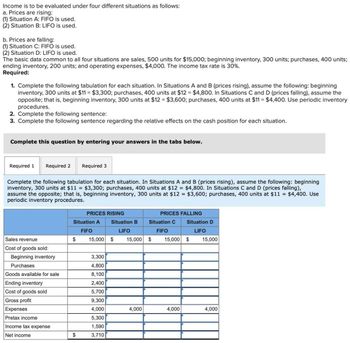
Transcribed Image Text:Income is to be evaluated under four different situations as follows:
a. Prices are rising:
(1) Situation A: FIFO is used.
(2) Situation B: LIFO is used.
b. Prices are falling:
(1) Situation C: FIFO is used.
(2) Situation D: LIFO is used.
The basic data common to all four situations are sales, 500 units for $15,000; beginning inventory, 300 units; purchases, 400 units;
ending inventory, 200 units; and operating expenses, $4,000. The income tax rate is 30%.
Required:
1. Complete the following tabulation for each situation. In Situations A and B (prices rising), assume the following: beginning
inventory, 300 units at $11 = $3,300; purchases, 400 units at $12 = $4,800. In Situations C and D (prices falling), assume the
opposite; that is, beginning inventory, 300 units at $12 = $3,600; purchases, 400 units at $11 - $4,400. Use periodic inventory
procedures.
2. Complete the following sentence:
3. Complete the following sentence regarding the relative effects on the cash position for each situation.
Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below.
Required 1
Required 2 Required 3
Complete the following tabulation for each situation. In Situations A and B (prices rising), assume the following: beginning.
inventory, 300 units at $11 = $3,300; purchases, 400 units at $12 = $4,800. In Situations C and D (prices falling),
assume the opposite; that is, beginning inventory, 300 units at $12 = $3,600; purchases, 400 units at $11 = $4,400. Use
periodic inventory procedures.
PRICES RISING
Situation A
FIFO
Situation B
LIFO
PRICES FALLING
Situation C
FIFO
Sales revenue
$
15,000 $
15,000 $
Situation D
LIFO
15,000 $
15,000
Cost of goods sold:
Beginning inventory
3,300
Purchases
4,800
Goods available for sale
8,100
Ending inventory
2,400
Cost of goods sold
5,700
Gross profit
9,300
Expenses
4,000
4,000
4,000
4,000
Pretax income
5,300
Income tax expense
1,590
Net income
$
3,710
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education