
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
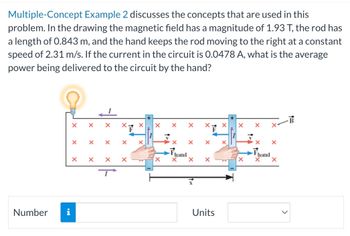
Transcribed Image Text:Multiple-Concept Example 2 discusses the concepts that are used in this
problem. In the drawing the magnetic field has a magnitude of 1.93 T, the rod has
a length of 0.843 m, and the hand keeps the rod moving to the right at a constant
speed of 2.31 m/s. If the current in the circuit is 0.0478 A, what is the average
power being delivered to the circuit by the hand?
Number
i
X
X
X
X
X X
X
X
X
hand
X
X
Units
X
X
x X
hand
X
X
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- In the figure (Figure 1) a conducting rod of length L = 31.0 cm moves in a magnetic field B of magnitude 0.480 T directed into the plane of the figure. The rod mc with speed v = 5.30 m/s in the direction shown. Figure X X X X X b X χαχ X X 1 of 1 X X X What is the potential difference between the ends of the rod? Express your answer in volts. NO | ΑΣΦΑ ▼ V = Submit Part B Which point, a or b, is at higher potential? b Submit Part C Request Answer E = Submit Request Answer When the charges in the rod are in equilibrium, what is the magnitude of the electric field with Express your answer in volts per meter. VG ΑΣΦΑ V Request Answer V/marrow_forwardThe two conducting rails in the drawing are tilted upward so they each make an angle of 30.0° with respect to the ground. The vertical magnetic field has a magnitude of 0.040 T. The 0.29-kg aluminum rod (length - 1.6 m) slides without friction down the rails at a constant velocity. How much current flows through the rod? Number i Conducting Units 16m-arrow_forwardAn electron moves in a circular path perpendicular to a magnetic field of magnitude 0.230 T. If the kinetic energy of the electron is 3.70 x 10-19 J, find the speed of the electron and the radius of the circular path. (a) the speed of the electron 9.02e5 ✔ m/s (b) the radius of the circular path Your response is off by a multiple of ten. umarrow_forward
- A piece of copper wire has a resistance per unit length of 5.12 × 10-3/m. The wire is wound into a thin, flat coil of many turns that has a radius of 0.149 m. The ends of the wire are connected to a 12.0-V battery. Find the magnetic field strength at the center of the coil.arrow_forwardA piece of copper wire has a resistance per unit length of 5.40 × 10³/m. The wire is wound into a thin, flat coil of many turns that has a radius of 0.118 m. The ends of the wire are connected to a 12.0-V battery. Find the magnetic field strength at the center of the coil. Number Unitsarrow_forwardA metal rod 40 cm long moves in a plane perpendicular to a magnetic field of 600 G. The velocity of the rod is perpendicular to its length. Find the speed of the rod if the potential difference between the ends is 4 V. m/sarrow_forward
- A stationary square coil of area 0.1 m2 is brought over time of 2 s into the magnetic field 9.1 T with its plane perpendicular to the magnetic field. The coil has 2112 turns. Calculate the magnetic flux linkage through the coil. Give your answer in SI units.arrow_forwardWhen operated on a household 110.0 V line, typical hair dryers draw about 1450 W of power. The current can be modeled as a long, straight wire in the handle. During use, the current is about 2.25 cm from the user's hand. What is the current in the hair dryer? 13.2 A What is the resistance of the hair dryer? 8.41 Ω What magnetic field does the hair dryer produce at the user's hand? The permeability of free space is Ho = 47 × 10-' N/A?. 1.1 x10¬4 Incorrectarrow_forwardThe circuit in the figure below is located in a magnetic field whose magnitude varies with time according to the expression B = 1.00 x 10³ t, where B is in teslas and t is in seconds. Assume the resistance per length of the wire is 0.099 /m. Find the current in section PQ of length a = 60.0 cm. magnitude μA direction from Q to P a xxxxx * * * ** x Bin * * x X xx * * * xx x X xx 2a x x x x xx P xxxx xxxx **** * x x x x Q aarrow_forward
- The loop in the figure is being pushed into the 0.20 T magnetic field at 45 m/s . The resistance of the loop is 0.50 N. (Figure 1) You may want to review (Pages 849 - 851) . Figure 1 of 1 V В 5.0 cmarrow_forwardAn astronaut is connected to her spacecraft by a 29-m-long tether cord as she and the spacecraft orbit Earth in a circular path at a speed of 4.1 103 m/s. At one instant, the voltage measured between the ends of a wire embedded in the cord is measured to be 0.44 V. Assume the long dimension of the cord is perpendicular to the vertical component of Earth's magnetic field at that instant. (a) What is the magnitude of the vertical component of Earth's field at this location? uT(b) Does the measured voltage change as the system moves from one location to another? Explain.arrow_forwardMultiple-Concept Example 2 discusses the concepts that are used in this problem. In the drawing the magnetic field has a magnitude of 1.59 T, the rod has a length of 0.756 m, and the hand keeps the rod moving to the right at a constant speed of 4.51 m/s. If the current in the circuit is 0.0532 A, what is the average power being delivered to the circuit by the hand? 4 X X x- X X X X X XV x X X x X Fond X x Number i X X X T Units X T X ➜ hand Xarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON