
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question
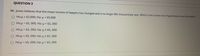
Transcribed Image Text:QUESTION 3
Mr. Jones believes that the mean income of lawyers has changed and is no longer $65 thousand per year. Which is the correct set of hypotheses to test this belief?
O Ho:p 2 65,000; Ha: µ < 65,000
O Ho:p = 65, 000; Ha: µ > 65, 000
O Ho:u = 65, 000; Ha: µ + 65, 000
Ho:p < 65, 000; Ha: p > 65, 000
O Ho:u = 65, 000; Ha: µ > 65, 000
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A nationwide test taken by high school sophomores and juniors has three sections, each scored on a scale of 20 to 80. In a recent year, the national mean score for the writing section was 50.4with a standard deviation of 9.1 a. According to Chebyshev's theorem at least ? of the score lies between 3.2 and 68.6 b. According to Chebyshev's theorem at least 56% of the fares lies between ? and ? (Round your answer to 2 decimal places.)arrow_forwardA random sample of 37 MBAs working in New York revealed that their mean annual salary was $132,000. Suppose that the population standard deviation o is $31,000 but that the population mean μ is unknown. What is the point estimate (i.e. the "best guess") of the mean salary μ of all MBAs in this city? O $99,000 O $132,000 O $116,000 O $31,000arrow_forwardI need help to solve this question.arrow_forward
- Which of the following is an accurate definition for the power of a statistic test?arrow_forwardEach person in random samples of 227 male and 293 female working adults living in a certain town in Canada was asked how long, in minutes, his or her typical daily commute was. Is there enough evidence to show that there is a difference in mean commute times for male and female working residents of this town? (Use males females) Male Female Sample size X S Sample size x S 227 30.2 24.0 293 27.9 24.3 Find the test statistic. (Round your answer to two decimal places.) Find the df. (Round your answer down to the nearest whole number.) df= Use technology to find the P-value. (Round your answer to four decimal places.) P-value= Is there enough evidence to show that there is a difference in mean commute times for male and female working residents of this town? Use a significance level of 0.05. Yes Noarrow_forwardA random sample of 10,000 bottles of cola was taken to see whether the mean weight was 16 fluid ounces, as marked on the container. The null hypothesis is that the population mean is 16 ounces. Use the read-out below to test the hypothesis that the colas do not have a population mean of 16 fluid ounces. You do not have to do any calculations; just interpret the given data clearly and thoroughly in the context of the problem. | One-Sample T: ounces Test of u = 16 vs = 16 Variable Mean StDev SE Mean 95 CI T P ounces 10000 15.9988 0.0985 0.0010 (15.9969, 16.0007) -1.21 0.225arrow_forward
- You run a publishing company and you are assessing your proofreaders. You hope that they can proofread an average of 1000 words per hour, an industry benchmark, If they average fewer than 1000 words per hour you will need to reconfigure the staffing. You test the proofreading times of a sample of 100 of the proofreaders and find the sample average words per hour is = whether the population mean words per hour is greater than 1000 with a 95% confidence level. The z-critical value for this test is Z = Zo.05 975 and the sample standard deviation is s = 600. Test 1.645. Show all your steps clearly and illustrate your answer with a graph. %3Darrow_forwardA random sample of five observations from three normally distributed populations produced the following data: (You may find it useful to reference the F table.) (table is the screenshot picture) a. Calculate the grand mean. (Round intermediate calculations to at least 4 decimal places and final answer to 4 decimal places.) b. Calculate SSTR and MSTR. (Round intermediate calculations to at least 4 decimal places and final answers to 4 decimal places.) c. Calculate SSE and MSE. (Round intermediate calculations to at least 4 decimal places and final answers to 4 decimal places.) d. Specify the competing hypotheses in order to determine whether some differences exist between the population means. _H0: μA = μB = μC; HA: Not all population means are equal. _H0: μA ≤ μB ≤ μC; HA: Not all population means are equal. _H0: μA ≥ μB ≥ μC; HA: Not all population means are equal. e-1. Calculate the value of the F(df1, df2) test statistic. (Round intermediate calculations to at least 4 decimal…arrow_forwardWhy do deviation scores have to be squared before calculating the standard deviation? Squaring is necessary when calculating inferential statistics. If deviation scores are not squared, then the average distance from the mean will always equal 0. Squaring deviation scores allows for degrees of freedom to be calculated. If deviation scores are not squared, then the interquartile ranges are incalculable.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman