
|
For items 1 - 5, use the data below that gives the humerus bone length (in cm) and height (in inches) for a sample of female skeletons. [The data was provided by Dr. Ayers-Darling, former professor at MVCC.]
|
Compute the
As the humerus length increases, does the female height increase or decrease? (Use the result of #1 or a drawn
If the height of the female is to be predicted from the length of the humerus, is female height the explanatory or response variable?_______________________
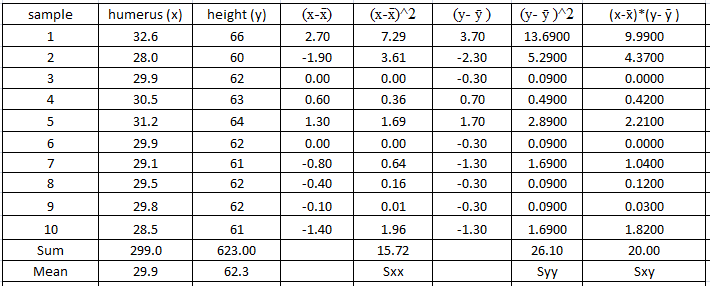
sample mean (x̄) = Σx/n =299/10 = 29.9
sample mean (ȳ) = Σy/n = 623/10 = 62.3
Sxx = 15.72
Syy = 26.10
Sxy = 20.00
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

- sleth the regcon r=2 cuso -1arrow_forwardplease answerarrow_forwardA sample of human brain volumes (cm3) is given below. Use the given data values to identify the corresponding z scores that are used for a normal quantile plot,then identify the coordinates of each point in the normal quantile plot. a. List the z scores for the normal quantile plot. (Round to two decimal places as needed. Use ascending order.) b. Identify the coordinates of each point in the normal quantile plot. Use ordered pairs for the form (x,y), where x is the sorted human brain volumes in ascending order, and y is the corresponding z score. (Round to two decimal places as needed. Use ascending order.)arrow_forward
- Please answer all 4arrow_forwardSTATE: How heavy a load (in pounds) is needed to pull apart pieces of Douglas fir 44 inches long and 1.5 inches square? Given are data from students doing a laboratory exercise. 33,190 31,860 32,590 26,520 33,280 32,320 33,020 32,030 30,460 32,700 23,040 30,930 32,720 33,650 32,340 24,050 30,170 31,300 28,730 31,920 We are willing to regard the wood pieces prepared for the lab session as an SRS of all similar pieces of Douglas fir. Engineers also commonly assume that characteristics of materials vary Normally. Suppose that the strength of pieces of wood like these follows a Normal distribution with standard deviation 3000 pounds. PLAN: We will estimate μ by giving a 95% confidence interval. SOLVE: Find the sample mean x¯ . (Enter your answer rounded to the nearest whole number.) x¯= Give a 95% confidence interval, [low, high] , for the mean load required to pull the wood apart. (Enter your answers rounded to the nearest whole number.) low=…arrow_forwardAn article gave the data, shown in the table below, on dimensions of 27 representative food products. Product Material Height MaximumWidth MinimumWidth Elongation Volume 1 glass 7.7 2.50 1.80 1.50 121 2 glass 6.2 2.90 2.70 1.07 139 3 glass 8.5 2.15 2.00 1.98 178 4 glass 10.4 2.90 2.60 1.79 288 5 plastic 8.0 3.20 3.15 1.25 328 6 glass 8.7 2.00 1.80 2.17 94 7 glass 10.2 1.60 1.50 3.19 115 8 plastic 10.5 4.80 3.80 1.09 517 9 plastic 3.4 5.90 5.00 0.29 332 10 plastic 6.9 5.80 4.75 0.59 567 11 tin 10.9 2.90 2.80 1.88 340 12 plastic 9.7 2.45 2.10 1.98 177 13 glass 10.1 2.60 2.20 1.94 236 14 glass 13.0 2.60 2.60 2.50 237 15 glass 13.0 2.70 2.60 2.41 358 16 glass 11.0 3.10 2.90 1.77 314 17 cardboard 8.7 5.10 5.10 0.85 635 18 cardboard 17.1 10.20 10.20 0.84 1250 19 glass 16.5 3.50 3.50 2.36 651 20 glass 16.5 2.70 1.20 3.06 300 21 glass 9.7 3.00 1.70 1.62 312 22 glass 17.8 2.70 1.75 3.30 303 23 glass 14.0 2.50 1.70 2.80 247 24 glass 13.6 2.40…arrow_forward
- Question 8 The following data set contains the number of minutes spent by each of 20 students in the class to write the assignment. 42 48 59 61 62 62 64 65 66 68 68 70 71 71 72 72 78 79 84 88 a. Find the median, the first and the third quartiles, and the interquartile range. b. Find the left outer fence, left inner fence, right inner fence, and right outer fence. c. Find the length of left whisker and the length of right whisker in the box – whisker plot. d. List all outliers (if any) in the last row. If there are no outliers state “none”.List all extreme values (if any) in the last row. If there are no extreme values state “none”. Show work for the calculations for Part B and Part C.arrow_forwardThe densities of several common metals are shown in the following table. Metal Density (g/cm³) iron 7.87 silver 10.49 lead 11.36 zinc 7.13 aluminum 2.70 For her chemistry lab, Kamila needs to identify three metal samples by density. The data she collected is shown in the following table. The metal samples are all rectangular prisms.arrow_forwardConsider the following data set. Draw a dotplot for the given data set. 03 n = 10 measurements: 8, 5, 6, 9, 4, 5, 7, 8, 4, 6 03 . 4 + 4 USE SALT 5 5 6 · 6 7 7 . 8 : 8 9 ↑ 9 10 10 Ⓒ 4 . 5 6 . 7 . 8 9 Are the data mound-shaped? Can you use Tchebysheff's Theorem to describe the data? The Empirical Rule? Explain. O The data set is not mound-shaped. Hence we can use Empirical Rule, but not the Tchebysheff's Theorem to describe the data. O The data set is relatively mound-shaped. Hence we can use Tchebysheff's Theorem, but not the Empirical Rule to describe the data. O The data set is relatively mound-shaped. Hence we can use Empirical Rule, but not the Tchebysheff's Theorem to describe the data. O The data set is relatively mound-shaped. Hence you can use both Tchebysheff's Theorem and the Empirical Rule to describe the data. O The data set is not mound-shaped. Hence we can use Tchebysheff's Theorem, but not the Empirical Rule to describe the data. 10 Q 03 4 5 6 7 9 10arrow_forward
- The ratio of the lengths of the second and the fourth fingers, denoted 2D:4D, is an indicator of the level of prenatal testosterone. It is known that higher prenatal testosterone levels are associated with a lower 2D:4D value. Since testosterone levels are known to be related to behavioural traits, it has been conjectured that certain types of aggressive and dominant behaviours may be associated with lower 2D:4D values. van der Meij et al. (2012) conducted a study that investigated the possible relationship between 2D:4D and so-called "sociable" and "aggressive" dominance. For the study, 84 male students completed two questionnaires, measuring sociable and aggressive dominance respectively, on which high scores related to increased aggression. After some adjustments, a score between 1 and 6 was recorded for each subject on each questionnaire. The participants' hands were scanned and measurements taken, on which a 2D:4D measure could be recorded per subject by averaging the ratio for…arrow_forwardHere are some data on the petal lengths of irises in cm. This is actually part of one of the built-in data sets in R (there are many data sets built into R): 6.0 5.1 5.9 5.6 5.8 6.6 4.5 6.3 5.8 6.1 5.1 5.3 5.5 5.0 5.1 5.3 5.5 6.7 6.9 5.0 5.7 4.9 6.7 4.9 5.7 6.0 4.8 4.9 5.6 5.8 6.1 6.4 5.6 5.1 5.6 6.1 5.6 5.5 4.8 5.4 5.6 5.1 5.1 5.9 5.7 5.2 5.0 5.2 5.4 5.1 a) Make a stem and leaf plot of these data (do not use R). b) Make a histogram of these data (do not use R).arrow_forwardPulling Apart Wood. How heavy a load (in pounds) is 4step needed to pull apart pieces of Douglas fir 4 inches long and 1.5 inches square? Here are data from students doing a laboratory exercise: 33,190 31,860 32,590 26,520 33,280 32,320 33,020 32,030 30,460 32,700 23,040 30,930 32,720 33,650 32.340 24,050 30,170 31,300 28,730 31,920 We are willing to regard the wood pieces prepared for the lab session as an SRS of all similar pieces of Douglas fir. Engineers also commonly assume that characteristics of materials vary Normally. Suppose that the strength of pieces of wood like these follows a Normal distribution, with standard deviation 3000 pounds. Is there statistically significant evidence at thea = 0.10 level against the hypothesis that the meanis 32,500 pounds for the two-sided alternative? Is there statistically significant evidence at thea = 0.10 level against the hypothesis that the meanis 31,500 pounds for the two-sided alternative?arrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





