
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
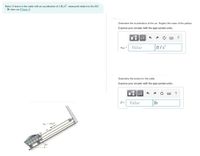
Transcribed Image Text:Motor M draws in the cable with an acceleration of 4 ft/s?, measured relative to the 200
lb mine car.(Figure 1)
Determine the acceleration of the car. Neglect the mass of the pulleys.
Express your answer with the appropriate units.
Value
ft/s
acar =
Determine the tension in the cable.
Express your answer with the appropriate units.
HA
T =
Value
lb
ape =4 ft/s?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 4. 4) The hydraulic cylinder Dextends, moves the rigid rod ABC, and causes the collar A to move with velocity and acceleration both to the left. If the dimensions/₁ 1.0 ft, and /2 = 2.0 ft, vµ = 5.5 ft/s, aµ = 2.1 ft/s², and the angle 0 = 30°, determine the angular acceleration (in rad/s²) of rod ABC. Negative sign must be included if the angular acceleration is clockwise. Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 2 places after the decimal point. Your Answer: 1₁ Answer B 12 ÏÏ a =arrow_forwardFor a short period of time, a m = 3400 kg truck has a frictional driving force of FD= (650- +²) N acting on the wheels, where t is in seconds. At t = 0, the truck has a speed of of v₁. V₁ t = 0 21 Values for the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value m 5- s v2 = m Using the Principle of Linear Impulse and Momentum, a. Determine the speed of the truck when t = 3 s, v2. FD = f(t) Round your final answers to 3 significant digits/figures. m S V₂ t2arrow_forward1. A chain of blocks is moving upward at 3 m/s. The tension in the cable connected to the top of the chain is To = 800 N. a. What is the acceleration of the chain of blocks? b. What is the tension in the cable connecting Block C and Block D? v = 3 m/s To = 800 N mA = 21 kg mB = 25 kg mc = 20 kg mp = 18 kg mg = 17 kg mp = 15 kg a = ? TCD = ?arrow_forward
- Learning Goal: In 1687, Isaac Newton presented three basic laws that describe the motion of a particle: • First law: A particle originally at rest, or moving in a straight line with a constant velocity, will remain in this state provided that the particle is not subjected to an unbalanced force. Second law: A particle acted upon by an unbalanced force, F experiences an acceleration, a, that has the same direction as the force and a magnitude that is directly proportional to the force. Figure 1 1 1 V 1 of 2arrow_forwardPlease helparrow_forwardFigure 6.35 shows a proposed roller-coaster track. Each car starts from rest atpoint A, where ya = 21 mand it will roll freely without friction along the track.It is important that there be at least some small normal force exerted by thetrack on the car at all points; otherwise, the car will leave the track. What is the minimum safe value for the radius of the curvature at point B?arrow_forward
- 5. A simple pendulum at the UCR department of physics and astronomy has a length of 20 m, and the acceleration due to gravity at this location is measured to be 9.803 m/s². Calculate the period of the pendulum.arrow_forwarda.) What is the angle, measured relative to the positive x-axis, of the load's acceleration? (The correct answer is: -10.219 degrees) Just need the steps to get there b.) Three horses pull and guide a 132 kg payload down a river, exerting the forces shown in the figure, with F1 = 29 N, F2 = 38 N, F3 = 58 N, θ1 = 30°, and θ2 = 60°. What is the magnitude of the payload's acceleration? (The correct answer is: 0.7861 m/s^2)Just need the correct steps to get therearrow_forwardConsider the given pulley system. The rope is drawn towards the motor with a speed of 3 m/s. What is the speed of mass A and in what direction is it moving?arrow_forward
- 1. Two blocks are connected by a pulley system shown in the figure below. Neglect friction between the block on the left and the ramp sloped at angle 0. Suppose that the block on the left has mass m, and that the block on the right is moving downward at a constant speed v. m Given m, 0, and v, answer the questions below. (a) Find the mass of the block on the right? (b) Find the velocity of the block on the left. (c) If the block on the right was moving at a constant speed v upward, instead of downward, how would your answer to Question la change?arrow_forwardKOREK a "la KOREK + HW2 SOLUTION: Write the kinematic relationships for the dependent motions and accelerations of the blocks. • Write the equations of motion for the blocks and pulley. 300 kg B Combine the kinematic relationships with the equations of motion to solve for the The two blocks shown start accelerations and cord tension. from rest. The horizontal plane and the pulley are frictionless, and the pulley is assumed to be of negligible mass. Determine the acceleration of each block and the tension in the cord. 12 12arrow_forwardA small box of mass m is placed on top of a larger box of mass 2m as shown in Figure. When a force is applied to the large box, both boxes accelerate to the right with the same acceleration. If the coefficient of friction (static/kinetic) between all surfaces is µ, what would be the magnitude of the force and what would be the acceleration ? 2m F O 1. The information given in the problem is insufficient. O 2. 3m( µ+ g), g O 3. 3µmg, µg O 4. 6µmg, µgarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY