
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
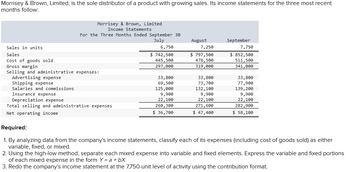
Transcribed Image Text:Morrisey & Brown, Limited, is the sole distributor of a product with growing sales. Its income statements for the three most recent
months follow:
Morrisey & Brown, Limited
Income Statements
For the Three Months Ended September 30
July
Sales in units
Sales
Cost of goods sold
Gross margin
Selling and administrative expenses:
Advertising expense
Shipping expense
Salaries and commissions
Insurance expense
Depreciation expense
Total selling and administrative expenses
Net operating income
6,750
$ 742,500
445,500
297,000
33,800
69,500
125,000
9,900
22,100
260,300
$ 36,700
August
7,250
$ 797,500
478,500
319,000
33,800
73,700
132, 100
9,900
22, 100
271, 600
$ 47,400
September
7,750
$ 852,500
511,500
341,000
33,800
77,900
139, 200
9,900
22,100
282,900
$ 58,100
Required:
1. By analyzing data from the company's income statements, classify each of its expenses (including cost of goods sold) as either
variable, fixed, or mixed.
2. Using the high-low method, separate each mixed expense into variable and fixed elements. Express the variable and fixed portions
of each mixed expense in the form Y = a +bX.
3. Redo the company's income statement at the 7,750-unit level of activity using the contribution format.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.]Ferris Company began January with 4,000 units of its principal product. The cost of each unit is $7. Merchandise transactions for the month of January are as follows: Purchases Date of Purchase Units Unit Cost* Total Cost Jan. 10 3,000 $ 8 $ 24,000 Jan. 18 4,000 9 36,000 Totals 7,000 60,000 * Includes purchase price and cost of freight. Sales Date of Sale Units Jan. 5 2,000 Jan. 12 1,000 Jan. 20 3,000 Total 6,000 5,000 units were on hand at the end of the month. 2. Calculate January's ending inventory and cost of goods sold for the month using LIFO, periodic system.arrow_forwardThe data shown were obtained from the financial records of Italian Exports, Inc., for March: Estimated Sales $580,000 Sales 567,930 Purchases 294,832 Ending Inventory* 10% Administrative Salaries 50,280 Marketing Expense** 5% Sales Commissions 2% Rent Expense 7,700 Depreciation Expense 1,200 Utilities 2,500 Taxes*** 15% *of next month's sales **of estimated sales ***of income before taxes Sales are expected to increase each month by 10%. Prepare a budgeted income statement. Round your answers to the nearest dollar. Italian Exports, Inc.Budgeted Income StatementFor the Month Ending Mar. 31, 2020 $Sales Cost of Goods Sold $Beginning Inventory Purchases $Cost of Goods Available for Sale Ending Inventory $Cost of Goods Sold Gross Profit Operating Expenses $Administrative Salaries Marketing Expenses Sales Commissions Rent Expense Depreciation Expense Utilities Total…arrow_forwardThe following data relate to the operations of Shilow Company, a wholesale distributor of consumer goods: Current assets as of March 31: Cash $ 9,100 Accounts receivable $ 26,400 Inventory $ 49,200 Building and equipment, net $ 106,800 Accounts payable $ 29,550 Common stock $ 150,000 Retained earnings $ 11,950 The gross margin is 25% of sales. Actual and budgeted sales data: March (actual) $ 66,000 April $ 82,000 May $ 87,000 June $ 112,000 July $ 63,000 Sales are 60% for cash and 40% on credit. Credit sales are collected in the month following sale. The accounts receivable at March 31 are a result of March credit sales. Each month’s ending inventory should equal 80% of the following month’s budgeted cost of goods sold. One-half of a month’s inventory purchases is paid for in the month of purchase; the other half is paid for in the following month. The accounts payable at March 31 are the result of March purchases of inventory.…arrow_forward
- The following is the year ended data for Tiger Company: Sales Revenue $58,000 Cost of Goods Manufactured 21,000 Beginning Finished Goods Inventory 1,100 Ending Finished Goods Inventory 2,200 Selling Expenses 15,000 Administrative Expenses 3,900 What is the gross profit? A. $22,100 B. $38,100 C. $19,200 D.arrow_forwardIn April, Holderness Incorporated, a merchandising company, had sales of $286,000, selling expenses of $20,500, and administrative expenses of $31,500. The cost of merchandise purchased during the month was $168,000. The beginning balance in the merchandise inventory account was $40,500 and the ending balance was $54,500 Required: Prepare a traditional format income statement for April. Holderness Incorporated For the month of April Traditional Format Income Statement Sales Cost of goods sold Gross margin Selling and administrative expenses Selling expense Administrative expense $ 20,500 31,500 5 286.000 154.000 132.000 52.000 $ 80,000 4arrow_forwardSmith & Chief Ltd. of Sydney, Australia, is a merchandising firm that is the sole distributor of a product that is increasing in popularity among Australian consumers. The company's income statements for the four most recent quarters follow. SMITH & CHIEF LTD. Income Statements For the Four Quarters Ending December 31 Quarter 1 Quarter 2 6,100 5.600 A$610,000 A$560,080 A$692,000 366,000 336,000 415,280 244,800 224,800 276,800 Sales in units Sales revenue Less: Cost of goods sold Gross margin Less: Operating expenses: Advertising expense Shipping expense Salaries and commissions Insurance expense Depreciation expense Total operating expenses Net income Advertising expense Shipping expense Salaries and commissions expense (Note: Smith & Chief Ltd.'s Australian-formatted income statement has been recast into the format common in Canada. The Australian dollar is denoted by A$.) S Advertising expense 22,600 22,600 22,600 40,408 42.400 42,080 87,600 81,200 97,840 94,288 7,500 7,600 7,600…arrow_forward
- Provide Answer please providearrow_forwardRevenue and expense data for the current calendar year for Tannenhill Company and for the electronics industry are as follows. Tannenhill’s data are expressed in dollars. The electronics industry averages are expressed in percentages. TannenhillCompany ElectronicsIndustryAverage Sales $800,000 100 % Cost of goods sold 512,000 70 Gross profit $288,000 30 % Selling expenses $176,000 17 % Administrative expenses 64,000 7 Total operating expenses $240,000 24 % Operating income $48,000 6 % Other revenue 16,000 2 $64,000 8 % Other expense 8,000 1 Income before income tax $56,000 7 % Income tax expense 24,000 5 Net income $32,000 2 % a. Prepare a common-sized income statement comparing the results of operations for Tannenhill Company with the industry average. If required, round percentages to one decimal place. Enter all amounts as positive numbers.arrow_forwardAnthony Corporation reported the following amounts for the year: Net sales 296,000 Cost of goods sold 138,000 Average inventory 50,000 Anthony's gross profit ratio is: 53.4%. 51.9%. 50.3%. 46.6%. Anthony's average days in inventory is: 70 days. 114 days. 132 days. 151 days. A company's sales equal $60,000 and cost of goods sold equals $20,000. Its beginning inventory was $1,600 and its ending inventory is $2,400. The company's inventory turnover ratio equals: 5 times. 10 times. 20 times. 30 times. [Last question is in the picture attached]arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education