
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
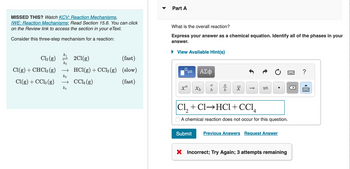
Transcribed Image Text:MISSED THIS? Watch KCV: Reaction Mechanisms,
IWE: Reaction Mechanisms; Read Section 15.6. You can click
on the Review link to access the section in your e Text.
Consider this three-step mechanism for a reaction:
k₁
Cl₂(g)
k₂
Cl(g) + CHCl3 (g) →
k3
Cl(g) + CC13 (g)
→
k4
2Cl(g)
(fast)
HCl(g) + CCl3(g) (slow)
CCL (g)
(fast)
Part A
What is the overall reaction?
Express your answer as a chemical equation. Identify all of the phases in your
answer.
► View Available Hint(s)
0
xa
ΑΣΦ
Xb
a
b
06
18
Cl,+Cl→HCl+CC1,
A chemical reaction does not occur for this question.
Submit Previous Answers Request Answer
X Incorrect; Try Again; 3 attempts remaining
冈
?
www
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- One mechanism for the destruction of ozone in the upper atmosphere is Os (9) + NO(g) → NO₂(g) + O2(g) Slow NO₂(g) + 0(g) → NO(g) + O₂(g) Fast Overall reaction O3(g) + O(g) → 20₂ (g) a. Which species is a catalyst? ONO 003 002 O NO2 b. Which species is an intermediate? ONO 003 002 O NO₂ c. E₂ for the uncatalyzed reaction 03 (g) + 0(g) → 20₂ (g) is 14.0 kj. E for the same reaction when catalyzed is 11.9 kJ. What is the ratio of the rate constant for the catalyzed reaction to that for the uncatalyzed reaction at 85°C? Assume the frequency factor A is the same for each reaction. Ratio = [References) Submit Answer Try Another Version frem atempt remaning (Pr Previousarrow_forwardTime, s C3H8], M 0.0 0.26 10.0 0.18 20.0 0.14 30.0 0.10 . 40.0 0.064 .50.0 0.052 Marrow_forwarda) Determine the total order of the reaction.b) You want to increase the reaction rate as much as you can by doubling the initial concentration of one of the reactants. Which reactant would you choose? Explain your reasoning.arrow_forward
- What is the average reaction rate for 2 NOB1(g) → Br,(g)+2 NO(g) over the first 10 seconds? Time [NOBr] (s) (mol/L) 0.00 0.0100 2.00 0.0071 4.00 0.0055 6.00 0.0045 8.00 0.0038 10.00 0.0033 [NOBI] (mol/L) mol/L 0.0100 0.0090 0.0080 0.0070 0.0060 0.0050 0.0040 0.0030 0.0020 0.00 5.00 10.00 time (s) 6.7 x 10-3 M/s d. 3.4 x 10-4 Mls a. b. 6.7 x 10-4 Mls e. 1.3 x 10-3 M/s c. 3.3 x 10-3 M/s Oxygen gas is formed by the decomposition of potassium chlorate at high temperatures according to the reaction 2 KC10, (s) → 2 KCI(s)+3 O,(g). Suppose 1.23 g KCIO; is placed in a container connected to an open-end mercury manometer on a day when atmospheric pressure is 1.00 atm. Once the reaction is complete, the height of the mercury column in the U-tube on the side of the reaction container rises by 172 mmHg. What is the pressure of O2 gas produced by the reaction? d. 0.774 atm e. 36.7 in Hg a. 1348 torr b. 22.9 kPa c. 0.559 bararrow_forward13. The production of nitric oxide is governed by the following reaction: 4NH3(g) +502(g) → 4NO(g) + 6H2O(g). produced? If the rate at which NO is produced is 6.35 x 10-2 mol/ L*s, at what rate is H₂O a. 8.29 x 10-3 mol/L✶ s b. 9.53 x 10-2 mol/L*s c. 6.35 x 10-2 mol/L*s d. 7.94 x 10-2 mol/L*s 14. Sulfur trioxide production follows the reaction: 2 SO2(g) + O2(g) → 2 SO3(g) consumed? If the rate at which SO3 is produced is 4.28 x 10 mol L-'s-', at what rate is O2 a. 4.28 × 10-4 mol L-'s-1 b. 1.08 x 10-3 mol L-'s-1 c. 1.07 × 10-4 mol L-'s-1 d. 2.14 x 104 mol L-'s-1 15. Consider the following reaction: 2A+B→ C. A kinetics study on this reaction yielded the following data: [A] mol/L [B] mol/L Rate=mol/L/s 0.0450 0.0250 5.03 x 10-3 0.0450 0.0500 2.01 x 10-2 0.0900 0.0250 5.03 x 10-3 What is the order of the reaction with respect to ([A], [B])? a. 1, 2 b. 2, 1 c. 2, 0 d. 0, 2arrow_forwardThe kinetic data shown below were observed for the reaction: BF3 (g) + NH3 (g) ---------> F3B·NH3 (g) Trial # [BF3] (mol/L) [NH3] (mol/L) Rate (M/s) 1 0.250 0.250 0.2130 2 0.250 0.125 0.1065 3 0.200 0.100 0.0682 4 0.350 0.100 0.1193 5 0.175 0.100 0.0596 b. What is the order with respect to [BF3]? (Hint: provide the number for the order, i.e. fourth order = 4)arrow_forward
- A chemistry graduate student is studying the rate of this reaction: H₂CO3 (aq) → H₂O (aq) + CO₂ (aq) He fills a reaction vessel with H₂CO3 and measures its concentration as the reaction proceeds: time (seconds) 0 10. 0.0334M 20. [H₂CO3] 0.100M 30. 0.0200M 0.0143 M 40. 0.0111 M Use this data to answer the following questions. Write the rate law for this reaction. Calculate the value of the rate constant k. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. Also be sure your answer has the correct unit symbol. rate = k k = 0 x10 ロ・ロ Xarrow_forwardA. Consider the following proposed mechanism for the production of chlorine dixoide from chlorine and ozone. Draw a reaction coordinate diagram for this reaction. Label reactants, products, transition states, intermediates, and activation energy on your sketch. Assume the reaction is endothermic. NOTE: CI is chlorine, not Carbon lodide Overall: Cl₂ (g) + 203 (g) → 2 CIO₂ (g) + O₂ (g) Step 1: Cl₂ (g) → 2 Cl (g) fast Step 2: Cl (g) + Os (g) CIO₂ +O fast Step 3: O (g) + O3 (g) → 202 (g) fast Step 4: Cl (g) + O2 (g) → CIO2 (g) slowarrow_forward9.arrow_forward
- True or False _____ The kinetics of reaction deals with the energies of the products and the reactants. _____ Thermodynamics deals with reaction rates. _____ Understanding the reactions kinetics can help you understand the mechanism of a reaction. _____ Transition states are stable. _____ This is an example of an overall second order reaction (rate = kr[CH3Br][CH3-]) _____ The rate determining step is the step with the lowest activation energy.arrow_forwardA chemistry graduate student is studying the rate of this reaction: 2H1 (g) - H₂ (g) +1₂ (g) She fills a reaction vessel with HI and measures its concentration as the reaction proceeds: time (seconds) 0 0.10 [HI] 1.00 M 0.227M 0.20 0.128M 0.30 0.0894M 0.40 0.0686M Use this data to answer the following questions. Write the rate law for this reaction. Calculate the value of the rate constant k Round your answer to 2 significant digits. Also be sure your answer has the correct unit symbol. rate=& D.Darrow_forwardEnter your answer in the provided box. For the simple decomposition reaction AB(g)→ A(g) + B(g) rate = k[AB]2 and k = 0.10 L/mol·s. How long will it take for [AB] to reach 1/3 of its initial concentration of 1.50 M? t =_____sarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY