
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Two members AB and AC are made of material with E= 91 Gpa and each member has cross sectional area of A= 290 mm2. The members are used to support bar BC. If P=2079 N, L1= 202 mm , L2= 313 mm and L3= 480 mm . Answer the following questions.
The tension in member AB
The tension in member CD
The elongation in member AB
The elongation in member CD
Vertical displacement of point E
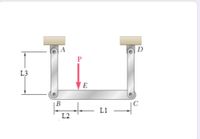
Transcribed Image Text:A
D
P
L3
E
|B
L1
L2
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A rigid plate C is used to transfer a 20-kip load P to a steel (E = 30,000 ksi) rod A and to an aluminum alloy (E = 10,000 ksi) pipe B as shown. The supports at the top of the rod and the bottom of the pipe are rigid, and the materials were unstressed before the load was applied. The cross-sectional areas of rods A and pipe B are 0.80 in2 and 3.00 in2 respectively. Determine The normal stress in rod A in ksi, The normal stress in pipe B in ksi and The displacement of plate C in inches. Note: Draw the Free Body Diagram, include the units/dimensions, use the proper formula and round-off all the answers and final answers to 5 decimal places.arrow_forward2. Use the Force Method to determine the forces in all eight members of the truss shown, and state whether they are in tension or compression. (Truss members BD and EC do not intersect.) Select member EC as the redundant member. AE is constant. 3 m 3 m D 12 kN 3 marrow_forwardThe rigid bar BDE is supported by two links AB and CD. Link AB is made of aluminum (E = 70 GPa) and has a cross-sectional area of 519 mm2; link CE is made of steel (E = 200 GPa) and has a cross-sectional area of 619 mm?. For the 41 kN force shown, determine the deflection of B (mm) *deflection should have a negative sign if compression and positive if tension. Also, your final answer should have two decimal places 04 m 0.3 m E 0.4 m 0.2 marrow_forward
- The members of the truss shown have identical cross- 3P sectional area of 200 mm². Determine the largest force P that can be applied to the truss if the allowable stress in member AD and the axial displacement of member AB is not to exceed 40 MPa and 0.1 mm, respectively. The elastic modulus of the members is 70 Gpa. A P 0.9 m D E -1.2 m 1.2 m-arrow_forwardA pin-connected structure is supported as shown in the figure. Bar (1) is made of brass [E = 105 GPa], and bar (2) is made of an aluminum alloy [E = 70 GPa]. Bars (1) and (2) each have cross-sectional areas of 375 mm². Rigid bar ABCD is supported by a pin in a double-shear connection at B. If the allowable shear stress for pin B is 130 MPa, calculate the minimum allowable diameter for the pin at B when P = 107 kN. P A 880 mm D B 720 mm 430 mm (2) (1) 260 mm 400 mmarrow_forwardThe aluminum bar ABC has a cross-sectional area of 20 mm2 is supported by a pin at A and a steel wire at B. If P = 50 kN calculate the horizontal displacement of P. The cross-sectional area of the wire is 1.5 mm2, modulus of elasticity of aluminum is 70 GPa and the modulus of elasticity of steel is 200 GPa. 90 cm B 90 cm 200 cm A 120 cmarrow_forward
- 8. A rigid bar AB is supported by three rods. A load P = 350 kN is applied to the bar. The %3D modulus of elasticity of copper is 110 x 10^6 kN/m^2 and modulus of elasticity of steel is 200 x 10^6 kN/m^2. Steel rod A = 900 sq. mm Steel rod A = 900 sq. mm 2 m |Copper A = 1200 sq. mm 2 m A B 1 m - 1 m Determine the deformation in the rods (in mm). * Your answer Вack Next Clear form Never submit passwords through Google Forms. This form was created inside of Saint Louis University, Inc..arrow_forwardThe static indeterminacy of the structure shown below is G F Hinge. С E B (A)Unstable (B) Stable, determinate (C) Stable, 5th degree indeterminate (D)Stable, 3rd degree indeterminatearrow_forwardAll bars in the truss have the same cross section and material properties. Find the total change in length of the cord A-B-C, and the stress at point p in the coordinate system given. ⁹00 lb AABC = σ= in ksi A = 0.64 in² E 30000 ksi V = 0.29 point p A Y 800 lb. 5 ft B 11200 lb 5 ft C 800 lb F 4 ft 4 ftarrow_forward
- Force member CF is what? P= 78 kN Subject: Structural Theoryarrow_forwardSelect all true statements regarding the effect of the steel moment arm, gamma, on normalized P-M interaction diagrams. O As gamma increases, the column flexural strength capacity increases As gamma increases, the column flexural strength capacity decreases O As gamma increases, the column axial strength capacity increases O As gamma increases, the column axial strength capacity decreasesarrow_forwardThe three equally spaced vertical rods in Fig. (a) are securely attached to a rigid horizontal bar. The two outer rods are made of an aluminum alloy, and the middle rod is steel. The cross- sectional areas of the rods are shown in the figure. Determine the residual stresses in the rods after the load P has been increased from zero to the limit load and then removed. The material properties are E = 70 GPa, Oyp = 330 M Pafor aluminum, and E = 200 GPa, Typ 290 MPa for steel. Neglect the weight of the bar. Aluminum 600 mm² Steel (a) շատ (06 Aluminum 600 mm² 250 mm 100 mmarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning