
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
![Match the regeneration capacity of the following tissues:
Skeletal muscle
Smooth muscle
Cardiac muscle
Areolar connective tissue
Tendons and ligaments
Bone
Nervous tissue of brain and
spinal cord.
[Choose ]
[Choose ]
[Choose ]
[Choose ]
[Choose ]
[Choose ]
[Choose]
SEYINV](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/067c3ecc-f7f5-46c9-9da9-35bff87f63ab/0911aa0a-2dec-4e72-ab8c-bcfe3d108a11/5zd2e9b_thumbnail.jpeg)
Transcribed Image Text:Match the regeneration capacity of the following tissues:
Skeletal muscle
Smooth muscle
Cardiac muscle
Areolar connective tissue
Tendons and ligaments
Bone
Nervous tissue of brain and
spinal cord.
[Choose ]
[Choose ]
[Choose ]
[Choose ]
[Choose ]
[Choose ]
[Choose]
SEYINV
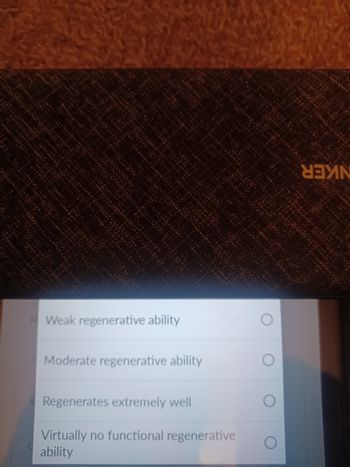
Transcribed Image Text:MWeak regenerative ability
Moderate regenerative ability
Regenerates extremely well
Virtually no functional regenerative
ability
O
SEXIN
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 8 +++ ➤ In the following table (Table 1), briefly describe the location and a function of each type of muscle tissue, with respect to the digestive system, and to the respiratory system: Table 1. The Role of Muscle Tissue in the Digestive and Respiratory Systems Muscle Location in our body tissue type skeletal cardiac smooth Focus Mode Function of that muscle tissue type with respect to the digestive system the respiratory systemarrow_forwardsend a small electrical current through the One way to characterise biological tissue is tissue and measure the opposition to flow of that current through the tissue. In humans, the resistivity of fat is considerably greater than for muscle, which in turn is considerably greater than for blood and other body fluids. This can be used to analyse body composition, in particular, to estimate body fat percentage. (a) Using a simple model of fat versus non-fat tissue, draw a circuit diagram to represent the possible flows of current through the tissue (b) Why would the analysis of body composition need to take into account the height and weight of the person? (c) How could the level of hydration or electrolyte abnormalities in the person affect the results of the analysis? DII E3 Prt Scn F3 Home 9 ES F6 F7 % &arrow_forwardLabel A-F as the following: -Intercalated disks -Nucleus of cardiac muscle cell -Nuclei -Skeletal muscle fiber (cell) -Cardiac muscle tissue -Skeletal muscle tissuearrow_forward
- Identify the tissue that contains smooth muscle. Multiple Choice Blood vessels Limb muscles Facial muscles Heartarrow_forwardIn which type(s) of muscle cells does each cell have its own neuromuscular junction? skeletal only unitary smooth and skeletal skeletal and cardiac 2. The follow is NOT true of CARDIAC muscle fibers: - connected by gap junctions - include pacemaker cells that can produce produce action potentials at regular intervals without innervation - without calcium cross bridge cycles will not occur and fibers will not shorten - each cell in a motor unit has a neuromuscular junction with the same motor neuron actin and myosin filaments are arranged in sarcomeres produce greater force when stretched than at resting length 3. Match the following: -Skeletal muscle -Cardiac muscle -Smooth muscle Can maintain prolonged isometric contractions with very little energy Striated muscle fibers with gap…arrow_forwardWhich is NOT a component of a sarcomere? Group of answer choices F-zone A-band M-line Z-discarrow_forward
- Muscle cells, neurons, and red blood cells (from left to right) Sources: Jose Luis Calvo/Shutterstock; nobeastofierce/Shutterstock; Phonlamai Photo/Shutterstock Cell Type Cell Structure Differences Justification Muscle cells Neurons Red blood cellsarrow_forwardDescribe the tendon continuumarrow_forwardSmooth muscle cells have features that can be like Skeletal muscle, Cardiac muscle, or that can be unique to smooth muscle cells themselves. Match the 3 options below to the description of smooth muscle cells on the left. do NOT possess sarcomeres do NOT possess troponin or tropomyosin neurotransmitters and hormones regulate contraction different cells of the same muscle type can contract or relax in response to the 1. similar to skeletal muscle same neurotransmitter 2. similar to cardiac muscle possess gap junctions for coordinating contraction of multiple cells 3. unique to smooth muscle can generate contraction through an influx of Ca2+ across the plasma membrane use calmodulin and myosin light-chain kinase to start the cross-bridge cycle make use of motor units to control contraction >arrow_forward
- What type of tissue organization is represented by Polysiphonia or Sarcodiotheca? A thallus cross section of Sarcodiotheca is shown below (100x). How does your answer above reflect what you see in this cross section? MacBook Pro @ 23 $ % & 2 3 4 5 6. 8arrow_forwardOne way to characterise biological tissue is to send a small electrical current through the tissue and measure the opposition to flow of that current through the tissue. In humans, the resistivity of fat is considerably greater than for muscle, which in turn is considerably greater than for blood and other body fluids. This can be used to analyse body composition, in particular, to estimate body fat percentage. (a) Using a simple model of fat versus non-fat tissue, draw a circuit diagram to represent the possible flows of current through the tissue. (b) Why would the analysis of body composition need to take into account the height and weight of the person? (c) How could the level of hydration or electrolyte abnormalities in the person affect the results of the analysis? DII Prt Scn a Home 9 F4 ES F6 F7 2$ & 4 6 7 8. 9arrow_forwardDiscuss the motor protein associated with the MF in detail, but do not include structure (include muscle and non-muscle) regarding cell Bioarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)Anatomy and PhysiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)Anatomy and PhysiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Anatomy & PhysiologyAnatomy and PhysiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyAnatomy and PhysiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Human AnatomyAnatomy and PhysiologyISBN:9780135168059Author:Marieb, Elaine Nicpon, Brady, Patricia, Mallatt, JonPublisher:Pearson Education, Inc.,
Human AnatomyAnatomy and PhysiologyISBN:9780135168059Author:Marieb, Elaine Nicpon, Brady, Patricia, Mallatt, JonPublisher:Pearson Education, Inc., Anatomy & Physiology: An Integrative ApproachAnatomy and PhysiologyISBN:9780078024283Author:Michael McKinley Dr., Valerie O'Loughlin, Theresa BidlePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Anatomy & Physiology: An Integrative ApproachAnatomy and PhysiologyISBN:9780078024283Author:Michael McKinley Dr., Valerie O'Loughlin, Theresa BidlePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Human Anatomy & Physiology (Marieb, Human Anatomy...Anatomy and PhysiologyISBN:9780321927040Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (Marieb, Human Anatomy...Anatomy and PhysiologyISBN:9780321927040Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja HoehnPublisher:PEARSON

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Anatomy and Physiology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Anatomy & Physiology
Anatomy and Physiology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Human Anatomy
Anatomy and Physiology
ISBN:9780135168059
Author:Marieb, Elaine Nicpon, Brady, Patricia, Mallatt, Jon
Publisher:Pearson Education, Inc.,

Anatomy & Physiology: An Integrative Approach
Anatomy and Physiology
ISBN:9780078024283
Author:Michael McKinley Dr., Valerie O'Loughlin, Theresa Bidle
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (Marieb, Human Anatomy...
Anatomy and Physiology
ISBN:9780321927040
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON