
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Course List)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305580343
Author: Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
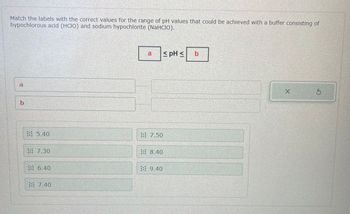
Transcribed Image Text:Match the labels with the correct values for the range of pH values that could be achieved with a buffer consisting of
hypochlorous acid (HCIO) and sodium hypochlorite (NaHCIO).
b
5.40
7.30
:: 6.40
:: 7.40
7.50
8.40
9.40
≤ pH s
b
X
S
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- What is the pH of a buffer that is 0.150 M in a weak acid and 0.150 M in the acids conjugate base? The acids ionization constant is 6.8 106.arrow_forwardWhat is meant by the capacity of a buffer? Describe a buffer with low capacity and the same buffer with greater capacity.arrow_forwardA solution of weak base is titrated to the equivalence point with a strong acid. Which one of the following statements is most likely to be correct? a The pH of the solution at the equivalence point is 7.0. b The pH of the solution is greater than 13.0. c The pH of the solution is less than 2.0. d The pH of the solution is between 2.0 and 7.0. e The pH of the solution is between 7.0 and 13.0. The reason that best supports my choosing the answer above is a Whenever a solution is titrated with a strong acid, the solution will be very acidic. b Because the solution contains a weak base and the acid (titrant) is used up at the equivalence point, the solution will be basic. c Because the solution contains the conjugate acid of the weak base at the equivalence point, the solution will be acidic.arrow_forward
- Each symbol in the box below represents a mole of a component in one liter of a buffer solution; represents the anion (X-), = the weak acid (HX), = H+, and =OH. Water molecules and the few H+ and OH- ions from the dissociation of HX and X- are not shown. The box contains 10 mol of a weak acid, , in a liter of solution. Show what happens upon (a) the addition of 2 mol of OH- (2 ). (b) the addition of 5 mol of OH- (5 ). (c) the addition of 10 mol of OH- (10 ). (d) the addition of 12 mol of OH- (12 ). Which addition (a)-(d) represents neutralization halfway to the equivalence point?arrow_forwardTwo samples of 1.00 M HCl of equivalent volumes are prepared. One sample is titrated to the equivalence point with a 1.00 M solution of sodium hydroxide, while the other sample is titrated to the equivalence point with a 1.00 M solution of calcium hydroxide. a Compare the volumes of sodium hydroxide and calcium hydroxide required to reach the equivalence point for each titration. b Determine the pH of each solution halfway to the equivalence point. c Determine the pH of each solution at the equivalence point.arrow_forwardAmmonia gas is bubbled into 275 mL of water to make an aqueous solution of ammonia. To prepare a buffer with a pH of 9.56, 15.0 g of NH4Cl are added. How many liters of NH3; at 25C and 0.981 atm should be used to prepare the buffer? Assume no volume changes and ignore the vapor pressure of water.arrow_forward
- A quantity of 0.15 M hydrochloric acid is added to a solution containing 0.10 mol of sodium acetate. Some of the sodium acetate is converted to acetic acid, resulting in a final volume of 650 mL of solution. The pH of the final solution is 4.56. a What is the molar concentration of the acetic acid? b How many milliliters of hydrochloric acid were added to the original solution? c What was the original concentration of the sodium acetate?arrow_forwardA quantity of 0.25 M sodium hydroxide is added to a solution containing 0.15 mol of acetic acid. The final volume of the solution is 375 mL and the pH of this solution is 4.45. a What is the molar concentration of the sodium acetate? b How many milliliters of sodium hydroxide were added to the original solution? c What was the original concentration of the acetic acid?arrow_forwardYou have 0.10-mol samples of three acids identified simply as HX, HY, and HZ. For each acid, you make up 0.10 M solutions by adding sufficient water to each of the acid samples. When you measure the pH of these samples, you find that the pH of HX is greater than the pH of HY, which in turn is greater than the pH of HZ. a Which of the acids is the least ionized in its solution? b Which acid has the largest Kd?arrow_forward
- A chemist needs a buffer with pH 3.50. How many milliliters of pure formic acid (density = 1.220 g/mL) must be added to 375 mL of 0.0857 M NaOH solution to obtain such a buffer?arrow_forwardBlood contains several acid base systems that tend to keep its pH constant at about 7.4. One of the most important buffer systems involves carbonic acid and hydrogen carbonate ion. What must be the ratio of [HCO3] to [H2CO3] in the blood if the pH is 7.40?arrow_forwardA 0.239-g sample of unknown organic base is dissolved in water and titrated with a 0.135 M hydrochloric acid solution. After the addition of 18.35 mL of acid, a pH of 10.73 is recorded. The equivalence point is reached when a total of 39.24 mL of HCl is added. The base and acid combine in a 1:1 ratio. a What is the molar mass of the organic base? b What is the Kb value for the base? The Kb value could have been determined very easily if a pH measurement had been made after the addition of 19.62 mL of HCl. Why?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580343
Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:Cengage Learning

General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285853918
Author:H. Stephen Stoker
Publisher:Cengage Learning

World of Chemistry, 3rd edition
Chemistry
ISBN:9781133109655
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079113
Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning