
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780134753119
Author: Sheldon Ross
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Match the following statistics to unbiased or biased estimators of the population parameters.
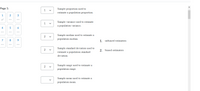
Transcribed Image Text:Page 1:
Sample proportion used to
estimate a population proportion.
1
1
2
3
--
Sample variance used to estimate
1
a population variance.
4
--
Sample median used to estimate a
population median.
7
8
9
1. unbiased estimators
Sample standard deviation used to
2
2. biased estimators
estimate a population standard
deviation.
Sample range used to estimate a
2
population range.
Sample mean used to estimate a
population mean.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, probability and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1. When applying one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), all the following are key assumptions that should be satisfied EXCEPT: A. Samples are obtained independently and randomly from the population defined by the factor level. B. The mean of the samples taken from the population is always equal. C. The population at each factor level is approximately normally distributed. D. The population have a common variance. 4. The sum of squares for treatment (SST) measures: A. the variation above the k sample means. B. the variation below the k sample means. C. the variation between the k sample means. D. the variation within the k sample means. 5. Which of the following is NOT true for the F- distribution? A. It is generally skewed to the left. B. It has two degrees of freedom. C. It is continuous. D. Its units are non-negative. 2. Which of the following components in an ANOVA table are NOT additive? A. Mean squares B. Degree of freedom C. Sum of squares D. It is not possible to tell. 3. The…arrow_forwardThe average income of a large sample of households is $63,000 and the s.d. is $7,000. Assume that the data is approximately bell-shaped. What percent of these households have incomes between $42,000 and $77,000? Don’t forget to properly justify your answer using the empirical rule.arrow_forwardCalculate the most appropriate measures of central tendency and dispersion for the following variable. Respondents were asked to rank how likely they would support ending Obamacare on a scale ranging from 0, definitely would not support, to 10, would definitely support. Here are their scores: 0, 0, 5, 5, 6, 8, 10, 7, 1, 2, 3, 0, 4, 5, 1, 9, 10, 7, 1, 2, 0, 6, 8arrow_forward
- Choose the appropriate statistical test. When computing, be sure to round each answer as indicated. A dentist wonders if depression affects ratings of tooth pain. In the general population, using a scale of 1-10 with higher values indicating more pain, the average pain rating for patients with toothaches is 6.8. A sample of 30 patients that show high levels of depression have an average pain rating of 7.1 (variance 0.8). What should the dentist determine? 1. Calculate the estimated standard error. (round to 3 decimals). [st.error] 2. What is thet-obtained? (round to 3 decimals). 3. What is the t-cv? (exact value) 4. What is your conclusion? Only type "Reject" or Retain"arrow_forwardSuppose we want to compare scores (which can take on any value within a specified range) at baseline and at follow-up for a given sample. Using the data in the table below, compute a 95% CI for the mean difference in scores. Subject ID Baseline Follow-Up 1 13 6 2 10 8 3 9 11 4 12 11 5 8 5arrow_forwardGroup 1. Mean= 24.08 Group 2. Mean= 26.5 STD Dev= 4.42 STD Dev= 5.2 Sample Size=16 Sample Size=16 What is tcomputed =arrow_forward
- A. Determine the test statistic B. What are the critical values C. What is the p valuearrow_forwardConsider the following research questions/study scenarios. For each study, discuss the most appropriate methods for describing the data (graphically and numerically). What statistical method would be most appropriate for addressing the research questions? Be sure to provide justification of the statistical method. When a statistical test is needed, provide appropriate null and research hypotheses. A study investigating the effects of second-hand smoke in working environments asked the following question: “How often do you experience second-hand smoke in a work environment/function? Never, Occasionally, Fairly Often, Very Often, Almost Always.” The question was asked of managers and employees to determine whether there was an association between position and the amount of second-hand smoke exposure. The responses to the questions were grouped into Little/Non and Often, where Little/None was defined as responses of Never or Occasionally and Often was defined as responses of Fairly…arrow_forwardA method or a set of procedures of using sample data to estimate a population parameter is called A. statistical inference B. statistical interference C. statistical appliance D. statistical descriptionarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)ProbabilityISBN:9780134753119Author:Sheldon RossPublisher:PEARSON
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)ProbabilityISBN:9780134753119Author:Sheldon RossPublisher:PEARSON

A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Probability
ISBN:9780134753119
Author:Sheldon Ross
Publisher:PEARSON
