
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
14 - |
Masses m1=1kg and m2=2kg are connected to each other by a light rope passing through a frictionless pulley. While mass m1 is connected to a spring with constant k=100 N/m in the horizontal plane with a friction coefficient of µ=0.4, mass m2 hangs freely. It is released when the spring is at its normal length. Calculate the distance h that the m2 mass will descend the most. |

Transcribed Image Text:ww.
A) 0,76 m
B) 0,99 m
OC) 1,67 m
OD) 1,23 m
DE) 0,32 m
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
The normal reaction on mass1 is
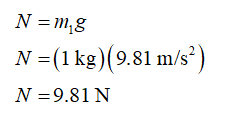
The friction force on mass1 can be determined as,
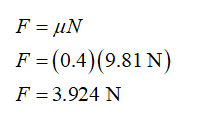
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The coefficient of friction between all surfaces is us = 0.4 and μK = 0.3. The mass of A is 11 kg and the mass of B is 36 kg. Assume the pulley is mass less and frictionless. Determine the smallest force P required to keep the system moving. P A A Barrow_forwardQuestion 2 A rope of length L = 2.8 m and mass m = 2 kg is initially at rest and can slide on an inclined surface with incline = 20° as shown in the figure. Assume that the part of the rope that is not on the inclined surface hangs down vertically at all times and that the static friction coefficient between the rope and the surface is μ = 0.49. 0 b a) Calculate the maximum value of b for which the rope will not start sliding down the slope.arrow_forwardThe 60-kg crate shown in (Figure 1) starts from rest and attains a speed of 6 m/s when it has traveled a distance of 15 m. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and the ground is μ = 0.3. Figure 1 of 1 (> ▲ Part A Determine the force P acting on the crate. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. P= DH μA 6 Submit Value Provide Feedback Request Answer Units ?arrow_forward
- Q14. As shown in the image below, the 20-kg box is pulled up the inclined plane with a constant velocity of 4.7 m/s. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the box and the inclined plane is µ = 0.1, determine the power of force F. Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 1 place after the decimal point, and proper SI unit. Take g = 9.81 m/s². F Your Answer: Answer 30° unitsarrow_forwardThe force Pis applied to the 52-kg block when it is at rest. Determine the magnitude and direction of the friction force exerted by the surface on the block if (a) P = 0, (b) P = 184 N, and (c) P = 245 N. (d) What value of P is required to initiate motion up the incline? The static and kinetic coefficients of friction between the block and the incline are ug = 0.20 and µ = 0.16, respectively. The friction force is positive if up the incline, negative if down the incline. 52 kg 21° H, = 0.20 H = 0.16 13 Answers: (a) F= i N (b) F = i N (c) F= i N (d) P= i Narrow_forwardA rope of Length L = 3m and mass m= 3Kg is initially At rest and can slide on an inclined surface with Inclined theta = 15° as shown in the figure. Assume that the part of the rope that is not on the Inclined surface hanges down vertically at all times and that the static friction coefficient between the rope and the surface is MUs = 0.36 a) calculate the maximum value of b for which the rope will NOT start sliding down the slope. Assume that b = 0.33m and that the coefficient of kinetic friction between the rope and the Inclined surface is MUk = 0.27. Let y (in metres) be the distance travelled by the rope after it has been released from rest. b) calculate the initial acceleration of the rope Calculate the work done by gravity as a function of y c) calculate the work done by the friction force as a function of y Hence calculate the velocity of the rope at the moment the rope has just completely left the Inclined surfacearrow_forward
- Two blocks of mass m1 = 2kg and m2 = 8kg are connected by a light string and a smooth pulley. block m1 lies on a smooth horizontal plane and block m2 lies on a rough inclined plane with a friction coefficient of 0.5 (see picture). first the two blocks are held still. The tension in the rope when the two blocks are released is ... (sin 37° = 0.6) 340arrow_forwardA rope of Length L = 3m and mass m= 3Kg is initially At rest and can slide on an inclined surface with Inclined theta = 15° as shown in the figure. Assume that the part of the rope that is not on the Inclined surface hanges down vertically at all times and that the static friction coefficient between the rope and the surface is MUs = 0.36 a) calculate the maximum value of b for which the rope will NOT start sliding down the slope. Assume that b = 0.33m and that the coefficient of kinetic friction between the rope and the Inclined surface is MUk = 0.27. Let y (in metres) be the distance travelled by the rope after it has been released from rest. b) calculate the initial acceleration of the rope c) Calculate the work done by gravity as a function of yarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY