
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Please do not give image format
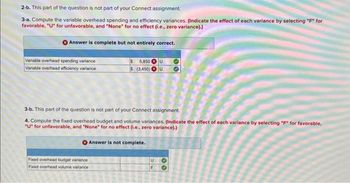
Transcribed Image Text:2-b. This part of the question is not part of your Connect assignment.
3-a. Compute the variable overhead spending and efficiency variances. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for
favorable, "U" for unfavorable, and "None" for no effect (i.e., zero variance).)
Answer is complete but not entirely correct.
Variable overhead spending variance
Variable overhead efficiency variance
5,850 U
$ (3,450) U
3-b. This part of the question is not part of your Connect assignment.
4. Compute the fixed overhead budget and volume variances. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable,
"U" for unfavorable, and "None" for no effect (i.e., zero variance).)
Answer is not complete.
Fixed overhead budget variance
Fixed overhead volume variance
U
F

Transcribed Image Text:Marc Goudreau, administrator of Clearwater Hospital, was puzzled by the prior month's reports. "Every month, it's anyone's guess
whether the lab will show a profit or a loss. Perhaps the only answer is to increase our lab fees again."
"We can't," replied Rhoda Groves, the controller. "There are still a lot of complaints about the last increase, particularly from the
insurance companies and government health units. They're now paying only about 80% of what we bill. I'm beginning to think the
problem is on the cost side."
To determine if the Clearwater lab costs are in line with those of other hospital labs, Goudreau has asked you to evaluate the costs for
the past month, Groves has provided you with the following information:
a. Two basic types of tests are performed in the lab-smears and blood tests. During the past month, 2,700 smears and 1,200 blood
tests were performed in the lab.
b. Small glass plates are used in both types of tests. During the past month, the hospital purchased 12,000 plates at a cost of $20,952.
This cost is net of a 3% purchase discount. A total of 1,200 of these plates were unused at the end of the month; no plates were on
hand at the beginning of the month.
c. During the past month, 1,600 hours of labour time were used in performing smears and blood tests. The cost of this labour time was
$13,120.00.
d. The lab's variable overhead cost last month totalled $5,200.
e. Fixed overhead cost last month totalled $9,050.
Clearwater Hospital has never used standard costs. By searching industry literature, however, you have determined the following
nationwide averages for hospital labs:
Plates: Three plates are required per lab test. These plates cost $1.80 each and are disposed of after the test is
completed.
Labour: Each smear should require 0.3 hours to complete, and each blood test should require 0.6 hours to complete. The
average cost of this lab time is $10 per hour.
Overhead Overhead cost is based on direct labour-hours. The average rate of variable overhead is $3 per hour. The
average rate of fixed overhead is $6 per hour. These rates are based on a denominator activity level of 1,500
hours per month.
Required:
1. Compute the materials price variance for the plates purchased last month, and compute a materials quantity variance for the plates
used last month. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable. "U" for unfavorable, and "None" for no effect
(i.e., zero variance).)
Answer is complete but not entirely correct.
Materials price variance
Materials quantity variance
00
$ 8,952 FO
$
300
2-a. Compute a labour rate variance and a labour efficiency variance for the lab. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F"
for favorable, "U" for unfavorable, and "None" for no effect (i.e., zero variance). Do not round intermediate calculation and round
your final answers to 1 decimal place.)
Labour rate variance
Labour efficiency variance
Answer is complete but not entirely correct.
$ 2.880.0 F
$(42,500.0) U
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education