
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
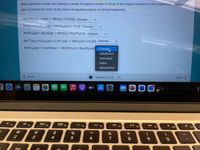
Transcribed Image Text:Many transition metals can undergo a series of reaction similar to those of the copper reactions in this experiment. Identify the
type of reaction for each of the chemical equations below involving manganese.
Mn(OH)2(s) + heat → MnO(s) + H20(g) Choose...
Mn(s) + 2 H2SO4(aq) → MnSO4(aq) + H2(g) Choose...
MNSO4(aq) + NaS(aq) → MnS(s) + Na2SO4(aq) Choose..
Mn2+(aq) + H202(aq) + 2 OH¯(aq) MnO2(s)+ 2 H20(1) Choose...
MnSO (aq) + 2 NaOH(aq) → Mn(OH)2(s) + Na2SO4(aq) v Choose.
metathesis
hydrolysis
redox
dehydration
< ВАСК
Question 4 of 6
NEXT
átv A
80
F3
F2
F4
FS
F7
FB
F9
F10
FW
%23
2$
%
&
3
5
6
7
8.
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1

Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- In the reaction Zn + CuSO4 - > Cu + ZnSO4 what has been oxidized?arrow_forwardUsing this reaction, which statement below is true? Pb(s) + PbO21s) + 2H2SO4(aq) → 2 PBSO4(aq) + 2H2O) Solid Pb undergoes reduction. Solid Pb is the oxidizing agent. Solid Pb is the reducing agent. O Oxygen in lead(IV) oxide undergoes reduction.arrow_forwardReducing agent (RA) IO3 (aq) + I (aq) → I_(s) B Part 3 O See Hir Write the balanced equation for the reaction that takes place in acidic aqueous solution. Неarrow_forward
- Balance the following chemical equation (if necessary): ZnS(s) + AIP(s) → Al,S3(s) + Zn3P2(s)arrow_forwardWrite appropriate balanced net ionic equations for each of the following processes. A3. Concentrated Nitric acid oxidizes Cu(s) to Cu²+ (aq): B2. NaOH converts Cu²+ (aq) to insoluble Cu(OH)₂(s). C1. Heat converts Cu(OH)₂(s) to CuO(s).arrow_forwardThe iron content of iron ore can be determined by titration with a standard KMNO4 solution. The iron ore is dissolved in HCl, and all the iron is reduced to Fe+ ions. This solution is then titrated with KMNO4 solution, producing Fe* and Mn2+ ions in acidic solution. If it required 42.41 mL of 0.0452 M KMNO4 to titrate a solution made from 1.236 g of iron ore, what is the mass percent of iron in the iron ore? Mass percent = %arrow_forward
- I need help on this question?arrow_forwardPlease answer the below two questionsarrow_forwardWrite a balanced redox reaction for the formation of rust on iron metal and identify the correct oxidizing agent and/or reducing agent. a. Iron is the reducing agent and O2 is the oxidizing agent b. Iron is the oxidizing agent and O2 is neither a reducing agent nor an oxidizing agent Oc. Iron is the oxidizing agent and-O2 is the reducing agentarrow_forward
- 2. Calculate the theoretical yield of potassium alum from 1.0000 g of aluminum, assuming that the aluminum is the limiting reagent. First, write the net reaction by adding the net ionic 1. Bring a prefer. (There's more people to share.) equations that represent the four steps in the synthesis: 2 Al +2 OH + 6 HOH → 2 Al(OH)4¯ + 3 H2 2 Al(OH)4+2 H* →2 Al(OH)3 +2 HOH 2 Al(OH)3 + 6 H* → 2 Al³+ + 6 HOH 2 K* + 2 Al3+ + 4 SO2- + 24 HOH →2 KAI(SO4)2·12 H20 shot on moto g' power Crystal H.arrow_forwardWhich one of the following statements is correct about the reaction below? Mg(s) + 2 HCI(aq) → M9CI,(s) + H,(g) A) Mg is the oxidizing agent because it is losing electrons. B) H is the reducing agent because it loses electrons. C) Cl is the reducing agent because it is an anion. D) H is the oxidizing agent because it gains electrons.arrow_forward2. A sample iron ore weighing 0.6428 g is dissolved in acid, the iron is reduce to Fe2+, and the solution is titrated with 36.30 mL of 0.01753 M K,Cr,O, solution. Calculate the percentage of iron (MM=55.85 g/mol) in the sample Rxn: 6 Fe 2* + Cr,072- + 14H* → 2Cr 3* + 6 Fe 3* + 7 H20 analyte titrantarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY