
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
- Use the "Statistics" function of your calculator to find the
mean and standard deviation for the data. (Round to tenths.) - Mean:_______
- Standard deviation:_________
- Use the
Normal Probability Distribution table or the built-infunctions of your calculator to find: a. What percent of male adults are taller than 6 feet (72 inches)? - What percent of male adults are taller than 5 feet (60 inches)?
- What percent of male adult heights are between 60 inches and 72 inches?
- Because of the high cost of leather, the company has decided they cannot profitably make leather pants in all sizes. Use the Normal Probability Distribution table or the built-in functions of your calculator to find the heights corresponding to the following percentages. These are the heights of the shortest and tallest males who can purchase leather pants from this company.
- The bottom 9%
- The upper 7%
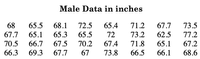
Transcribed Image Text:Male Data in inches
65.5
68.1 72.5
65.4
71.2
67.7
62.5
68
73.5
67.7
65.1
65.3 65.5
72
73.2
77.2
70.5
66.7
67.5
70.2
67.4
71.8
65.1
67.2
66.3
69.3
67.7
67
73.8
66.5
66.1
68.6
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Use the table below to find the percentage of data items in a normal distribution that lie between z= - 1 and z = 1. Click the icon to view the table. - X Data Table The percentage of data items in a normal distribution that lie between z = - 1 and z= 1 is %. z-SCORES AND PERCENTILES -Score Percentile z-Score Percentile z-Score Percentile -Score Percentile -4.0 0.003 -1.0 15.87 0.0 50.00 1.1 86.43 -3.5 0.02 -0.95 17.11 0.05 51.99 1.2 88.49 -3.0 0.13 -0.90 18.41 0.10 53.98 1.3 90.32 -2.9 0.19 -0.85 19.77 0.15 55.96 1.4 91.92 -2.8 0.26 -0.80 21.19 0.20 57.93 1.5 93.32 -2.7 0.35 -0.75 22.66 0.25 59.87 1.6 94.52 -2.6 0.47 -0.70 24.20 0.30 61.79 1.7 95.54 -2.5 0.62 -0.65 25.78 0.35 63.68 1.8 96.41 -2.4 0.82 -0.60 27.43 0.40 65.54 1.9 97.13 -2.3 1.07 -0.55 29.12 0.45 67.36 2.0 97.72 -2.2 1.39 -0.50 30.85 0.50 69.15 2.1 98.21 -2.1 1.79 -0.45 32.64 0.55 70.88 2.2 98.61 -2.0 2.28 -0.40 34.46 0.60 72.57 2.3 98.93 -1.9 2.87 -0.35 36.32 0.65 74.22 2.4 99.18 -1.8 3.59 -0.30 38.21 0.70 75.80 2.5…arrow_forwardUse the z-score formula, and the information below to find the mean, μ. Round your answer to one decimal place, if necessary. z=1.25, x=24.2, and σ=5.2arrow_forwardSuppose in 2000, the science scores for female students had a mean of 146 with a standard deviation of 35. Assume that these scores are normally distributed with the given mean and standard deviation. The value 41 is __________ the mean, and the value 251 is __________________ the mean. Group of answer choices Two standard deviations above; two standard deviations belowarrow_forward
- Thxarrow_forwardWrite True or False for the statement. If the statement is False, correct the statement. You are shown the following normal probability plot where the data set percentiles are on the y-axis. The sample size is n = 1,000. The data set can best be described as skewed to the left. Normal Q-Q Plot 2 -3arrow_forwardThe data in the table represent the ages of the winners of an award for the past five years. Use the data to answer questions (a) through (c). 25 30 61 48 42 a. Determine the population mean age, μ, of the five winners. μ=________________ (Type an integer or a decimal.) b. Consider samples of size 3 without replacement. Find the mean of the variable x. Ages x Ages x Full data set 25, 30, 61 38.67 25, 48, 42 38.33 25, 30, 48 34.33 30, 61, 48 46.33 25, 30, 42 32.33 30, 61, 42 44.33 25, 61, 48 44.67 30, 48, 42 40.00 25, 61, 42 42.67 61, 48, 42 50.33 The mean of the variable x is ______________. (Round to two decimal places as needed.) c. Find μx, using only the result of part (a). μx=_________________ (Type an integer or a decimal.)arrow_forward
- Find the area of the shaded region. The graph to the right depicts IQ scores of adults, and those scores are normally distributed with a mean of 100 and a standard deviation of 15. Click to view page 1 of the table. Click to view page 2 of the table. The area of the shaded region is (Round to four decimal places as needed.) 15 *** **** VI Vi More 70 1arrow_forward: Which one of the following statements is True? The units of the Variance are the same as the original data. The Mean can be found from a Box Plot. Relative Frequency equals Frequency multiplied by Total Frequency. An Ogive chart increases in height from left to right. For a unimodal mound shaped distribution that is Skewed Left the Mean is greater than the Median.arrow_forwardPlayer His Average Points Other's Average Points Other's Standard Deviation Fredo 153 163 15 Karl 163 183 35 Table 2.57 a. Which player had the higher average points when compared to the other players on his team? Fredo O Karl b. Use Table 2.57 to find the value that is three standard deviations above the mean for each team. Enter the exact answers. Fredo's team: Number Karl's team: Number C. Use Table 2.57 to find the value that is three standard deviations below the mean for each team. Enter the exact answers. Fredo's team: Number Karl's team: Number Next Back Question Menu- Quit & Save Submit Assignment 502 PM 200arrow_forward
- Instructions: Use the empirical rule to find the following probabilities. Remember to draw a normal curve, label the x-values for 1, 2, and 3 standard deviations from the mean, and write in the probabilities between each standard deviation before answering the questions. Suppose that the scores on a national achievement exam have a mean of 480 and a standard deviation of 90. What score is 3 standard deviations above the mean? What score is 2 standard deviations below the mean? Approximately 68% will fall between and Approximately 99.7% will fall between and What is the probability that a randomly selected student will score at least a 300? % What is the probability that a student will score at most a 390? %arrow_forwardAssume that a randomly selected subject is given a bone density test. Bone density test scores are normally distributed with a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1. Draw a graph and find P, the 11th percentile. This is the bone density score separating the bottom 11% from the top 89%. Which graph represents P ? Choose the correct graph below. O A. O B. OD. P11 P11 P11 P11 The bone density score corresponding to P1 is (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Click to select your answer(s). APR tv MacBook Air F9 F10 LLA 20 F3 F6 F8 F4 F5 F1 F2 & #3 7 8. %24arrow_forwardUsing the data in the photo. Find the correlation by hand. Round to three decimal places.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman