Question
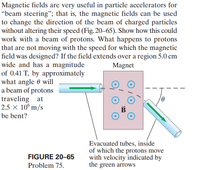
Transcribed Image Text:Magnetic fields are very useful in particle accelerators for
“beam steering"; that is, the magnetic fields can be used
to change the direction of the beam of charged particles
without altering their speed (Fig. 20-65). Show how this could
work with a beam of protons. What happens to protons
that are not moving with the speed for which the magnetic
field was designed? If the field extends over a region 5.0 cm
wide and has a magnitude
of 0.41 T, by approximately
what angle 0 will
a beam of protons
traveling at
2.5 x 10° m/s
Magnet
be bent?
Evacuated tubes, inside
of which the protons move
with velocity indicated by
the green arrows
FIGURE 20-65
Problem 75.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A mass spectrometer is being used to separate common oxygen-16 from the much rarer oxygen-18, taken from a sample of old glacial ice. The ratio of the masses of these two ions is 16 to 18, and the mass of oxygen-16 is 2.66×10^−26 kg. They are both singly charged, and they both travel at 4.84×10^6 m/swhen they enter the mass spectrometer with a 1.11T magnetic field that is perpendicular to the particle velocity. What is the separation between their paths, in meters, when they hit a target after traversing a semicircle?arrow_forward33. A proton P travels with a speed of 18 m/s toward the top of the page through a uniform magnetic field of 2.0 T directed into the page as shown in Figure 19-31. What are the magnitude a and direction of the magnetic force on the proton? SSM Figure 19-31 Problem 33arrow_forward20-4) In a mass spectrometer, a singly-charged particle has a speed of 1.00 × 106 m/s and enters a uniform magnetic field of 0.200 T at a right angle to the field. The radius of the resulting circular orbit is 20.75 cm. What is the mass of the particle? (e = 1.60 × 10-19 C) A) 3.20 × 10-27 kg B) 6.64 × 10-27 kg C) 1.67 × 10-27 kg D) 9.11 × 10-31 kgarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios